
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |


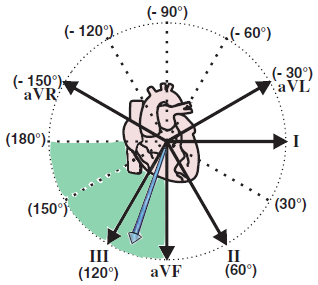
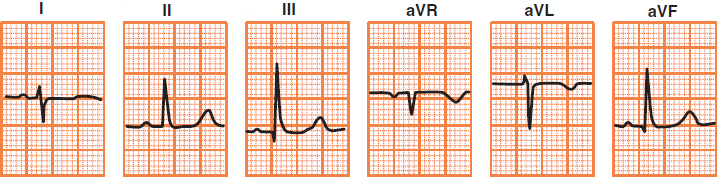
Right Axis Deviation

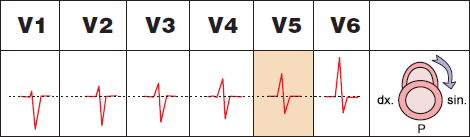
Clockwise Heart Rotation
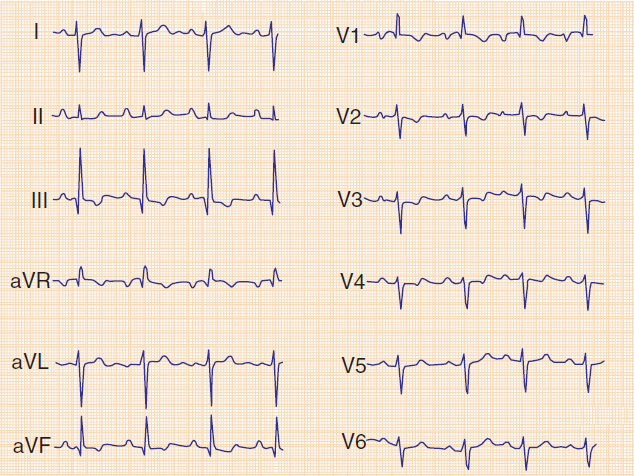
Acute Pulmonary Embolism
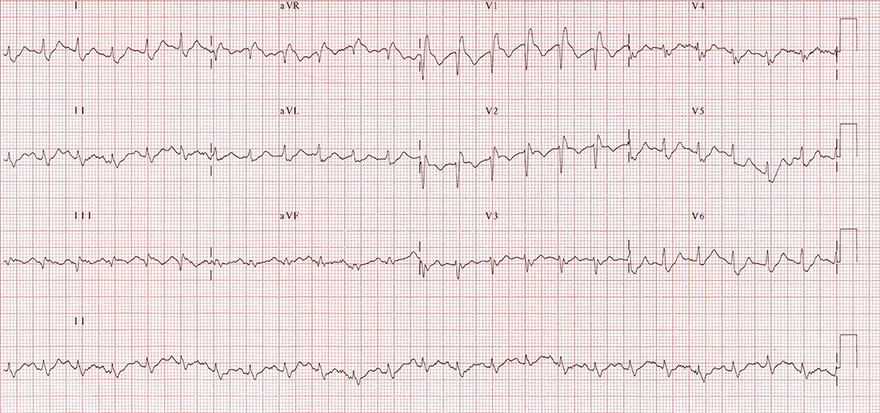
Acute Pulmonary Embolism
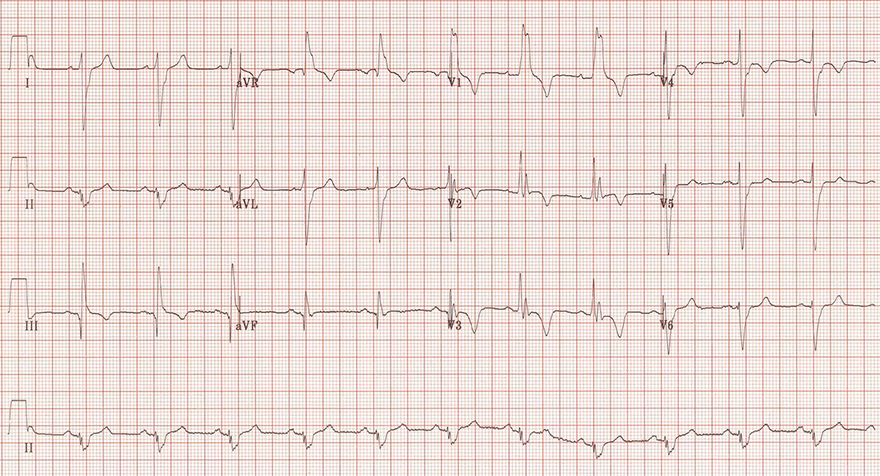
Acute Pulmonary Embolism
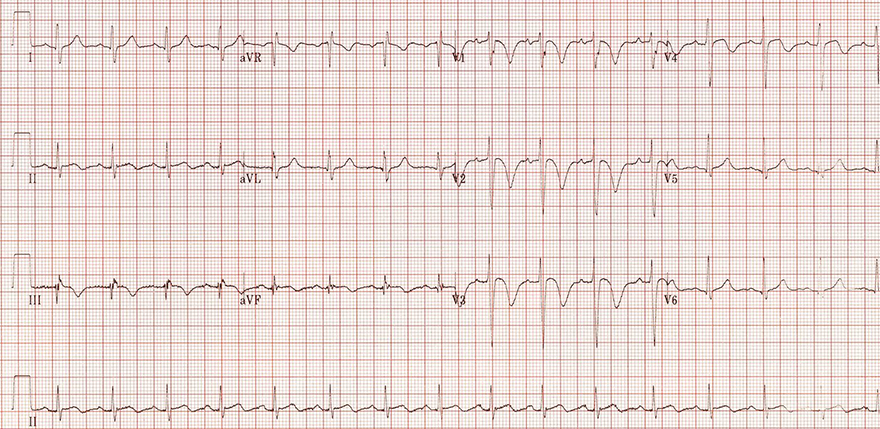
Massive Pulmonary Embolism
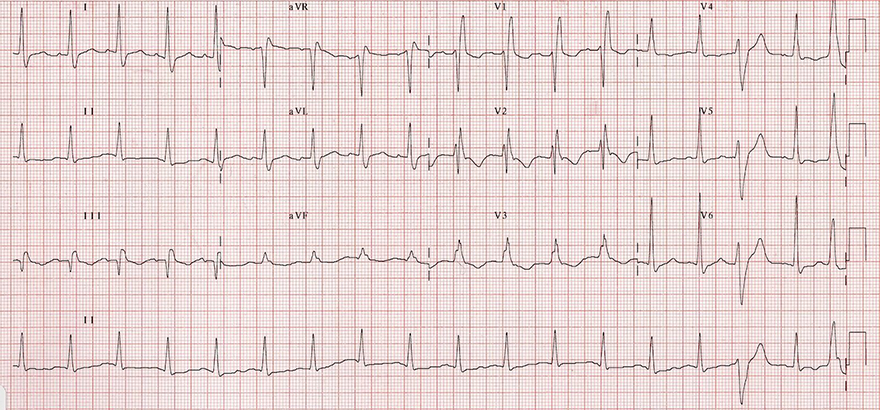
Acute Pulmonary Embolism
Sources
Cor Pulmonale
|
 |
Pulmonary Embolism
|

|

|
|
|
Right Axis Deviation
|

|
 |
 |
Clockwise Heart Rotation

Acute Pulmonary Embolism

Acute Pulmonary Embolism

Acute Pulmonary Embolism

Massive Pulmonary Embolism

Acute Pulmonary Embolism
Sources