Home /
Phase 3 Block (Tachycardia-Dependent Block)
Phase 3 aberracy, Phase 3 block, Tachycardia-dependent block, Rate-dependent bundle branch block
Phase 3 of the Action Potential
- Action potential (impulse) is a rapid change in the electrical voltage of cardiomyocytes
- It occurs due to the change in the concentration of intracellular and extracellular ions
- The action potential propagates
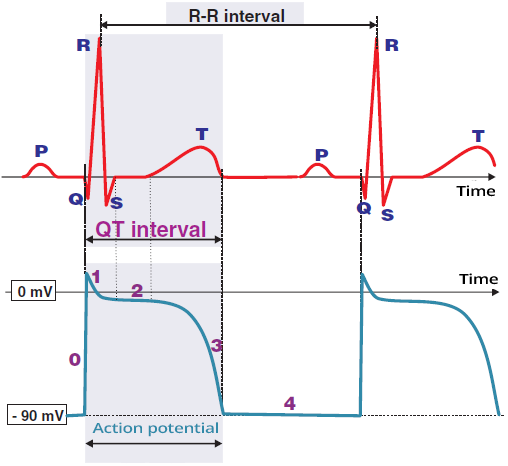
Phase 3 of the Action Potential
- On the ECG, it appears as the T wave (ventricular repolarization)
- It is the relative refractory period (RRP)
Action Potential and Refractory Period
- ARP (Absolute Refractory Period)
- During ARP, cardiomyocytes do not respond to another impulse
- RRP (Relative Refractory Period)
- During RRP, cardiomyocytes respond only to a suprathreshold impulse
- For example, if the right bundle branch is in ARP
- And a supraventricular impulse arrives at the branch during ARP
- This impulse will be blocked in the branch
- The next impulse will pass through the branch only outside ARP
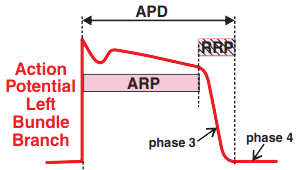
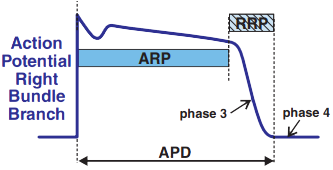
- Left bundle branch
- has a short ARP (Absolute Refractory Period)
- Right bundle branch
- has a long ARP (Absolute Refractory Period)
Block in Phase 3
- A block occurs when a supraventricular impulse arrives at some part of the ventricular conduction system
- in the 3rd phase of the action potential (Relative Refractory Period)
- This supraventricular impulse is blocked in the affected part of the conduction system
- It is the most common cause of aberrant conduction
- It is a temporary disorder of the ventricular conduction system
- It is an abnormal conduction of the impulse (action potential) through the ventricular conduction system
- It is a physiological response of the conduction system to overload
- On an ECG, it may appear as
- Phase 3 block creates a tachycardia-dependent block during supraventricular tachycardias
- Ashman Phenomenon
ECG and Block in Phase 3
- The Right Bundle Branch (RBB) has a longer Absolute Refractory Period (ARP)
- than the Left Bundle Branch (LBB)
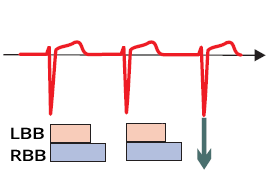
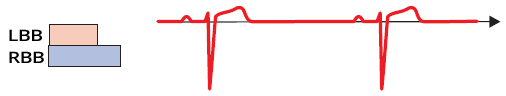
Physiological Conduction
- Supraventricular impulse
- Passes through the branches
- outside the RRP
- The impulse is not blocked
- QRS complexes are narrow and have the same shape
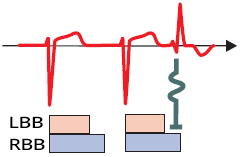
Aberrant Conduction
Atrial Extrasystole and Block in Phase 3
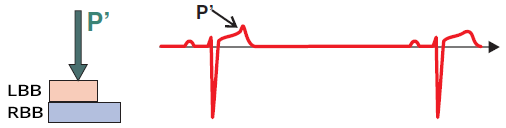
Sinus Rhythm
Atrial Extrasystole (Blocked)
- Conducts to the ventricles during the T wave (both bundle branches are in phase 3 - RRP)
- It is completely blocked in the bundle branches
- If atrial tachycardia arose and P waves occurred during the RRP of the bundle branches
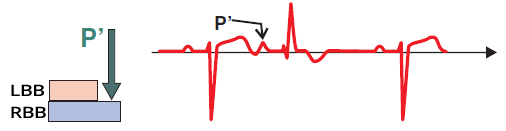
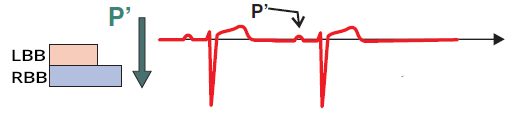
Atrial Extrasystole (with RBBB Pattern)
- Extrasystole conducts to the ventricles during the RRP (phase 3) of the right bundle branch
- It is blocked in the right bundle branch
- On the ECG, a pattern of right bundle branch block (RBBB) is observed
- This is a case of aberrant conduction of the atrial extrasystole
Atrial Extrasystole (Unblocked)
- Extrasystole conducts to the ventricles outside the RRP (phase 3) of the bundle branches
- It is not blocked
- A premature QRS complex occurs (which has the same shape as the sinus QRS)
Tachycardia-Dependent Blockade
- Block in phase 3 is most commonly seen in supraventricular tachycardias (SVT)
- During SVT, impulses begin to pass through the bundle branches during the RRP (in phase 3)
- This is a functional block of the conduction system
- The block is most often in the right bundle branch (due to the longest refractory period)
- The block is present only during tachycardia
- When tachycardia subsides, the functional block disappears
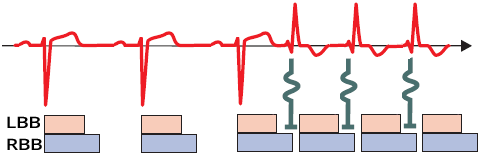
Functional Bundle Branch Block and Supraventricular Tachycardia
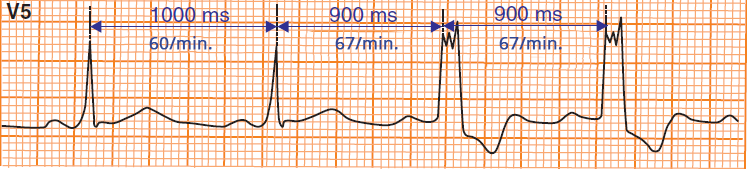
Functional Left Bundle Branch Block (block in phase 3)
- This is sinus rhythm with a frequency of 60/min.
- When the frequency rises to 67/min.
- This is a tachycardia-dependent block (even though a frequency of 67/min. is not considered tachycardia)
- If a functional bundle branch block occurs at a frequency below 100/min.

Functional Right Bundle Branch Block (block in phase 3)
- With sinus rhythm at a rate of 80/min.
- The patient did not have a bundle branch block
- Later experienced palpitations, and the recorded EKG showed the mentioned block
- It is paroxysmal SVT with a rate of 180/min.
- With an increase in rate to 180/min. a right bundle branch block appeared
- Because supraventricular impulses reach the right bundle in phase 3 of the action potential
- This is a tachycardia-dependent block
- Present only during tachycardia

Functional Left Bundle Branch Block (block in phase 3)
- The first 3 beats are sinus beats with a rate of 60/min.
- Then there was an increase in rate to 75/min.
- This is a tachycardia-dependent block (even though a rate of 75/min is not considered tachycardia)
- Which occurred with the increase in rate
- The left bundle blocks impulses in phase 3
- If a functional bundle branch block develops at a rate below 100/min.
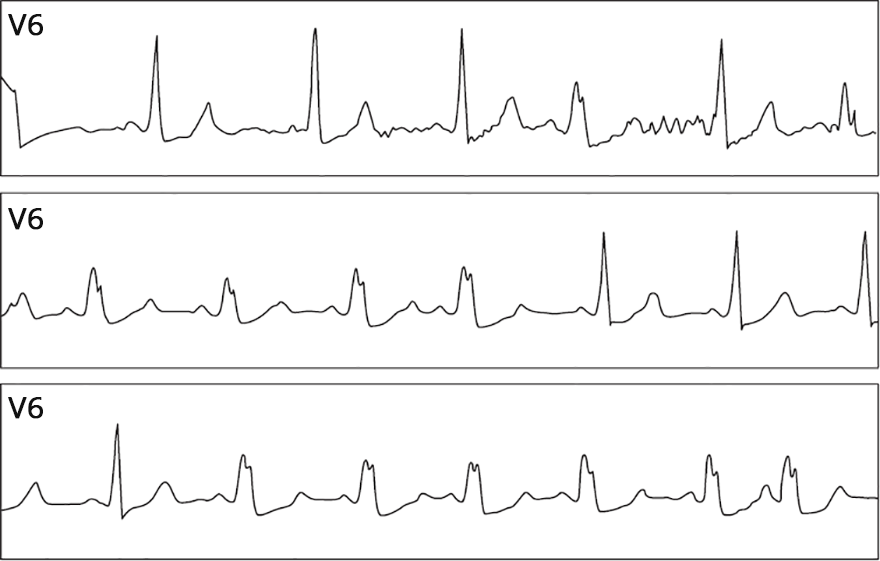
Functional Block of the Left Bundle Branch (Phase 3 Block)
- This is a sinus rhythm with a frequency of 70/min.
- With an increase in frequency above 70/min.
- An intermittent block of the left bundle branch began to occur
- This is a tachycardia-dependent block (even though a frequency above 70/min. is not considered tachycardia)
- If a functional bundle branch block occurs at a frequency below 100/min.

Aberrant Conduction and Sinus Rhythm
- Sinus rhythm
- Continuous lead II (lowest)
- Atrial extrasystoles
- Pass through the right bundle branch during RRP (phase 3)
- Therefore, they are blocked in the right bundle branch, and the ventricles are activated only through the left bundle branch
- This is an example of aberrant conduction (abnormal conduction of the impulse through the ventricular conduction system)
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers
Home /
Phase 3 Block (Tachycardia-Dependent Block)
Phase 3 aberracy, Phase 3 block, Tachycardia-dependent block, Rate-dependent bundle branch block
Phase 3 of the Action Potential
- Action potential (impulse) is a rapid change in the electrical voltage of cardiomyocytes
- It occurs due to the change in the concentration of intracellular and extracellular ions
- The action potential propagates

Phase 3 of the Action Potential
- On the ECG, it appears as the T wave (ventricular repolarization)
- It is the relative refractory period (RRP)
Action Potential and Refractory Period
- ARP (Absolute Refractory Period)
- During ARP, cardiomyocytes do not respond to another impulse
- RRP (Relative Refractory Period)
- During RRP, cardiomyocytes respond only to a suprathreshold impulse
- For example, if the right bundle branch is in ARP
- And a supraventricular impulse arrives at the branch during ARP
- This impulse will be blocked in the branch
- The next impulse will pass through the branch only outside ARP
- Left bundle branch
- has a short ARP (Absolute Refractory Period)
- Right bundle branch
- has a long ARP (Absolute Refractory Period)
|


|
Block in Phase 3
- A block occurs when a supraventricular impulse arrives at some part of the ventricular conduction system
- in the 3rd phase of the action potential (Relative Refractory Period)
- This supraventricular impulse is blocked in the affected part of the conduction system
- It is the most common cause of aberrant conduction
- It is a temporary disorder of the ventricular conduction system
- It is an abnormal conduction of the impulse (action potential) through the ventricular conduction system
- It is a physiological response of the conduction system to overload
- On an ECG, it may appear as
- Phase 3 block creates a tachycardia-dependent block during supraventricular tachycardias
- Ashman Phenomenon
ECG and Block in Phase 3
- The Right Bundle Branch (RBB) has a longer Absolute Refractory Period (ARP)
- than the Left Bundle Branch (LBB)

Physiological Conduction
- Supraventricular impulse
- Passes through the branches
- outside the RRP
- The impulse is not blocked
- QRS complexes are narrow and have the same shape
|

Aberrant Conduction
|
Atrial Extrasystole and Block in Phase 3

Sinus Rhythm

Atrial Extrasystole (Blocked)
- Conducts to the ventricles during the T wave (both bundle branches are in phase 3 - RRP)
- It is completely blocked in the bundle branches
- If atrial tachycardia arose and P waves occurred during the RRP of the bundle branches

Atrial Extrasystole (with RBBB Pattern)
- Extrasystole conducts to the ventricles during the RRP (phase 3) of the right bundle branch
- It is blocked in the right bundle branch
- On the ECG, a pattern of right bundle branch block (RBBB) is observed
- This is a case of aberrant conduction of the atrial extrasystole

Atrial Extrasystole (Unblocked)
- Extrasystole conducts to the ventricles outside the RRP (phase 3) of the bundle branches
- It is not blocked
- A premature QRS complex occurs (which has the same shape as the sinus QRS)
Tachycardia-Dependent Blockade
- Block in phase 3 is most commonly seen in supraventricular tachycardias (SVT)
- During SVT, impulses begin to pass through the bundle branches during the RRP (in phase 3)
- This is a functional block of the conduction system
- The block is most often in the right bundle branch (due to the longest refractory period)
- The block is present only during tachycardia
- When tachycardia subsides, the functional block disappears

Functional Bundle Branch Block and Supraventricular Tachycardia

Functional Left Bundle Branch Block (block in phase 3)
- This is sinus rhythm with a frequency of 60/min.
- When the frequency rises to 67/min.
- This is a tachycardia-dependent block (even though a frequency of 67/min. is not considered tachycardia)
- If a functional bundle branch block occurs at a frequency below 100/min.

Functional Right Bundle Branch Block (block in phase 3)
- With sinus rhythm at a rate of 80/min.
- The patient did not have a bundle branch block
- Later experienced palpitations, and the recorded EKG showed the mentioned block
- It is paroxysmal SVT with a rate of 180/min.
- With an increase in rate to 180/min. a right bundle branch block appeared
- Because supraventricular impulses reach the right bundle in phase 3 of the action potential
- This is a tachycardia-dependent block
- Present only during tachycardia

Functional Left Bundle Branch Block (block in phase 3)
- The first 3 beats are sinus beats with a rate of 60/min.
- Then there was an increase in rate to 75/min.
- This is a tachycardia-dependent block (even though a rate of 75/min is not considered tachycardia)
- Which occurred with the increase in rate
- The left bundle blocks impulses in phase 3
- If a functional bundle branch block develops at a rate below 100/min.

Functional Block of the Left Bundle Branch (Phase 3 Block)
- This is a sinus rhythm with a frequency of 70/min.
- With an increase in frequency above 70/min.
- An intermittent block of the left bundle branch began to occur
- This is a tachycardia-dependent block (even though a frequency above 70/min. is not considered tachycardia)
- If a functional bundle branch block occurs at a frequency below 100/min.

Aberrant Conduction and Sinus Rhythm
- Sinus rhythm
- Continuous lead II (lowest)
- Atrial extrasystoles
- Pass through the right bundle branch during RRP (phase 3)
- Therefore, they are blocked in the right bundle branch, and the ventricles are activated only through the left bundle branch
- This is an example of aberrant conduction (abnormal conduction of the impulse through the ventricular conduction system)
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers





























