Home /
Premature Atrial Complex
Premature atrial complex (PAC), Atrial ectopics, Atrial extrasystoles, Atrial premature beats, Atrial premature depolarisations
Heart Rhythm
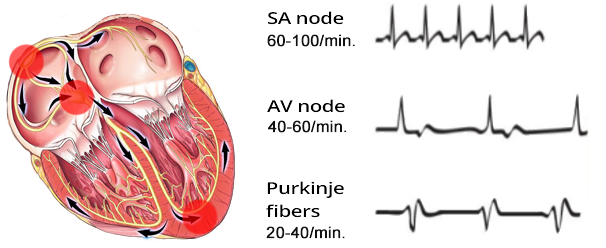
Basic Heart Rhythms
- Heart rhythm is determined by the site (sites) that generates impulses with the highest frequency (overdrive suppression)
- There are 3 basic heart rhythms
- Sinus Rhythm is the physiological heart rhythm
- Because the sinoatrial (SA) node generates impulses with the highest frequency (overdrive suppression)
- The SA node is referred to as the primary pacemaker
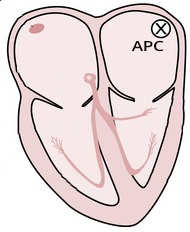
Atrial Premature Contraction (APC)
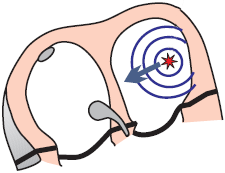
- Most commonly occurs during sinus rhythm
- Arises from an ectopic focus in the atrium
- Impulse originates before the expected depolarization of the SA node
- The P wave will differ from the sinus P wave
- Because the ectopic vector has a different direction than the sinus vector
- The QRS complex will be the same as the sinus QRS complex
- Because the ventricles are activated via the AV junction, as in sinus rhythm
- APCs commonly occur with:
- Stress, coffee, alcohol, smoking...
- APCs are usually benign and do not require treatment
- Sometimes patients experience them as palpitations (heart pounding)
- They are more common in structurally changed hearts
- APCs can trigger re-entry tachycardia:
- There are 3 types of extrasystoles:
ECG and Atrial Premature Contraction

- Abnormal ectopic P wave (has a different shape than the sinus)
- Retrograde (negative) P wave occurs:
- If the ectopic focus is at the AV junction
- It differs from junctional premature contraction by the PQ interval
- On the ECG, it appears earlier than the expected sinus P wave
- Incomplete compensatory pause
- APCs always reset the SA node
- Blocked APC
- If an APC occurs during the refractory phase of the AV junction
- It gets blocked in the AV junction
- An abnormal P wave without a QRS complex occurs
Incomplete Compensatory Pause
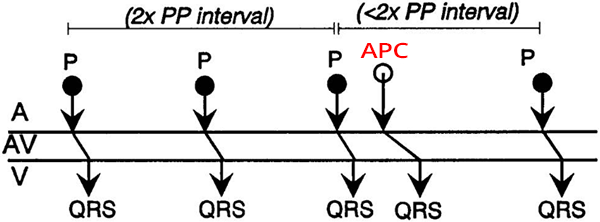
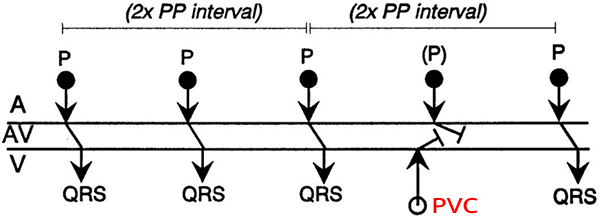
Atrial Premature Contraction and Incomplete Compensatory Pause
- Laddergram shows the propagation of impulses through the conduction system
- The PP (RR) interval with an APC is shorter than twice the PP (RR) interval without an APC
- Because the APC originates from a focus in the atria and resets the SA node
- Incomplete compensatory pause is caused by:

Atrial Premature Contraction and Incomplete Compensatory Pause
- PP (RR) interval with APC (36) is shorter than twice the PP (RR) interval without APC (2x20)
- Atrial Premature Contraction (APC)
- Occurs earlier than the expected sinus P wave (QRS complex)
- Narrow QRS complex (<0.12s)
- The P wave resembles the sinus P wave
- Because the ectopic focus is near the SA node, the atrial vector then has a similar direction
Complete Compensatory Pause
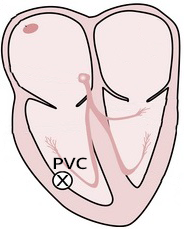
Ventricular Premature Contraction and Complete Compensatory Pause
- A complete compensatory pause occurs almost always with ventricular premature contraction (VPC)
- PP (RR) interval with VPC is exactly twice the PP (RR) interval without VPC
- Because VPC originates in the ventricle and does not pass through the AV node, VPC does not reset the SA node
- Thus, the SA node continues to generate impulses regularly (sinus rhythm)
- Rarely, VPC may retrogradely pass through the AV node and reset the SA node
- Therefore, a rare incomplete compensatory pause can occur with VPC

Ventricular Premature Contraction and Complete Compensatory Pause
- PP (RR) interval with VPC (42) is exactly twice the PP (RR) interval without VPC (2x21)
- Ventricular Premature Contraction (VPC)
- Occurred earlier than the expected sinus QRS complex
- Wide QRS complex (>0.12s)
- Indicated P wave just after the QRS
- VPC did not reset the SA node because VPC did not pass through the AV node
Aberrant Atrial Extrasystole
- Aberrant atrial extrasystole
- During the conduction of Atrial Extrasystole to the ventricles, some part of the conduction system may be in the refractory phase
- An atrial extrasystole occurs - an abnormal P wave, which may be followed by:
- Aberrant atrial extrasystole most commonly has the appearance of right Tawar bundle branch block

Sinus Rhythm Without Atrial Extrasystole
- The SA node generates impulses regularly (P waves), which are conducted to the ventricles (QRS complexes)
- LTR: Length of the refractory period of the Left Tawar bundle branch
- PTR: Length of the refractory period of the Right Tawar bundle branch
- The refractory period occurs shortly after an impulse passes through the conduction system
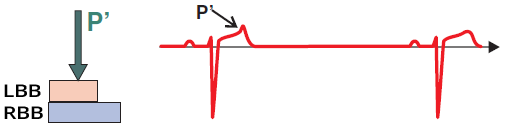
Sinus Rhythm and Blocked Atrial Extrasystole
- The extrasystole occurred during the refractory phase, during ventricular repolarization (T waves)
- The extrasystole depolarized part of the atria, but did not pass through the conduction system to the ventricles
- The extrasystole appears as a P´ wave on the T wave
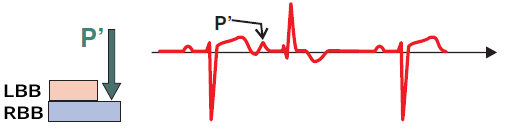
Aberrant Atrial Extrasystole
- The extrasystole (P´) occurred at a time when the left Tawar's branch is no longer in the refractory phase
- But the right branch is still in the refractory phase, causing the extrasystole to be blocked in the right Tawar's branch
- Therefore, the extrasystole (QRS complex) has a right Tawar's branch block shape

Atrial Extrasystole
- The extrasystole (P´) occurred at a time when the Tawar's branches are no longer in the refractory phase
- The extrasystole (QRS complex) has the shape exactly like a sinus QRS
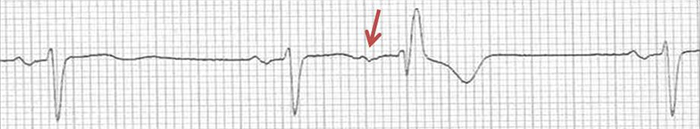
Aberrant Atrial Extrasystole
- The P wave of the atrial extrasystole has a different shape compared to the sinus P wave
- Incomplete compensatory pause
- The extrasystole occurred during the refractory period of the right Tawar's branch

Blocked Atrial Extrasystole
- The T wave has a different shape compared to the other T waves
- Within the T wave, there is a P wave from the atrial extrasystole
- However, the P wave did not proceed to the ventricles because the AV node was in the refractory phase
- Incomplete compensatory pause
Atrial Extrasystoles - Classification
- Atrial Extrasystoles by the number of ectopic foci
- Atrial Extrasystoles by frequency
- Isolated
- Bigeminy
- Trigeminy
- Quadrigeminy
- Couplet
- Triplet
Unifocal Atrial Extrasystole
- Unifocal (Monomorphic) Atrial Extrasystole
- Atrial Extrasystole originate from a single ectopic focus and have the same shape (hence monomorphic)
- Each unifocal Atrial Extrasystole has the same shape and the same P wave


Unifocal Atrial Extrasystole
- On the ECG, there are 2 unifocal atrial extrasystoles
- Narrow QRS complex (<0.12s)
- Occurred earlier than the expected sinus QRS complex
- P waves are different from sinus P waves
- Both ectopic P waves have the same shape
- Because they originated from the same ectopic focus
- Focal Atrial Tachycardia
- The ectopic focus generates impulses at a frequency > 100/min. and "shuts down" the SA node (overdrive suppression)
Multifocal Atrial Extrasystole
- Multifocal (Polytopic) Atrial Extrasystole
- Atrial Extrasystole originate from multiple ectopic foci
- Atrial Extrasystole from each focus generates an extrasystole (P wave) of a different shape
- On the ECG, atrial extrasystoles (P waves) have different shapes
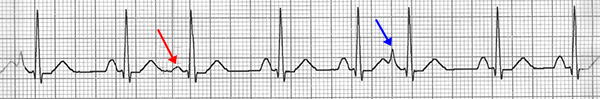
Multifocal Atrial Extrasystole
- On the ECG, there are 2 multifocal atrial extrasystoles
- Narrow QRS complex (<0.12s)
- Each Atrial Extrasystole is from a different ectopic focus, therefore:
- It has a different P wave
- It has a different coupling interval
- Distance between Atrial Extrasystole and the preceding QRS complex
- QRS complexes are the same because each supraventricular impulse activates the ventricles through the AV node
- If the heart rhythm is determined by only ectopic atrial extrasystoles without the SA node, it is:
Atrial Extrasystoles by Repetition
- Isolated Atrial Extrasystole
- Bigeminy
- Trigeminy
- Quadrigeminy
- Couplet
- Triplet

Isolated Atrial Extrasystole
- Isolated Atrial Extrasystole appear on the ECG sporadically
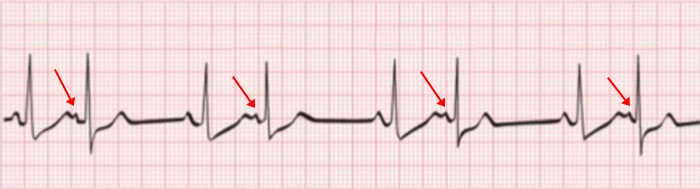
Atrial Bigeminy (Atrial Bigeminal Rhythm)
- Every second beat is an atrial extrasystole
- The heart beats alternately according to the SA node and the ectopic focus
- Atrial bigeminy is sometimes referred to as atrial bigeminal rhythm
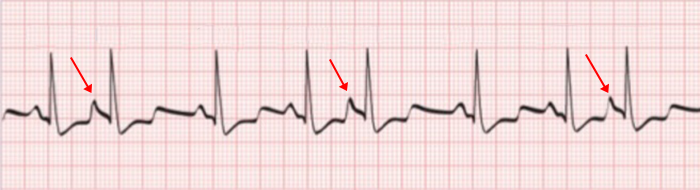
Atrial Trigeminy
- Every third beat is an atrial extrasystole

Atrial Quadrigeminy
- Every fourth beat is an atrial extrasystole
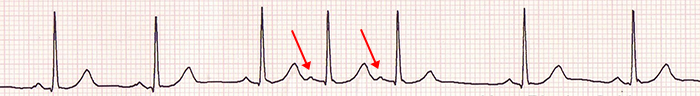
Atrial Couplet
- 2 atrial extrasystoles in a row
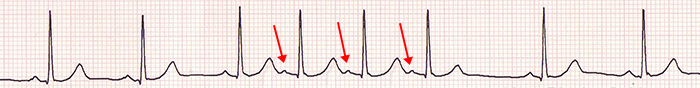
Atrial Triplet
- 3 atrial extrasystoles in a row
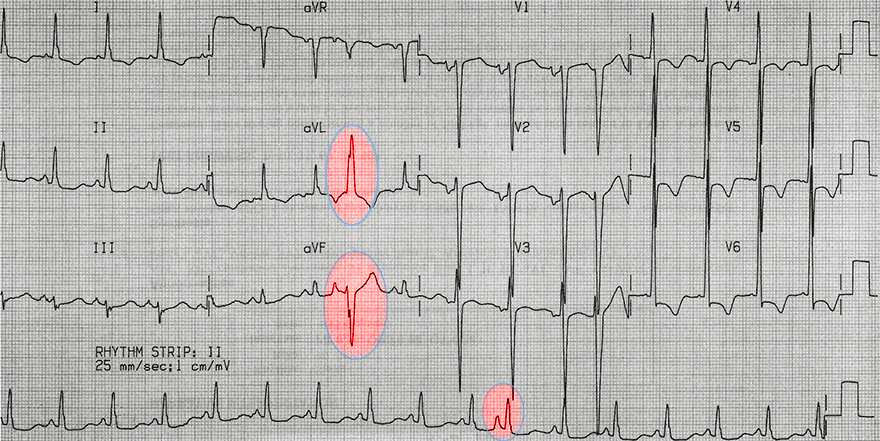
Aberrant Atrial Extrasystole
- In the limb leads (aVL, aVF, II), the extrasystole is recorded with a wide QRS (>0.12s)
- Continuous lead II does not align parallel with the limb leads
- This is an aberrant atrial extrasystole
- Because there is a deformed P wave before the wide QRS complex
- Fusion beat is not expected, as it would have a sine P wave before the QRS
- The extrasystole is not recorded in the precordial leads (V1, V6)
- Thus, it is not possible to precisely determine if it is an aberrant block of the left or right Tawar's bundle
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers

Home /
Premature Atrial Complex
Premature atrial complex (PAC), Atrial ectopics, Atrial extrasystoles, Atrial premature beats, Atrial premature depolarisations
Heart Rhythm

Basic Heart Rhythms
- Heart rhythm is determined by the site (sites) that generates impulses with the highest frequency (overdrive suppression)
- There are 3 basic heart rhythms
- Sinus Rhythm is the physiological heart rhythm
- Because the sinoatrial (SA) node generates impulses with the highest frequency (overdrive suppression)
- The SA node is referred to as the primary pacemaker
Atrial Premature Contraction (APC)
- Most commonly occurs during sinus rhythm
- Arises from an ectopic focus in the atrium
- Impulse originates before the expected depolarization of the SA node
- The P wave will differ from the sinus P wave
- Because the ectopic vector has a different direction than the sinus vector
- The QRS complex will be the same as the sinus QRS complex
- Because the ventricles are activated via the AV junction, as in sinus rhythm
- APCs commonly occur with:
- Stress, coffee, alcohol, smoking...
- APCs are usually benign and do not require treatment
- Sometimes patients experience them as palpitations (heart pounding)
- They are more common in structurally changed hearts
- APCs can trigger re-entry tachycardia:
- There are 3 types of extrasystoles:
|

|
ECG and Atrial Premature Contraction
- Abnormal ectopic P wave (has a different shape than the sinus)
- Retrograde (negative) P wave occurs:
- If the ectopic focus is at the AV junction
- It differs from junctional premature contraction by the PQ interval
- On the ECG, it appears earlier than the expected sinus P wave
- Incomplete compensatory pause
- APCs always reset the SA node
- Blocked APC
- If an APC occurs during the refractory phase of the AV junction
- It gets blocked in the AV junction
- An abnormal P wave without a QRS complex occurs
|

|
Incomplete Compensatory Pause

|

|
|
|
Atrial Premature Contraction and Incomplete Compensatory Pause
- Laddergram shows the propagation of impulses through the conduction system
- The PP (RR) interval with an APC is shorter than twice the PP (RR) interval without an APC
- Because the APC originates from a focus in the atria and resets the SA node
- Incomplete compensatory pause is caused by:
|

Atrial Premature Contraction and Incomplete Compensatory Pause
- PP (RR) interval with APC (36) is shorter than twice the PP (RR) interval without APC (2x20)
- Atrial Premature Contraction (APC)
- Occurs earlier than the expected sinus P wave (QRS complex)
- Narrow QRS complex (<0.12s)
- The P wave resembles the sinus P wave
- Because the ectopic focus is near the SA node, the atrial vector then has a similar direction
Complete Compensatory Pause

|

|
|
|
Ventricular Premature Contraction and Complete Compensatory Pause
- A complete compensatory pause occurs almost always with ventricular premature contraction (VPC)
- PP (RR) interval with VPC is exactly twice the PP (RR) interval without VPC
- Because VPC originates in the ventricle and does not pass through the AV node, VPC does not reset the SA node
- Thus, the SA node continues to generate impulses regularly (sinus rhythm)
- Rarely, VPC may retrogradely pass through the AV node and reset the SA node
- Therefore, a rare incomplete compensatory pause can occur with VPC
|

Ventricular Premature Contraction and Complete Compensatory Pause
- PP (RR) interval with VPC (42) is exactly twice the PP (RR) interval without VPC (2x21)
- Ventricular Premature Contraction (VPC)
- Occurred earlier than the expected sinus QRS complex
- Wide QRS complex (>0.12s)
- Indicated P wave just after the QRS
- VPC did not reset the SA node because VPC did not pass through the AV node
Aberrant Atrial Extrasystole
- Aberrant atrial extrasystole
- During the conduction of Atrial Extrasystole to the ventricles, some part of the conduction system may be in the refractory phase
- An atrial extrasystole occurs - an abnormal P wave, which may be followed by:
- Aberrant atrial extrasystole most commonly has the appearance of right Tawar bundle branch block

Sinus Rhythm Without Atrial Extrasystole
- The SA node generates impulses regularly (P waves), which are conducted to the ventricles (QRS complexes)
- LTR: Length of the refractory period of the Left Tawar bundle branch
- PTR: Length of the refractory period of the Right Tawar bundle branch
- The refractory period occurs shortly after an impulse passes through the conduction system

Sinus Rhythm and Blocked Atrial Extrasystole
- The extrasystole occurred during the refractory phase, during ventricular repolarization (T waves)
- The extrasystole depolarized part of the atria, but did not pass through the conduction system to the ventricles
- The extrasystole appears as a P´ wave on the T wave

Aberrant Atrial Extrasystole
- The extrasystole (P´) occurred at a time when the left Tawar's branch is no longer in the refractory phase
- But the right branch is still in the refractory phase, causing the extrasystole to be blocked in the right Tawar's branch
- Therefore, the extrasystole (QRS complex) has a right Tawar's branch block shape

Atrial Extrasystole
- The extrasystole (P´) occurred at a time when the Tawar's branches are no longer in the refractory phase
- The extrasystole (QRS complex) has the shape exactly like a sinus QRS

Aberrant Atrial Extrasystole
- The P wave of the atrial extrasystole has a different shape compared to the sinus P wave
- Incomplete compensatory pause
- The extrasystole occurred during the refractory period of the right Tawar's branch

Blocked Atrial Extrasystole
- The T wave has a different shape compared to the other T waves
- Within the T wave, there is a P wave from the atrial extrasystole
- However, the P wave did not proceed to the ventricles because the AV node was in the refractory phase
- Incomplete compensatory pause
Atrial Extrasystoles - Classification
- Atrial Extrasystoles by the number of ectopic foci
- Atrial Extrasystoles by frequency
- Isolated
- Bigeminy
- Trigeminy
- Quadrigeminy
- Couplet
- Triplet
Unifocal Atrial Extrasystole
- Unifocal (Monomorphic) Atrial Extrasystole
- Atrial Extrasystole originate from a single ectopic focus and have the same shape (hence monomorphic)
- Each unifocal Atrial Extrasystole has the same shape and the same P wave
Unifocal Atrial Extrasystole
- On the ECG, there are 2 unifocal atrial extrasystoles
- Narrow QRS complex (<0.12s)
- Occurred earlier than the expected sinus QRS complex
- P waves are different from sinus P waves
- Both ectopic P waves have the same shape
- Because they originated from the same ectopic focus
- Focal Atrial Tachycardia
- The ectopic focus generates impulses at a frequency > 100/min. and "shuts down" the SA node (overdrive suppression)
Multifocal Atrial Extrasystole
- Multifocal (Polytopic) Atrial Extrasystole
- Atrial Extrasystole originate from multiple ectopic foci
- Atrial Extrasystole from each focus generates an extrasystole (P wave) of a different shape
- On the ECG, atrial extrasystoles (P waves) have different shapes
Multifocal Atrial Extrasystole
- On the ECG, there are 2 multifocal atrial extrasystoles
- Narrow QRS complex (<0.12s)
- Each Atrial Extrasystole is from a different ectopic focus, therefore:
- It has a different P wave
- It has a different coupling interval
- Distance between Atrial Extrasystole and the preceding QRS complex
- QRS complexes are the same because each supraventricular impulse activates the ventricles through the AV node
- If the heart rhythm is determined by only ectopic atrial extrasystoles without the SA node, it is:
Atrial Extrasystoles by Repetition
- Isolated Atrial Extrasystole
- Bigeminy
- Trigeminy
- Quadrigeminy
- Couplet
- Triplet

Isolated Atrial Extrasystole
- Isolated Atrial Extrasystole appear on the ECG sporadically

Atrial Bigeminy (Atrial Bigeminal Rhythm)
- Every second beat is an atrial extrasystole
- The heart beats alternately according to the SA node and the ectopic focus
- Atrial bigeminy is sometimes referred to as atrial bigeminal rhythm

Atrial Trigeminy
- Every third beat is an atrial extrasystole

Atrial Quadrigeminy
- Every fourth beat is an atrial extrasystole

Atrial Couplet
- 2 atrial extrasystoles in a row

Atrial Triplet
- 3 atrial extrasystoles in a row

Aberrant Atrial Extrasystole
- In the limb leads (aVL, aVF, II), the extrasystole is recorded with a wide QRS (>0.12s)
- Continuous lead II does not align parallel with the limb leads
- This is an aberrant atrial extrasystole
- Because there is a deformed P wave before the wide QRS complex
- Fusion beat is not expected, as it would have a sine P wave before the QRS
- The extrasystole is not recorded in the precordial leads (V1, V6)
- Thus, it is not possible to precisely determine if it is an aberrant block of the left or right Tawar's bundle
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers





















































