
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Premature Junctional Complex (PJC), Junctional Ectopics, Junctional Extrasystoles, Junctional Premature Beats, Junctional Premature Depolarisations, Atrioventricular junctional premature complexes

Basic Heart Rhythms

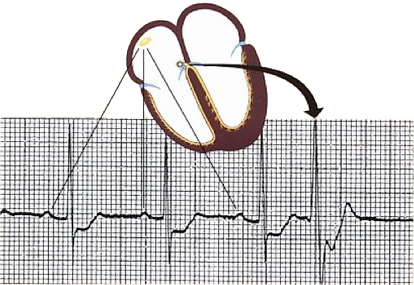


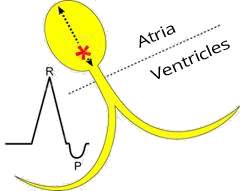
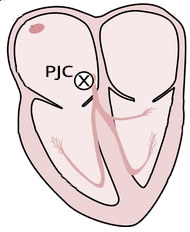
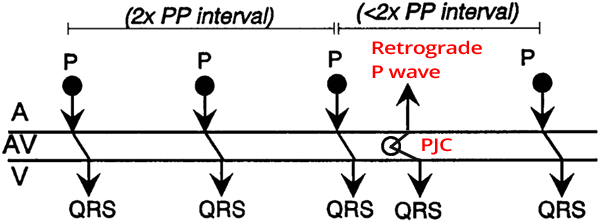
Premature Junctional Complex (PJC) and Incomplete Compensatory Pause

Premature Junctional Complex (PJC) and Incomplete Compensatory Pause
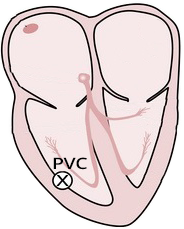
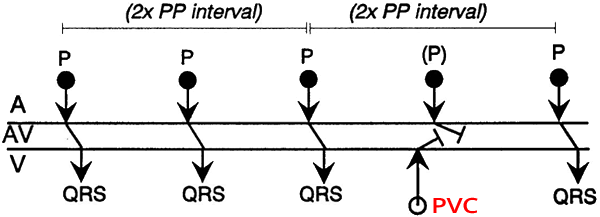
Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC) and Complete Compensatory Pause

Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC) and Complete Compensatory Pause
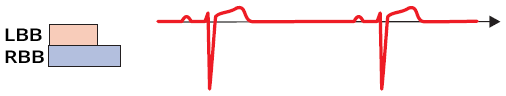
Sinus Rhythm Without Premature Junctional Complex (PJC)

Aberrant Premature Junctional Complex (PJC)
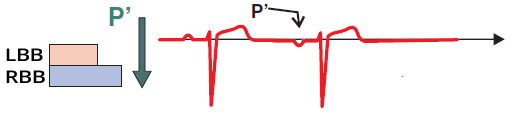
Premature Junctional Complex (PJC)


Premature Junctional Complex (PJC)


Premature Junctional Complex (PJC)

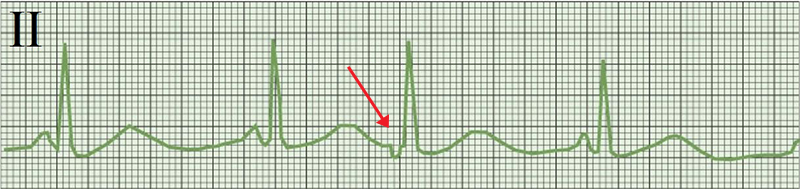
Premature Junctional Complex (PJC)

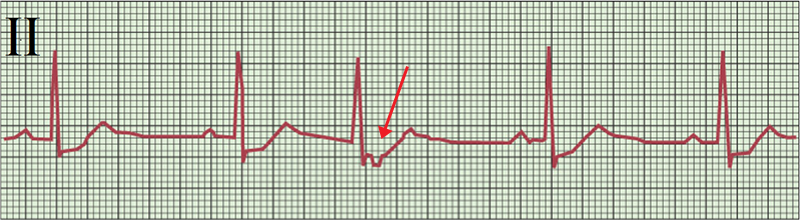
Junctional Extrasystole

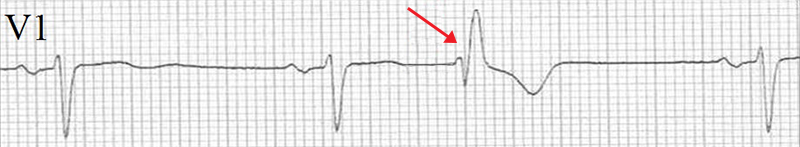
Aberrant Junctional Extrasystole
Sources
Home /
Premature Junctional Complex (PJC), Junctional Ectopics, Junctional Extrasystoles, Junctional Premature Beats, Junctional Premature Depolarisations, Atrioventricular junctional premature complexes

Basic Heart Rhythms
Premature Junctional Complex (PJC)
|

|
ECG and Premature Junctional Complex (PJC)
|

|

|

|

|
 |
 |
|
Premature Junctional Complex (PJC) and Incomplete Compensatory Pause
|

Premature Junctional Complex (PJC) and Incomplete Compensatory Pause
 |

|
|
Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC) and Complete Compensatory Pause
|

Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC) and Complete Compensatory Pause

Sinus Rhythm Without Premature Junctional Complex (PJC)

Aberrant Premature Junctional Complex (PJC)

Premature Junctional Complex (PJC)

|
Premature Junctional Complex (PJC)
|

|

|
Premature Junctional Complex (PJC)
|

|

|
Premature Junctional Complex (PJC)
|

|

|
Junctional Extrasystole
|

|

|
Aberrant Junctional Extrasystole
|

|
Sources