
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

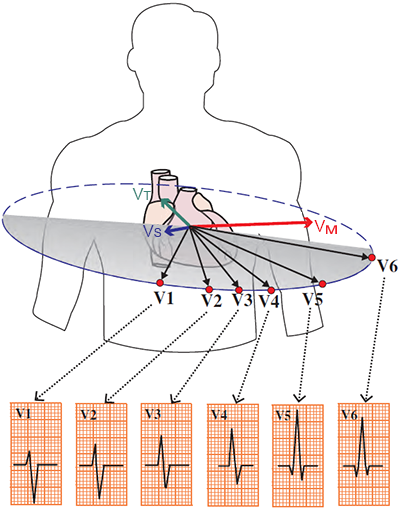
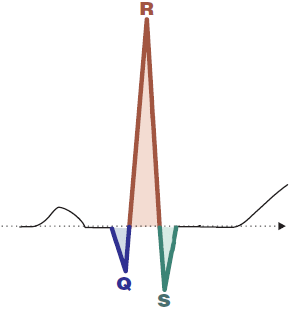
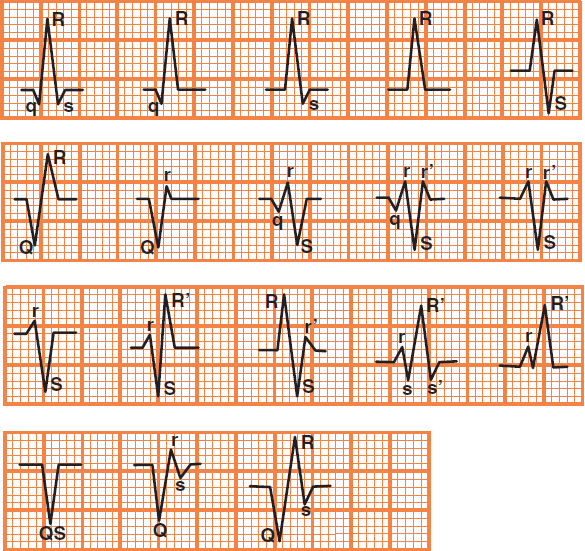
QRS Complex Nomenclature
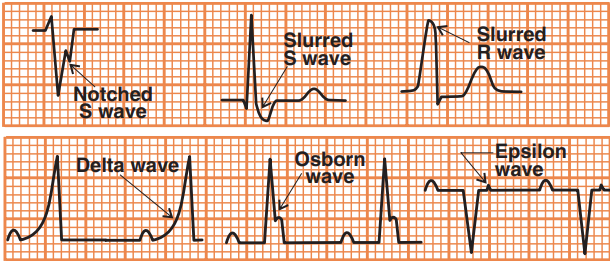
Fragmentation of the QRS Complex

Ventricular Tachycardia
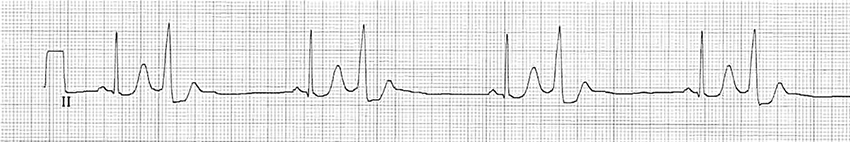
Bigeminal Ventricular Extrasystoles

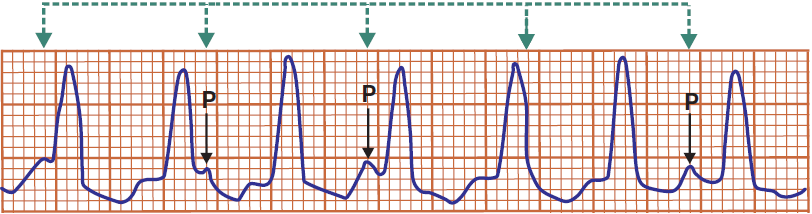
Ventricular Tachycardia
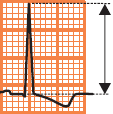

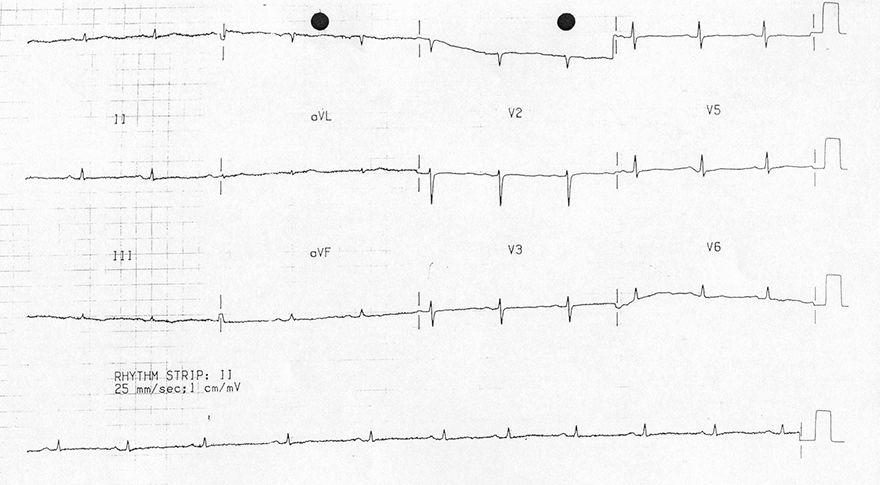
Low QRS Voltage
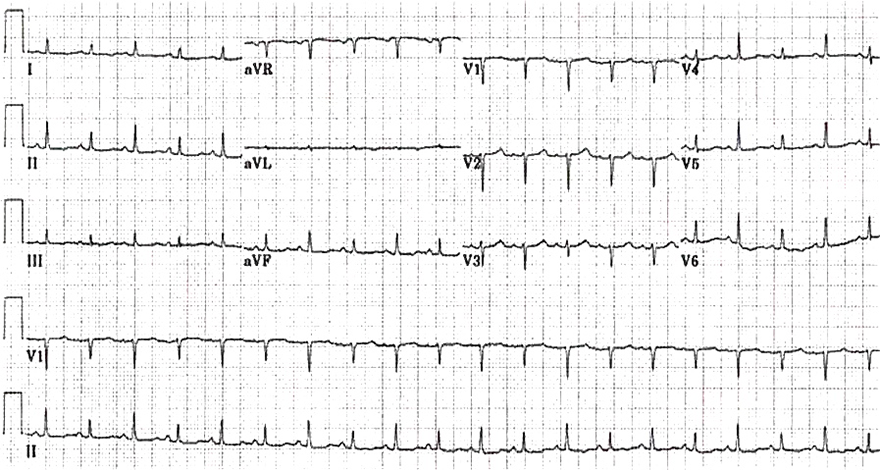
QRS Alternans
Sources
|
 |
|
 |
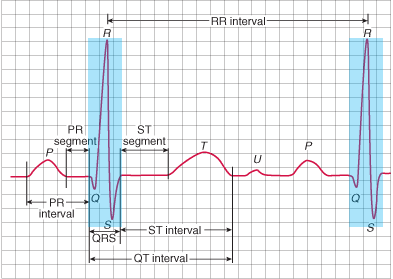
QRS Complex
|

|

QRS Complex Nomenclature

Fragmentation of the QRS Complex

Ventricular Tachycardia
QRS Complex Width
|

|

Bigeminal Ventricular Extrasystoles
Narrow QRS Complex (<110ms)
|

|
Wide QRS Complex (>110ms)
|

|

Ventricular Tachycardia
QRS Complex Amplitude
|

|
|

|

Low QRS Voltage

QRS Alternans
Sources