





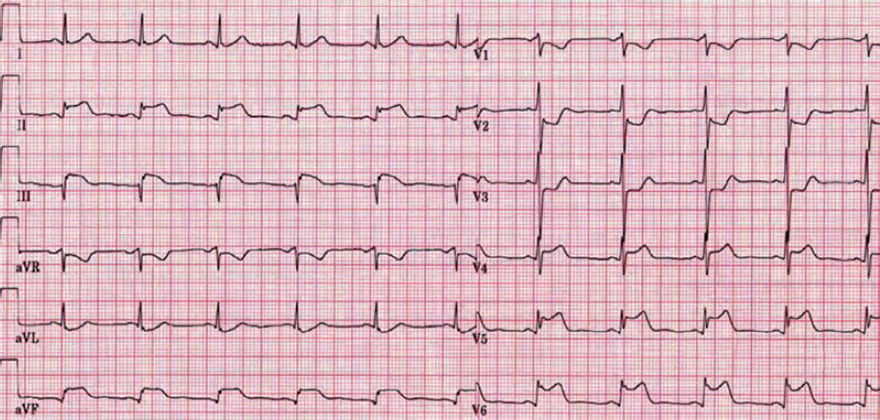
Acute Inferior, Posterior, and Lateral STEMI


Acute Inferior and Posterior STEMI


Acute Postero-Lateral STEMI

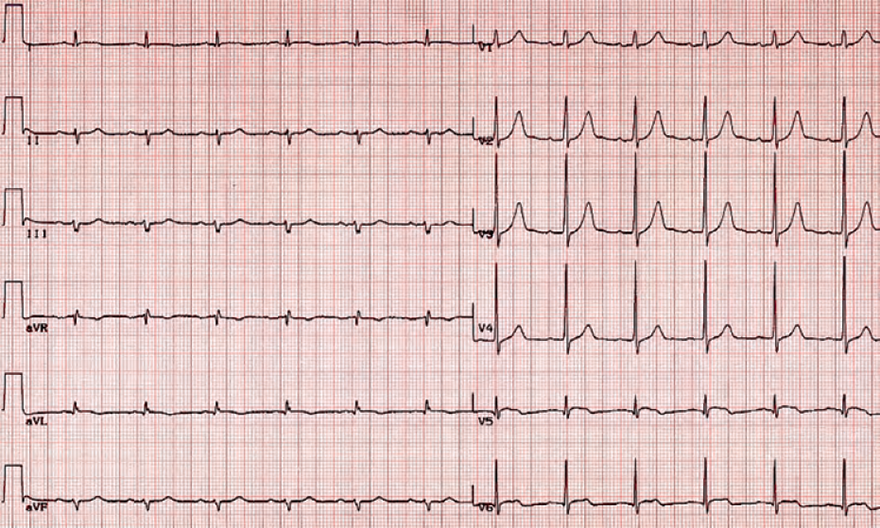
Old Posterior STEMI


Acute Inferior and Posterior STEMI

Acute STEMI?

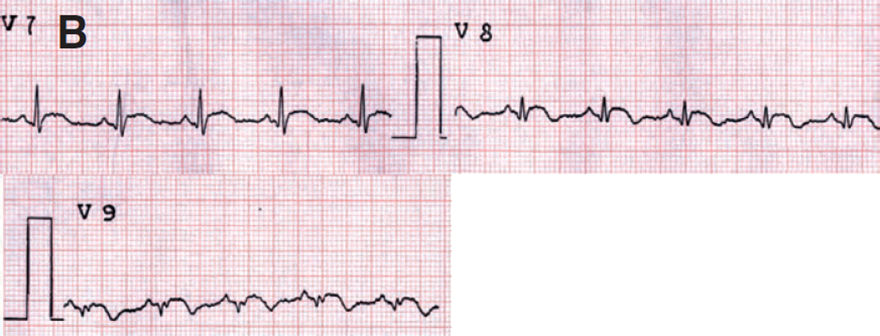
Acute Posterior Wall STEMI


Subacute Inferior Posterior Lateral STEMI
Sources
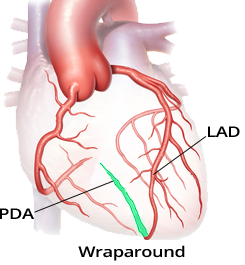
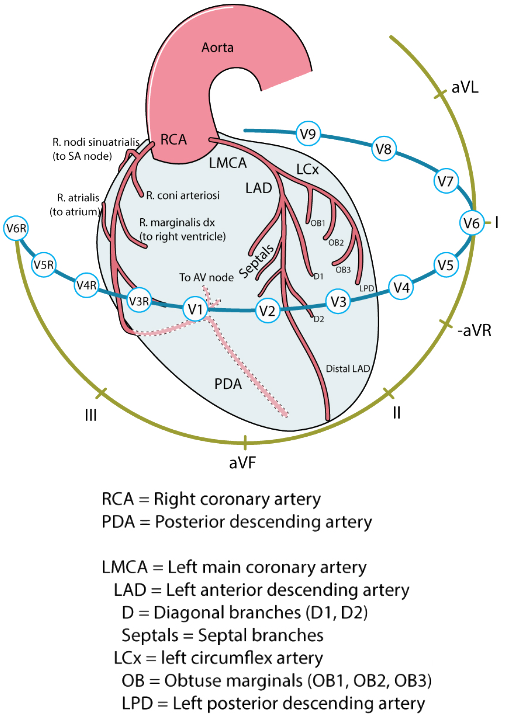
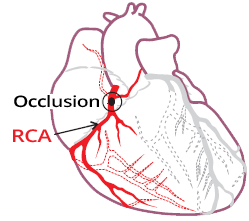
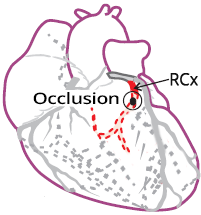
Coronary Artery Dominance
|

|

|

|

|
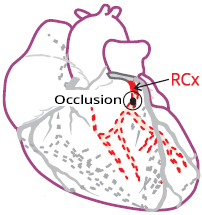
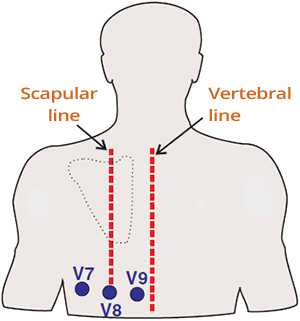
Posterior Wall Infarction
|

|
|

|
|

|
|

|
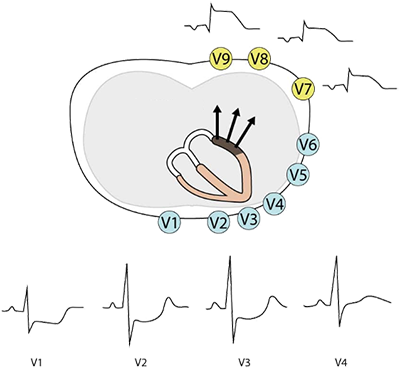
Posterior Leads (V7-V9)
|

|
ECG and Posterior STEMI
|


|

|
Acute Inferior, Posterior, and Lateral STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Inferior and Posterior STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Postero-Lateral STEMI
|

|

|
Old Posterior STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Inferior and Posterior STEMI
|

|

|
Acute STEMI?
|

|

|
Acute Posterior Wall STEMI
|

|

|
Subacute Inferior Posterior Lateral STEMI
|

|
Sources