
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Pacemaker (PCM), Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), Biventricular pacing

Leadless Pacemaker




CRT-P
CRT-D
Sources
Home /
Pacemaker (PCM), Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), Biventricular pacing
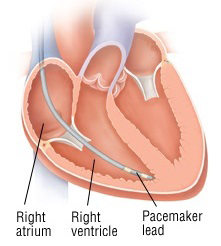
Pacemaker
|

|

|
|

|

|
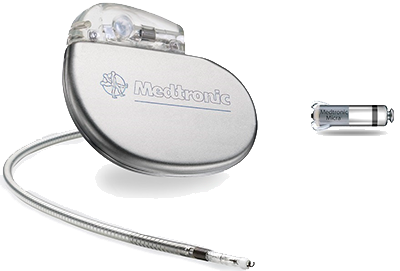
Leadless Pacemaker

|
|
|

|
|

|

|

|
|
CRT-P
|
CRT-D
|
Sources