Home /
Phase 4 Block (Bradycardia-Dependent Block)
Phase 4 block, Bradycardia-dependent aberration
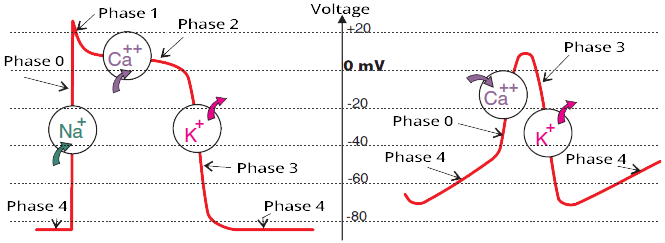
Action Potential
|
Working Myocardium
|
Conduction System
|
- Action potential is a rapid change in the electrical voltage of a cardiomyocyte
- The action potential spreads
- Impulses arise spontaneously in the SA node and the conduction system
- Because the 4th phase of the action potential spontaneously and slowly depolarizes
- When it reaches the threshold of -50mV, the depolarization triggers fully (phase 0)
- Cardiomyocytes of the working myocardium and Purkinje fibers
- Have a flat 4th phase, they do not spontaneously depolarize
- They begin to depolarize only if stimulated by an external impulse (from the conduction system)
ECG and Action Potential
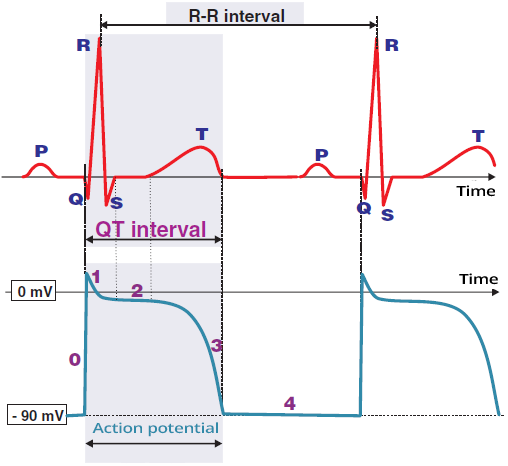
Phase 4 of the Action Potential
- This is the action potential curve of the working myocardium and Purkinje fibers in the ventricles
- We see the 4th phase on the ECG as the TQ interval (the segment between the T wave and the Q wave)
Block in Phase 4 (Bradycardia-dependent Block)
- It is an aberrant conduction of a supraventricular impulse through the ventricular conduction system
- This is a temporary conduction system disorder during bradycardia (with prolonged RR interval)
- It most commonly occurs in structurally damaged myocardium (e.g., cardiomyopathy, ischemia)
- In the presence of damaged Purkinje fibers
- In a damaged Purkinje system, cardiomyocytes begin to spontaneously depolarize during phase 4
- The longer phase 4 lasts (the TQ interval), the greater the spontaneous depolarization in phase 4 becomes
- Until it reaches the threshold, thereby blocking an external (supraventricular) impulse
- This is rare and occurs with a significant RR pause (frequency < 40/min.)
- Block in phase 4 most often manifests as a left bundle branch block
- Because the left ventricle (Purkinje fibers) is more sensitive to ischemic damage
- Occurs in a damaged Purkinje system with prolonged RR interval, such as:
- It is often referred to as a Bradycardia-dependent block
Action Potential and Left Bundle Branch
- Block in phase 4 most commonly manifests as a left bundle branch block
- Because the left ventricle (Purkinje fibers) is more sensitive to ischemic damage (than the right)
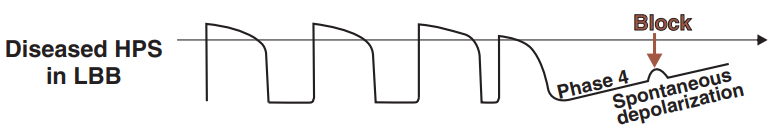
Damaged Left Bundle Branch (Action Potential)
- Block in phase 4 - Bradycardia-dependent block
- This is an action potential in the damaged Purkinje fibers of the left bundle branch
- The left bundle branch repeatedly conducts supraventricular impulses
- Followed by a sinus pause during which the Purkinje fibers begin to spontaneously depolarize in phase 4
- The supraventricular impulse is blocked in phase 4 of the action potential of the left bundle branch
- On the ECG, there will be an RR pause and a QRS complex with the pattern of a left bundle branch block
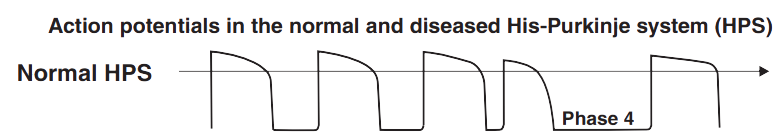
Undamaged Left Bundle Branch (Action Potential)
- This is an action potential in the undamaged Purkinje fibers of the left bundle branch
- During a sinus pause, there is no spontaneous depolarization in phase 4
- The supraventricular impulse is conducted through the left bundle branch
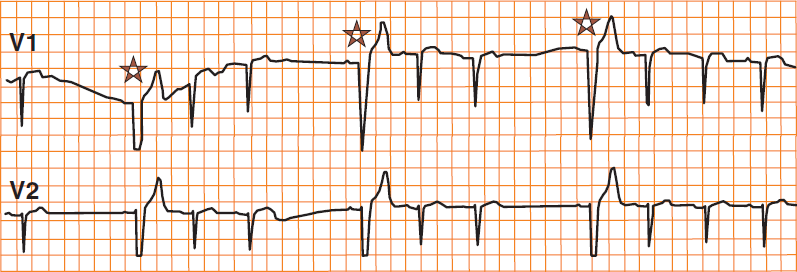
Block in Phase 4 (Bradycardia-dependent Block)
- After a sinus pause, a sinus QRS with the appearance of LBBB (asterisk) follows
- The sinus impulse is conducted to the ventricles only through the right bundle branch
- In the left bundle branch, it is blocked in phase 4 of the action potential
- A phase 4 block occurs only in a damaged Purkinje system (ischemia, cardiomyopathy)
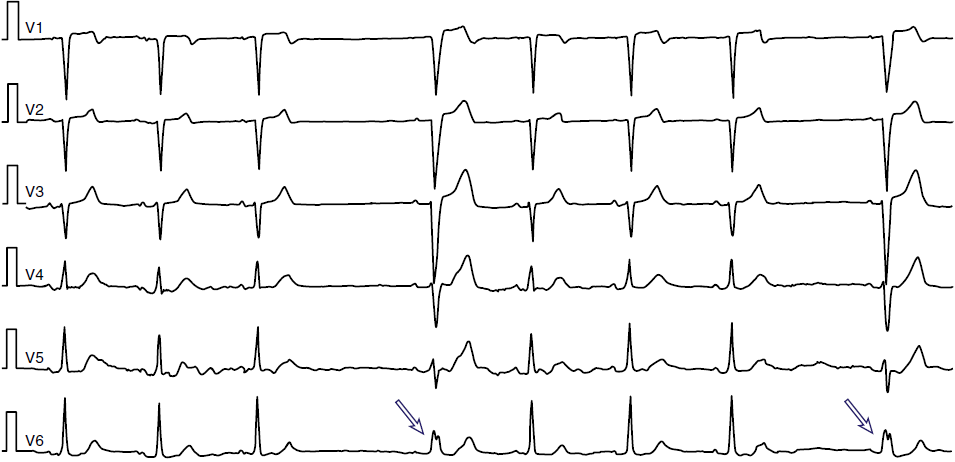
Block in Phase 4 (Bradycardia-dependent Block)
- After a sinus pause, a sinus QRS with the appearance of LBBB (arrows) follows
- The sinus impulse is conducted to the ventricles only through the right bundle branch
- In the left bundle branch, it is blocked in phase 4 of the action potential
- A phase 4 block occurs only in a damaged Purkinje system (ischemia, cardiomyopathy)
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers













