
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Pre-excitation syndrome, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, Lown-Ganong-Levine syndrome, Mahaim-type
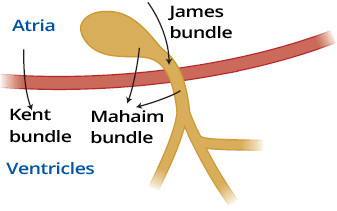

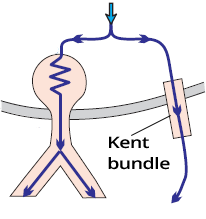
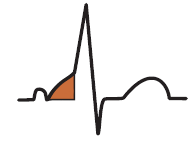
Kent Bundle and WPW Syndrome
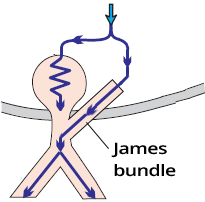

James Bundle and LGL Syndrome

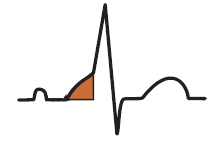
Mahaim Bundle and Mahaim Syndrome
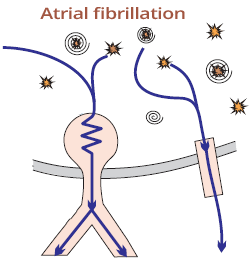
Atrial Fibrillation and WPW
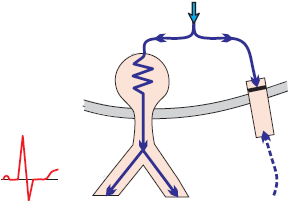
Sinus Rhythm

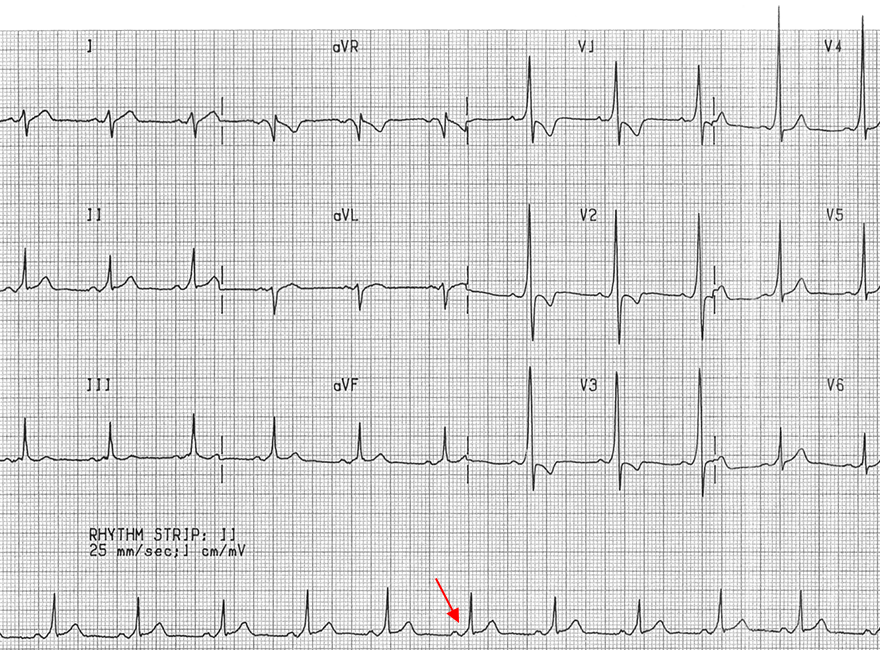
WPW Syndrome

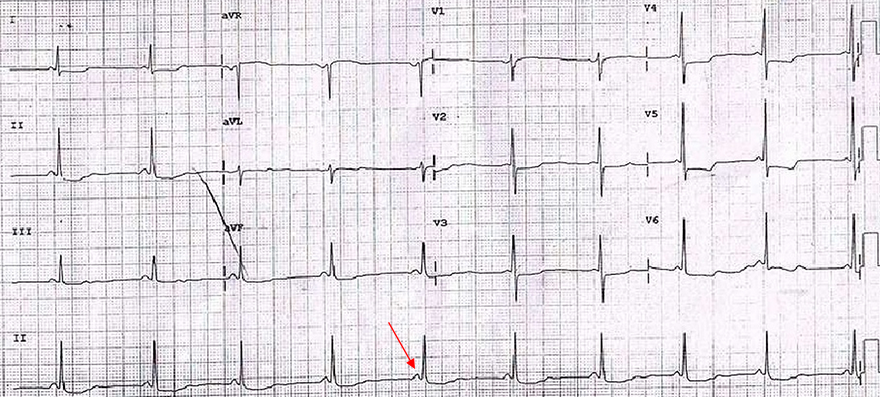
LGL Syndrome


Mahaim Syndrome
Sources
Home /
Pre-excitation syndrome, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, Lown-Ganong-Levine syndrome, Mahaim-type
|

|
Pre-excitation Syndrome
|
 |

|

|
Kent Bundle and WPW Syndrome

|

|
James Bundle and LGL Syndrome

|

|
Mahaim Bundle and Mahaim Syndrome

|
Atrial Fibrillation and WPW
|

|
Sinus Rhythm
|

|
WPW Syndrome
|

|

|
LGL Syndrome
|

|

|
Mahaim Syndrome
|

|
Sources