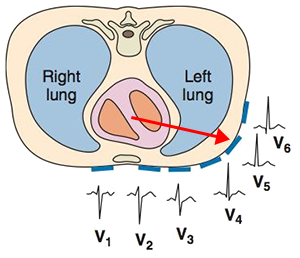
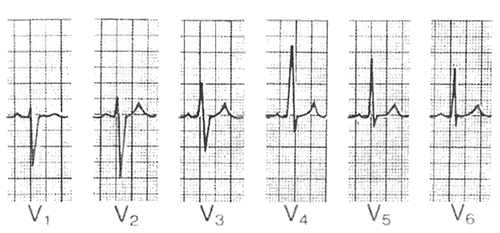
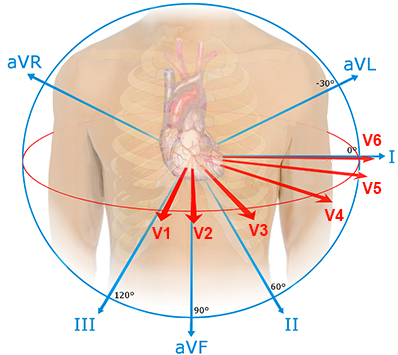
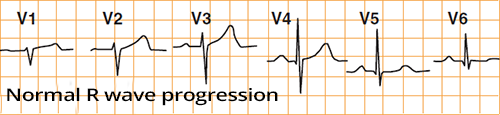
R Wave Progression and Transition Zone
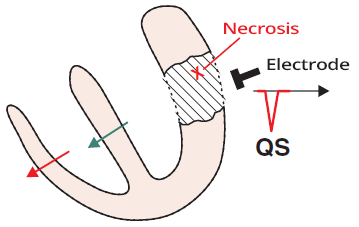
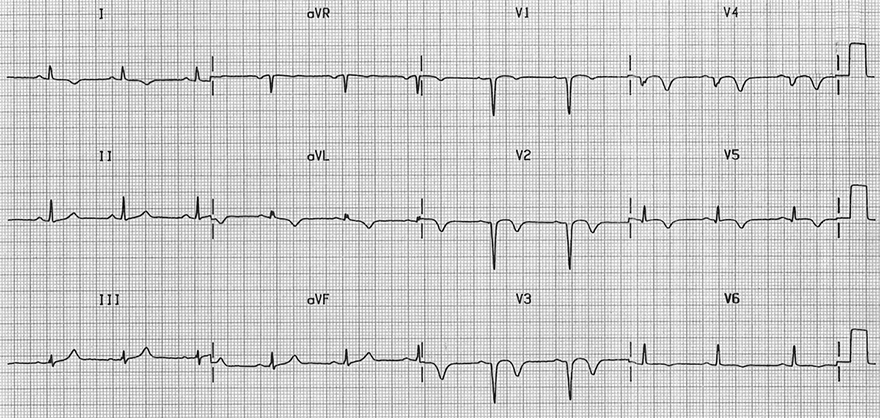
Amputated R Waves and Old Antero-septal Infarction
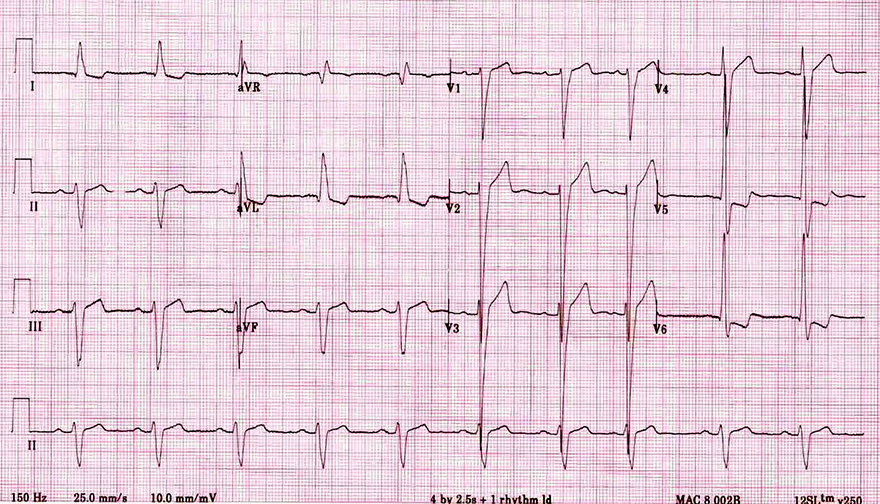
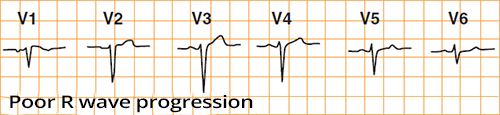
Decreased R Wave Progression and Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
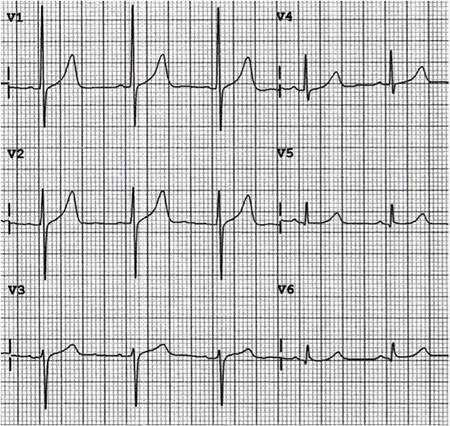
Decreased R Wave Progression and Swapped Leads V1 and V3
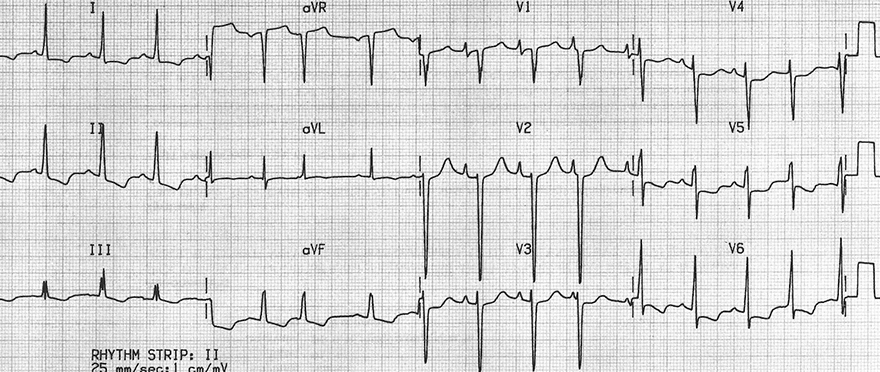
Decreased R Wave Progression and Dilated Cardiomyopathy
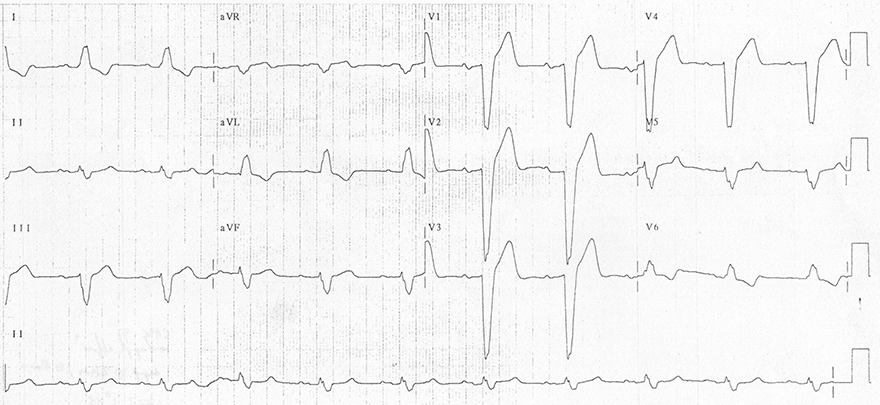
Amputated R and Left Bundle Branch Block
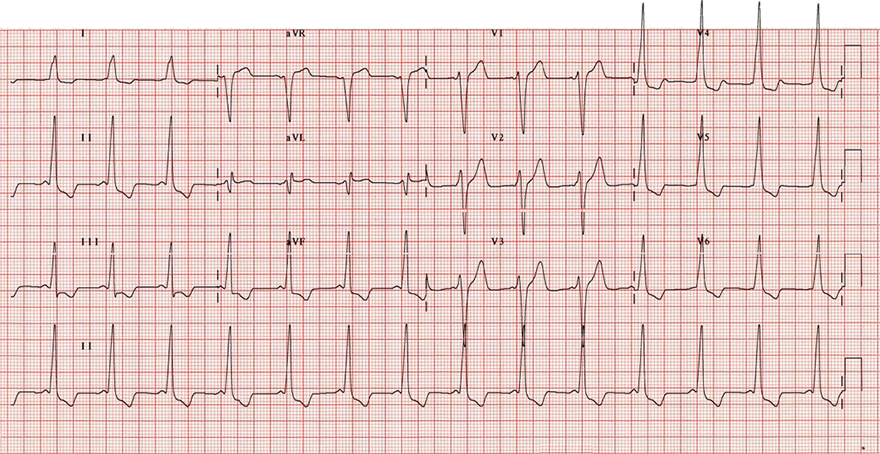
WPW Syndrome Type B
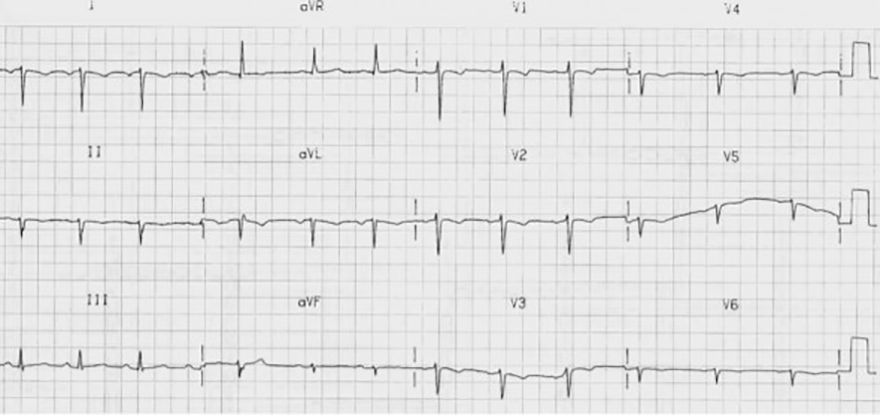
Reduced R Wave Progression and Dextrocardia
Sources
 |
 |
R Wave Progression and Transition Zone
Pathological R Wave
|
 |
|


|
|

|

Amputated R Waves and Old Antero-septal Infarction

Decreased R Wave Progression and Left Ventricular Hypertrophy

Decreased R Wave Progression and Swapped Leads V1 and V3

Decreased R Wave Progression and Dilated Cardiomyopathy

Amputated R and Left Bundle Branch Block

WPW Syndrome Type B

Reduced R Wave Progression and Dextrocardia
Sources