Home /
QT Interval - ECG
QT interval
QT Interval and Action Potential

- During action potential
- Ions pass through the cardiomyocyte membrane
- Electrical voltage changes
- A curve of action potential is generated
- Ventricular action potential creates the following on the ECG:
- QT Interval
- Starts with Q wave (beginning of ventricular depolarization)
- Ends with T wave (end of ventricular repolarization)
- Duration is 0.35 - 0.44s
Corrected QT Interval (QTc)
- QT interval changes with heart rate
- QT shortens with increasing frequency
- QT lengthens with decreasing frequency
- Only short QT syndrome has a QT interval independent of frequency
- Normal QT interval is 0.35s - 0.44s.
- This applies only to a rate of 60/min.
- Corrected QT interval (QTc)
- Is calculated for frequencies other than 60/min.
- QTc is the QT interval corrected to a rate of 60/min.
- Calculator for (QTc)
- The following patient has a QTc of 0.4s (neither prolonged nor shortened)
- Heart rate: 40/min., QT: 0.49s, QTc: 0.4s
- Heart rate: 60/min., QT: 0.40s, QTc: 0.4s
- Heart rate: 80/min., QT: 0.35s, QTc: 0.4s
- Heart rate: 100/min., QT: 0.31s, QTc: 0.4s
Formulas for Calculating (QTc)
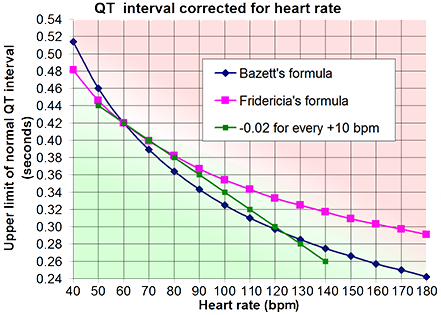
- There are many formulas for calculating QTc
- Each formula corrects the QT interval to a rate of 60/min.
- Bazett's Formula QTC = QT / √ RR
- Is most suitable for rates of 60-100/min.
- Fridericia's Formula QTC = QT / RR 1/3
- Framingham Formula QTC = QT + 0.154 (1 – RR)
- Fridericia's and Framingham's formulas
- Are suitable for rates other than 60-100/min.
- Hodges' Formula QTC = QT + 1.75 (frequency – 60)
- Principle of subtracting 0.02s
- Uses a baseline heart rate of 60/min.
- If the rate increases by 10/min.
- The QT interval physiologically shortens by 0.02s
ECG and QT Interval

- It is best visible in leads: II, V5, V6
- It is the distance from the beginning of the Q wave to the end of the T wave
- It ranges from 0.35s to 0.44s.
- QU interval = QT interval
- If the T and U waves are merged, then we measure the QU interval
- JT interval = QT interval
- If there are wide QRS complexes (ventricular rhythm), QT is measured:
- From the J point to the end of the T wave
- JTC > 330ms (analogous to QTC > 440ms)
- For assessing the QT interval, we always use QTC
- QTC is prolonged if it is:
- QTC is shortened < 350ms
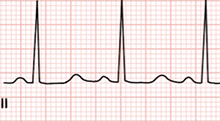
Prolonged and Normal QT Interval
- For a heart rate of 60 - 100/min., the following applies:
- The QT interval is normal if it is less than half of the RR interval

Prolonged QTC > 440ms
- The QT interval is prolonged if it is:
- Most common causes of prolonged QT interval
Prolonged QT Interval
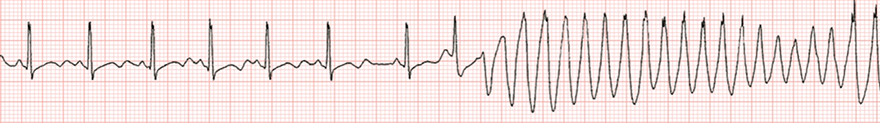
Prolonged QT Interval and Torsades de Pointes
- QTC = 0.58s
- A prolonged QTC > 0.5s regardless of the cause represents a risk for Torsades de Pointes
- Torsades de Pointes
Short QTC < 350ms
- QT interval is shortened if
- Most common causes of a shortened QT interval
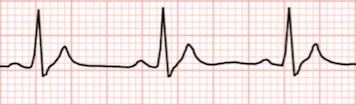
Short QT Interval
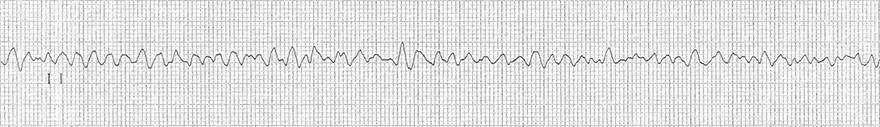
Ventricular Fibrillation

QT Interval (0.4s), QTC (0.4s)
- Frequency 60/min.
- No need to calculate QTC (at 60/min frequency, QT = QTC)
- QTC interval (0.4s) is not prolonged (0.35s - 0.44s)
- QT is less than half of the RR interval
- QT (0.4s) < 1/2 RR (0.49s)
- This rule applies only at frequencies of 60-100/min.

QT Interval (0.6s), QTC (0.5s)
- Frequency 43/min.
- QT Interval (0.6s)
- QTC interval (0.5s) is prolonged (>0.44s)
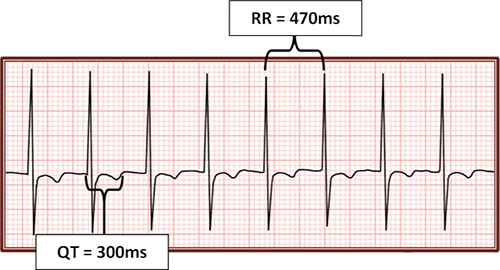
QT Interval (0.3s), QTC (0.45s)
- Frequency 136/min.
- QT Interval (0.3s)
- QTC interval (0.45s) is prolonged (>0.44s)
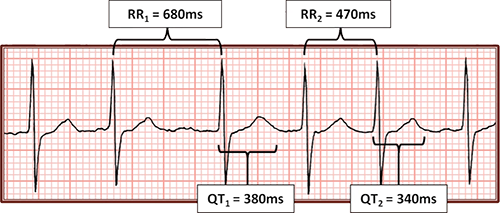
Atrial Fibrillation and QT Interval, QTC (0.478s)
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Heart rate is irregularly irregular
- QTC is calculated as the average QT interval after the longest and shortest RR intervals
- Average QTC = 0.478s
- QTC1 = 0.46s
- QTC2 = 0.496s
- QTC interval (0.478s) is prolonged (>0.44s)
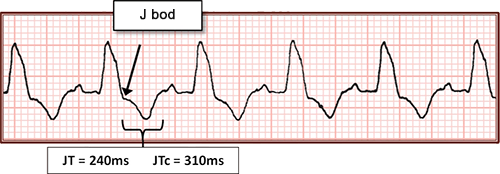
Wide QRS Complexes and QT Interval (JT Interval)
- In ventricular rhythm, QRS complexes are widened (>0.12s)
- As a secondary effect, QT interval also prolongs
- QT prolongs due to the widened QRS complex (depolarization)
- QT does not prolong due to widened T wave (repolarization)
- Therefore, widened QT interval in wide QRS complexes is irrelevant
- In wide QRS complexes, measure the JT interval and corrected (JTC) interval
- Calculated exactly like QT and QTC
- J point is the point where the ST segment deviates from the QRS complex
- JT = 0.24s
- JTC = 0.31s
- JTC > 0.33s is considered prolonged
- It is analogous to QTC > 0.44s

QT Interval and U Wave
- If the U wave is separated from the QT interval
- It is not included in the length of the QT interval
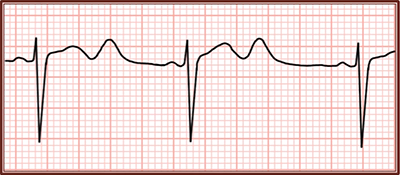
QT Interval and U Wave
- If the U wave is separated from the QT interval but is higher than 50% of the T wave
- There is no academic consensus on whether it should or should not be included in the length of the QT interval

Hypocalcemia and Prolonged QTC (0.53s)

Hyperkalemia and Shortened QTC (0.32s)
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers

































