
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
P dextrocardiale, Right atrial hypertrophy, Right atrial abnormality, Delay of right atrial activation, Right atrial dilatation, Right atrial distention, Right atrial overload
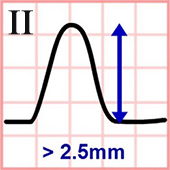
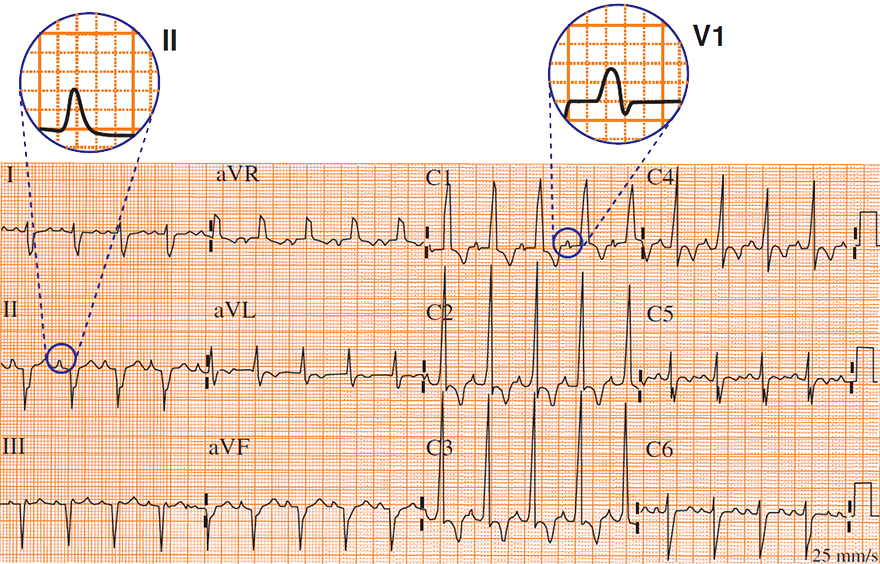
P Pulmonale and Lead II
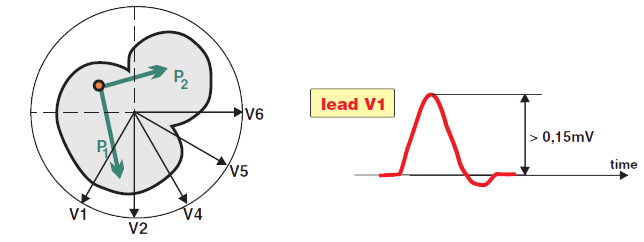
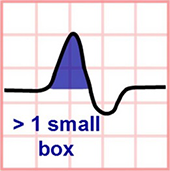
P Pulmonale and Lead V1
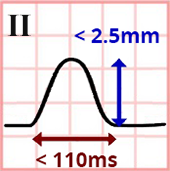

Normal P Wave



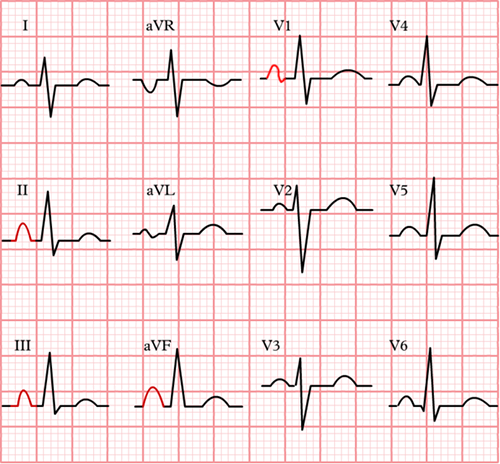
P Pulmonale
P Pulmonale
P Pulmonale

P Pulmonale

Cor Pulmonale (P Pulmonale + Right Ventricular Hypertrophy)
Sources
Home /
P dextrocardiale, Right atrial hypertrophy, Right atrial abnormality, Delay of right atrial activation, Right atrial dilatation, Right atrial distention, Right atrial overload
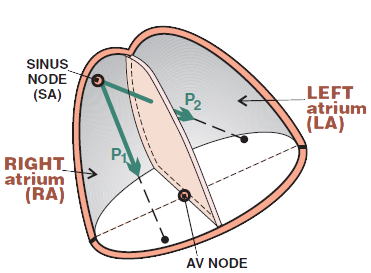
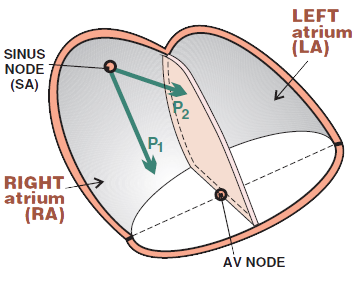
Physiological P Wave
|

|
|
 |
|
 |

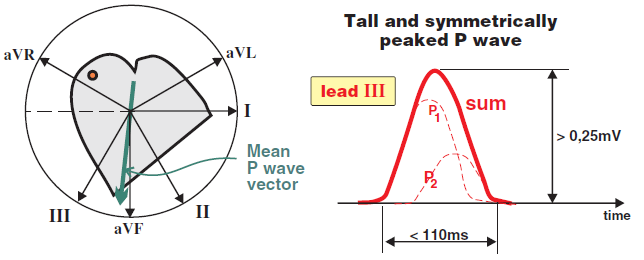
P Pulmonale and Lead II

P Pulmonale and Lead V1
ECG and P Pulmonale
|


|

|

|

|
Normal P Wave

|

|

|
P Pulmonale

P Pulmonale

P Pulmonale

P Pulmonale

Cor Pulmonale (P Pulmonale + Right Ventricular Hypertrophy)
Sources