Home /
P Wave - ECG
P wave
Mechanism of P Wave Formation
Limb Leads and the P Wave

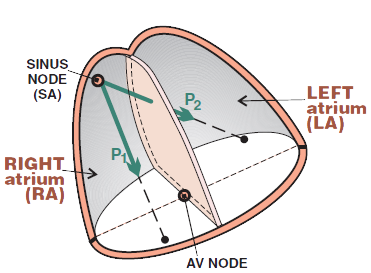
Limb Leads and the P Wave
- Limb leads (I, II, III, aVF, aVR, aVL) view the heart in the frontal plane
- Summation (P1 + P2) atrial vector points from the SA node to the AV node, directed
- The more direct the vector to the lead
- the more positive the wave
- Summation atrial vector
- directs straight to lead II (hence the P wave is best seen in lead II)
- directs away from lead aVR (hence the P wave is negative in lead aVF)
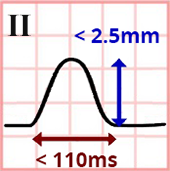
Lead II and the P Wave
- Physiological P wave in lead II has the following dimensions:
- Height < 2.5mm
- Width < 110ms

Precordial Leads and the P Wave
- The heart is rotated leftward in the horizontal plane
- The right side of the heart is oriented forward
- The left side of the heart is oriented backward
- The anatomical axis of the heart does not correspond to the electrical axis on the ECG
- The size of the vector on the ECG is directly proportional to the muscle mass in which the vector originates
- The thin atrial myocardium creates a small P wave
- The massive ventricular myocardium creates a large QRS complex
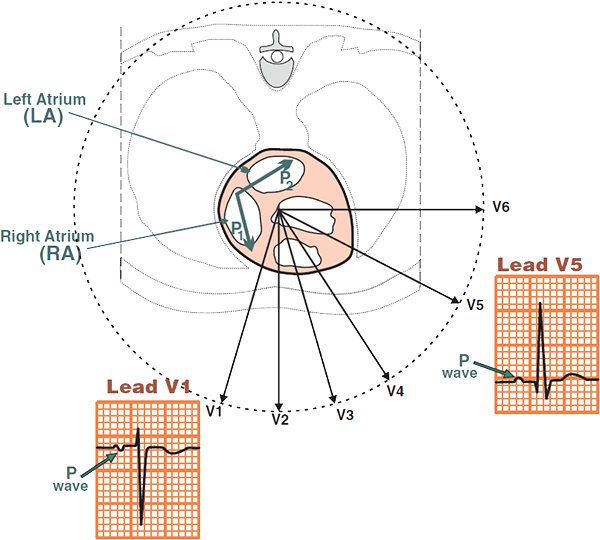
Precordial Leads and the P Wave
- Precordial leads (V1-V6) view the heart in the horizontal plane
- Precordial lead V1 views the atria from the front. The atria depolarize sequentially:
- First, the right atrium depolarizes (P1) from the SA node
- The vector of the right atrium points towards lead V1
- Then, the left atrium depolarizes (P2) from the SA node through the Bachmann's bundle
- The vector of the left atrium points away from lead V1
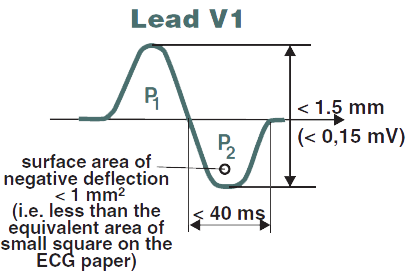
V1 and the P Wave
- The physiological P wave in lead V1 is biphasic:
- Height < 1.5mm
- Width of P2 < 40ms (depolarization of the left atrium)
- Area P2 is < 1mm2 (< 1 square)
ECG and the P Wave
- The P wave is evaluated in leads II and V1
- because they provide the best view of the atria
- Morphology
- Monophasic in lead II (positive)
- Biphasic in lead V1 (positive-negative)
- Frontal axis (0 - 75°)
- P wave is positive in I and II
- P wave is negative in aVR
- Duration
- < 110ms (max. 3 small squares)
- Atria depolarize within 110ms
- Amplitude

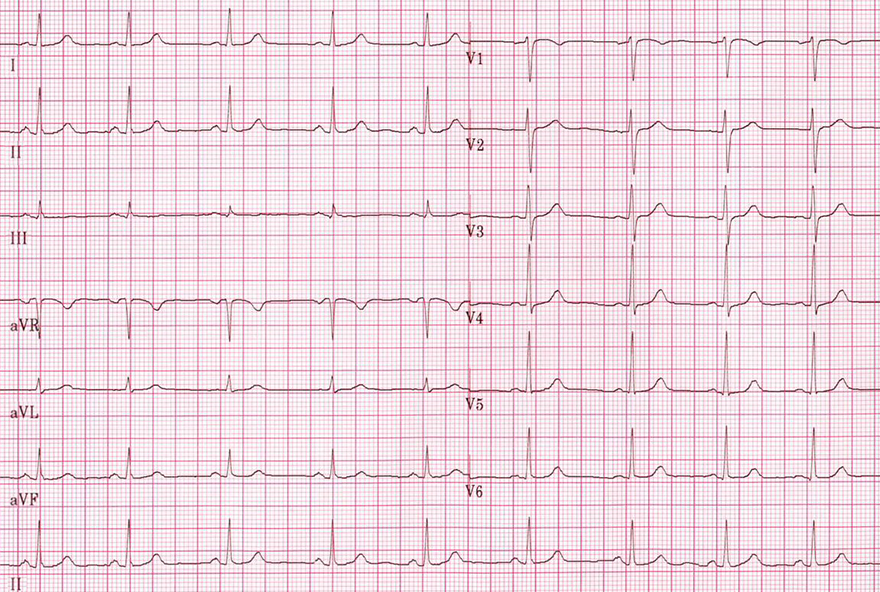
Normal P Wave and Sinus Rhythm
- Sinus rhythm with frequency of 75/min.
- P wave in lead II
- Is positive and monophasic
- Width < 110ms ( < 3 small squares)
- Amplitude < 2.5mm ( < 2.5 small squares)
- P wave in lead V1
- Biphasic (may merge with the isoelectric line)
- Amplitude < 1.5mm ( < 1.5 small squares)
- Negative wave area < 1 small square
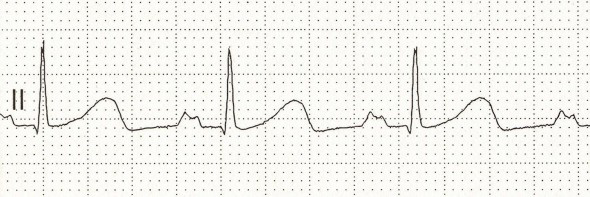
P Mitrale (Left Atrium Hypertrophy)
- Width of P > 110ms ( > 3 small squares)
- P wave has 2 peaks
- The patient had echocardiographically confirmed mitral stenosis
- Mitral stenosis is the most common cause of left atrial hypertrophy
- Therefore, left atrial hypertrophy on ECG is referred to as P Mitrale
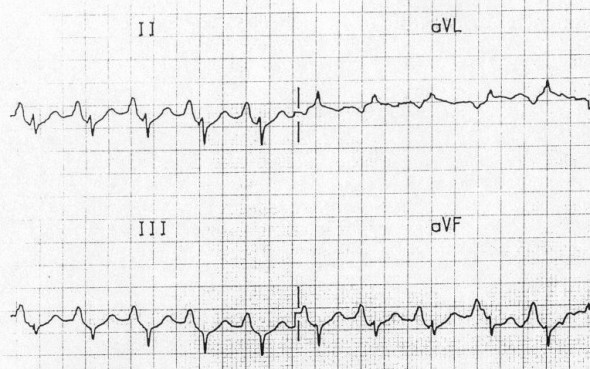
P Pulmonale (Right Atrium Hypertrophy)
- Amplitude of P wave > 2.5mm (in lead II)
- The patient has COPD and pulmonary hypertension
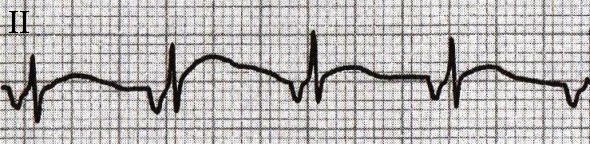
Retrograde (Negative) P Wave

Retrograde (Negative) P Wave
- Ectopic atrial rhythm with a frequency of 60/min.
- In ectopic atrial rhythm
- Impulses originate in an ectopic focus in the atria
- Not in the AV node as in junctional rhythm
- The ectopic focus is located near the AV node in this case
- Because P wave is retrograde in lead II
- This is a similar case to above
- However, in this case the PQ interval is > 120ms, and the P wave is less deep
- Thus, the atrial vector does not exactly point from lead II
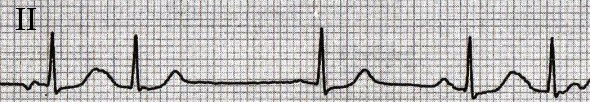
3 Different P Waves
- On the ECG, there is a multifocal atrial rhythm
- There are 3 ectopic foci in the atria
- which alternately generate impulses
- Each focus has a unique vector with a different direction
- Therefore, there are 3 different P waves on the ECG (biphasic, flat, positive)
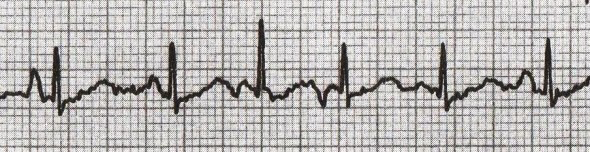
Different P Waves
- On the ECG, there is a multifocal atrial tachycardia, with a frequency > 100/min.
- The principle is exactly as described on the previous ECG
- except that it is a tachycardia (frequency > 100/min)
- On the ECG, there are 4 (or possibly 5) P waves of different shapes
- each ectopic focus has its own P wave
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers



























