


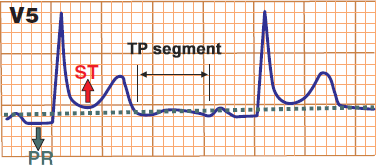
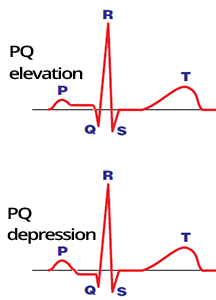
ST Elevations and PQ Depressions
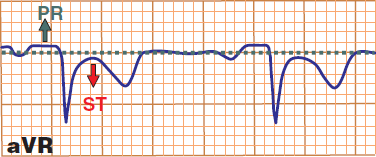
ST Depressions and PQ Elevations

Acute Pericarditis
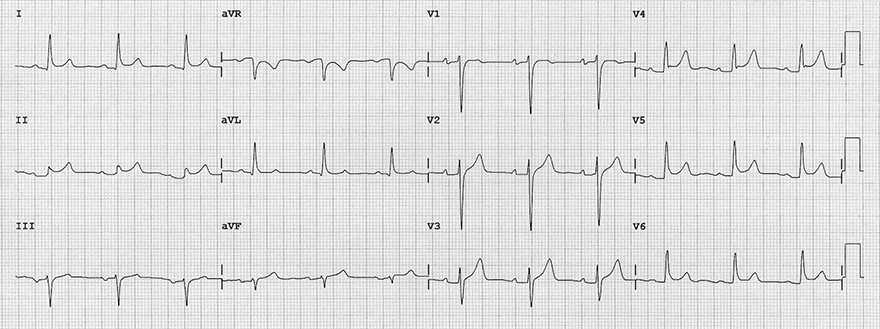
Acute Pericarditis
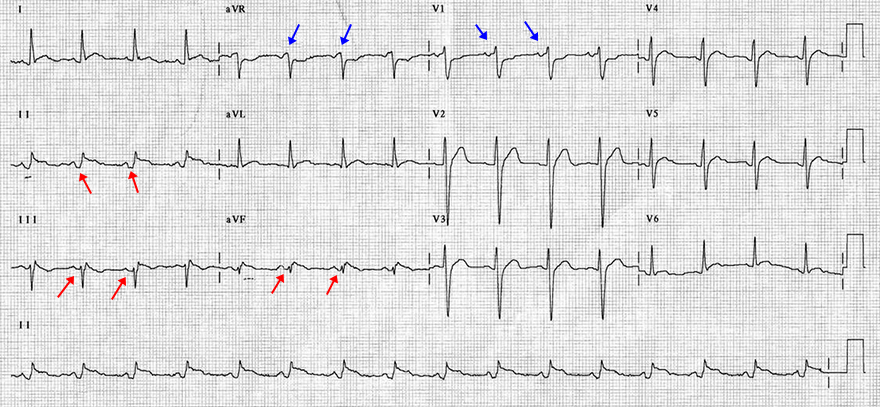
Atrial Infarction and Inferior Wall STEMI
Sources
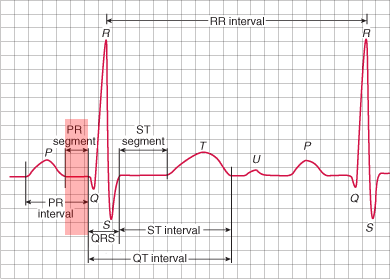
PQ Segment (PR Segment)
|

|
ECG Curve of the PQ Interval
|
 
|
ECG and PQ Segment
|

|

ST Elevations and PQ Depressions
|

ST Depressions and PQ Elevations
|

Acute Pericarditis

Acute Pericarditis
Atrial Infarction
|

|

Atrial Infarction and Inferior Wall STEMI
Sources