Home /
Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB) - ECG
Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
Wide QRS Complex
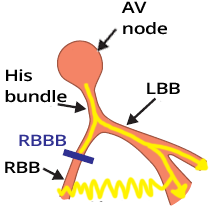

Wide QRS Complex (≥ 0.12s)
- In Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
- The impulse is blocked in the right bundle branch
- Supraventricular impulse activates the ventricles only through the left bundle branch
- The left ventricle is activated first
- Then the impulse passes through the myocardium to the right ventricle and activates it
- The impulse spreads through the myocardium more slowly than through the bundle branches
- Activation of the right ventricle is therefore delayed
- This results in a wide QRS complex ≥ 0.12s (≥ 3 squares)
Causes of RBBB

Heart Vector and RBBB

Ventricular Activation in Right Bundle Branch Block
- Both ventricles are activated only through the left bundle branch, with impulse activation occurring sequentially
- During the activation of different parts of the ventricles, heart vectors are generated
- 1. First, the interventricular septum is activated
- A small initial vector (VI) is created, directed to the right (1)
- The vector is small because the myocardial mass of the interventricular septum is small
- 2. Next, the left ventricle is activated
- The impulse exits the left bundle branch and activates the massive myocardium of the left ventricle
- A main largest heart vector (VM) is created, directed to the left (2)
- 3. Then, the right ventricle is activated
- The impulse slowly passes to the right ventricle through the myocardium (not through the blocked right bundle branch)
- A wide QRS complex ≥ 0.12s is created
- A small terminal vector (VT) is generated, directed to the right
- Vectors and ECG leads should be visualized in 3D space
- If a vector points towards an ECG lead, it creates a positive deflection
- If a vector points away from an ECG lead, it creates a negative deflection
RBBB and Leads (V1, V6)
- In RBBB, the vectors are "best viewed" in the chest leads V1 and V6
- If we have a wide QRS complex (≥ 0,12s) on the ECG, immediately assess leads V1 and V6
- Using leads V1 and V6, diagnose:
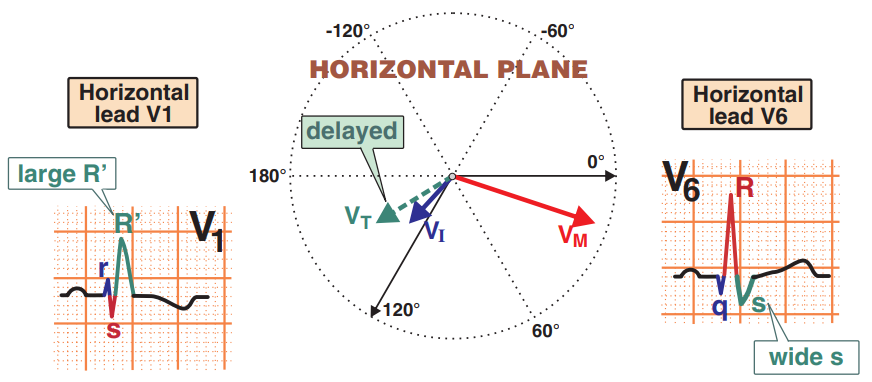
Leads (V1, V6) and Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
- The image shows vectors projected in the horizontal plane
- The best view of the vectors is with leads V1 and V6
- 1. A small initial (VI) vector is generated, creating
- Small r wave (V1)
- Small q wave (V6)
- 2. A massive main vector (VM) is generated, creating
- Small s wave (V1)
- Large R wave (V6)
- 3. A small terminal vector (VT) is generated, creating
- Large R' wave (V1)
- Wide S wave (V6)
- In V1, a letter "M" is formed
- In V6, a letter "W" is formed
ECG and RBBB

- Wide QRS ≥ 0,12s (≥ 3 squares)
- In V1, the QRS has an "M" shape
- Also in other right-sided leads (V1-V3)
- The second rabbit ear is almost always larger
- Can present with configurations such as: rsr', rsR', rSR'
- In V6, there is a wide S wave > 40ms
- In V1-V3, there are ST depressions or negative T waves

Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- If the QRS width is 0.10-0.12s, it indicates incomplete RBBB
- V1 (rsR')
- V1 (Negative T waves)
- V6 (Wide S wave)

RBBB (V1)

RBBB (V6)
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- V6 (wide S wave)
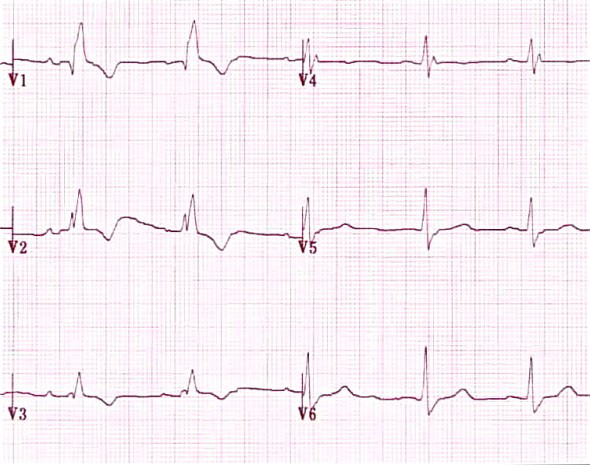
Right Bundle Branch Block (V1-V6)
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- V1 (rsR') and V2
- Negative T waves (V1-V3)
- V6 (wide S wave) and V5
ECG and Incomplete RBBB
- The right bundle branch is impaired but not interrupted ("cut off")
- Conducts impulses more slowly
- The only difference on ECG compared to complete block is the width of the QRS complex
- Complete RBBB
- Incomplete RBBB

Incomplete RBBB
- QRS width 0.1s (0.1 - 0.12s)
- V1 (RSr')
- Negative T waves
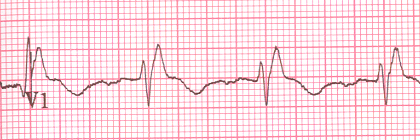
Complete RBBB
- QRS width 0.18s (≥ 0.12s)
- V1 (rSR')
- Negative T waves
Functional RBBB and Ashman Phenomenon
- It is a temporary RBBB that appears on the ECG and then disappears
- Functional RBBB occurs when an impulse arrives at the branch too early, during the refractory period
The branch blocks this impulse
- This premature impulse can reach the branch during

- With a lengthening RR interval, the refractory period of the conduction system also lengthens
- Ashman phenomenon is aberrant conduction that occurs when a lengthened RR interval is followed by a shortened RR interval
- Shortened RR interval has a prolonged refractory period
- which has not had time to shorten from the previous lengthened RR interval
- It is true that the right bundle branch (RBB) has a longer refractory period than the left bundle branch (LBB)
- If an impulse travels through the AV node to the ventricles at a time
- when the right bundle branch is in the refractory period
- it results in functional RBBB
- The functional block most commonly occurs during atrial fibrillation
- When a long RR interval is followed by a short RR with a QRS complex (which has the appearance of RBBB)
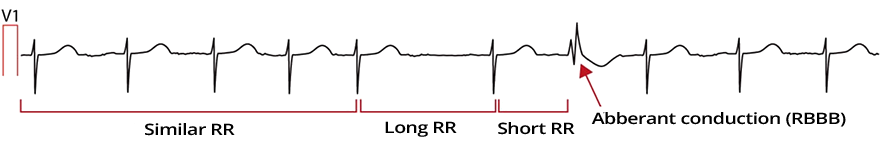
Functional RBBB and Atrial Fibrillation
- On the ECG, atrial fibrillation in lead V1 with calibration of 10mm
- Initially, RR intervals are relatively consistent
- Then a long-short RR interval occurs
- Long RR prolonged the refractory period
- Short RR ends with aberrant conduction showing a RBBB pattern
- The short RR impulse passes through the right branch during the refractory period and gets blocked
- Ashman phenomenon is most common in atrial fibrillation
- When RR intervals change irregularly

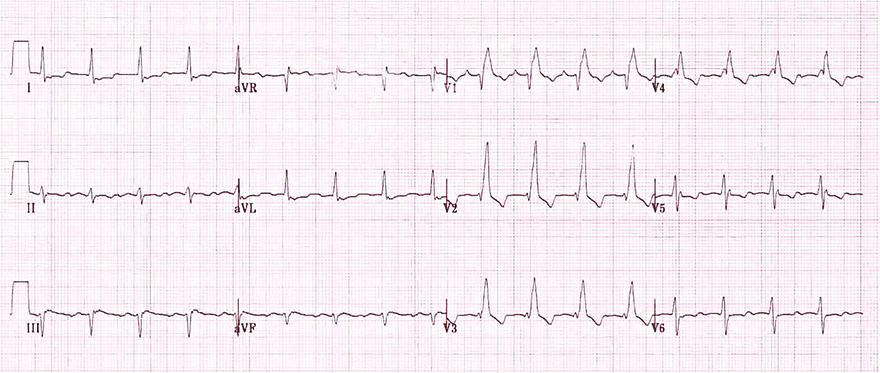
Right Bundle Branch Block
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- In V1 (V2) there is qR
- In V6 (V5, I) there is wide S
- In V1-3 there are negative T waves

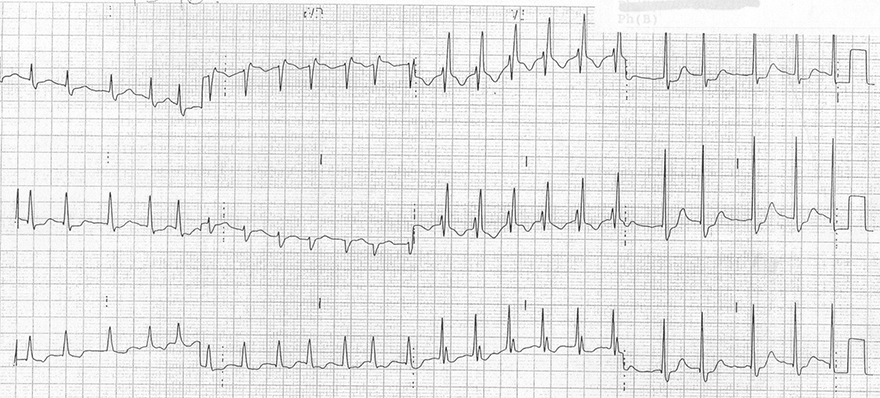
Right Bundle Branch Block
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- In V1 (V2) there is rSR'
- In V6 (V5-6, I, aVL) there is wide S
- In V1-3 there are negative T waves

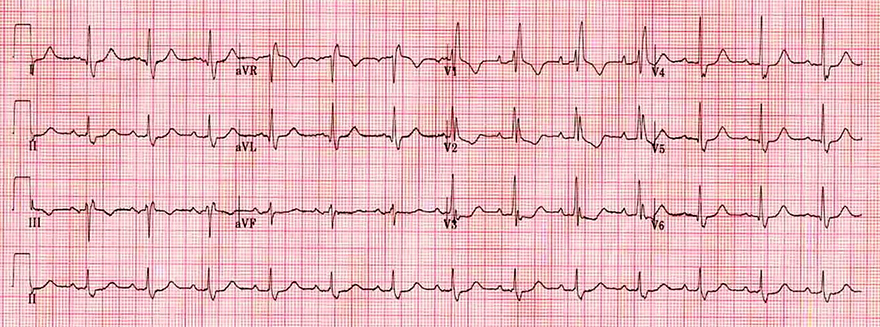
Right Bundle Branch Block
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- In V1 there is rSR'
- In V6 (V5-6, I, aVL) there is wide S
- In V1-3 there are negative T waves


Right Bundle Branch Block
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- In V1 there is rSR'
- In V6 (V5-6, I, aVL) there is wide S
- In V1 there is a negative T wave

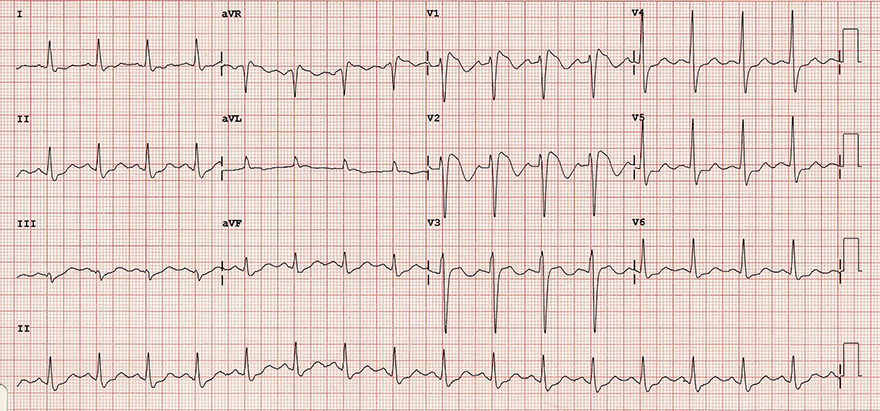
Incomplete Right Bundle Branch Block
- In V1 there is RSr'
- In V5 and I there is wide S
- In V1-3 there are negative T waves
- Narrow QRS < 0.12s
- The patient meets all criteria for RBBB, but the QRS complex is narrow
- Narrow QRS indicates incomplete RBBB
Brugada Syndrome
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- In V1 there is rSR'
- In V5 there is wide S
- In V1-3 there are negative T waves and descending ST elevations
- This ECG resembles RBBB, but RBBB does not have descending ST elevations in V1-3
- The ECG shows Brugada syndrome
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers
Home /
Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB) - ECG
Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
Wide QRS Complex

Wide QRS Complex (≥ 0.12s)
- In Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
- The impulse is blocked in the right bundle branch
- Supraventricular impulse activates the ventricles only through the left bundle branch
- The left ventricle is activated first
- Then the impulse passes through the myocardium to the right ventricle and activates it
- The impulse spreads through the myocardium more slowly than through the bundle branches
- Activation of the right ventricle is therefore delayed
- This results in a wide QRS complex ≥ 0.12s (≥ 3 squares)
|

|
Causes of RBBB
|

|
Heart Vector and RBBB

Ventricular Activation in Right Bundle Branch Block
- Both ventricles are activated only through the left bundle branch, with impulse activation occurring sequentially
- During the activation of different parts of the ventricles, heart vectors are generated
- 1. First, the interventricular septum is activated
- A small initial vector (VI) is created, directed to the right (1)
- The vector is small because the myocardial mass of the interventricular septum is small
- 2. Next, the left ventricle is activated
- The impulse exits the left bundle branch and activates the massive myocardium of the left ventricle
- A main largest heart vector (VM) is created, directed to the left (2)
- 3. Then, the right ventricle is activated
- The impulse slowly passes to the right ventricle through the myocardium (not through the blocked right bundle branch)
- A wide QRS complex ≥ 0.12s is created
- A small terminal vector (VT) is generated, directed to the right
- Vectors and ECG leads should be visualized in 3D space
- If a vector points towards an ECG lead, it creates a positive deflection
- If a vector points away from an ECG lead, it creates a negative deflection
RBBB and Leads (V1, V6)
- In RBBB, the vectors are "best viewed" in the chest leads V1 and V6
- If we have a wide QRS complex (≥ 0,12s) on the ECG, immediately assess leads V1 and V6
- Using leads V1 and V6, diagnose:

Leads (V1, V6) and Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
- The image shows vectors projected in the horizontal plane
- The best view of the vectors is with leads V1 and V6
- 1. A small initial (VI) vector is generated, creating
- Small r wave (V1)
- Small q wave (V6)
- 2. A massive main vector (VM) is generated, creating
- Small s wave (V1)
- Large R wave (V6)
- 3. A small terminal vector (VT) is generated, creating
- Large R' wave (V1)
- Wide S wave (V6)
- In V1, a letter "M" is formed
- In V6, a letter "W" is formed
ECG and RBBB
- Wide QRS ≥ 0,12s (≥ 3 squares)
- In V1, the QRS has an "M" shape
- Also in other right-sided leads (V1-V3)
- The second rabbit ear is almost always larger
- Can present with configurations such as: rsr', rsR', rSR'
- In V6, there is a wide S wave > 40ms
- In V1-V3, there are ST depressions or negative T waves
|

|

Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- If the QRS width is 0.10-0.12s, it indicates incomplete RBBB
- V1 (rsR')
- V1 (Negative T waves)
- V6 (Wide S wave)

RBBB (V1)
|

RBBB (V6)
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- V6 (wide S wave)
|

Right Bundle Branch Block (V1-V6)
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- V1 (rsR') and V2
- Negative T waves (V1-V3)
- V6 (wide S wave) and V5
ECG and Incomplete RBBB
- The right bundle branch is impaired but not interrupted ("cut off")
- Conducts impulses more slowly
- The only difference on ECG compared to complete block is the width of the QRS complex
- Complete RBBB
- Incomplete RBBB

Incomplete RBBB
- QRS width 0.1s (0.1 - 0.12s)
- V1 (RSr')
- Negative T waves
|

Complete RBBB
- QRS width 0.18s (≥ 0.12s)
- V1 (rSR')
- Negative T waves
|
Functional RBBB and Ashman Phenomenon
- It is a temporary RBBB that appears on the ECG and then disappears
- Functional RBBB occurs when an impulse arrives at the branch too early, during the refractory period
The branch blocks this impulse
- This premature impulse can reach the branch during

- With a lengthening RR interval, the refractory period of the conduction system also lengthens
- Ashman phenomenon is aberrant conduction that occurs when a lengthened RR interval is followed by a shortened RR interval
- Shortened RR interval has a prolonged refractory period
- which has not had time to shorten from the previous lengthened RR interval
- It is true that the right bundle branch (RBB) has a longer refractory period than the left bundle branch (LBB)
- If an impulse travels through the AV node to the ventricles at a time
- when the right bundle branch is in the refractory period
- it results in functional RBBB
- The functional block most commonly occurs during atrial fibrillation
- When a long RR interval is followed by a short RR with a QRS complex (which has the appearance of RBBB)

Functional RBBB and Atrial Fibrillation
- On the ECG, atrial fibrillation in lead V1 with calibration of 10mm
- Initially, RR intervals are relatively consistent
- Then a long-short RR interval occurs
- Long RR prolonged the refractory period
- Short RR ends with aberrant conduction showing a RBBB pattern
- The short RR impulse passes through the right branch during the refractory period and gets blocked
- Ashman phenomenon is most common in atrial fibrillation
- When RR intervals change irregularly

|
Right Bundle Branch Block
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- In V1 (V2) there is qR
- In V6 (V5, I) there is wide S
- In V1-3 there are negative T waves
|

|

|
Right Bundle Branch Block
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- In V1 (V2) there is rSR'
- In V6 (V5-6, I, aVL) there is wide S
- In V1-3 there are negative T waves
|

|

|
Right Bundle Branch Block
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- In V1 there is rSR'
- In V6 (V5-6, I, aVL) there is wide S
- In V1-3 there are negative T waves
|

|

|
Right Bundle Branch Block
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- In V1 there is rSR'
- In V6 (V5-6, I, aVL) there is wide S
- In V1 there is a negative T wave
|

|

|
Incomplete Right Bundle Branch Block
- In V1 there is RSr'
- In V5 and I there is wide S
- In V1-3 there are negative T waves
- Narrow QRS < 0.12s
- The patient meets all criteria for RBBB, but the QRS complex is narrow
- Narrow QRS indicates incomplete RBBB
|

|

Brugada Syndrome
- Wide QRS ≥ 0.12s
- In V1 there is rSR'
- In V5 there is wide S
- In V1-3 there are negative T waves and descending ST elevations
- This ECG resembles RBBB, but RBBB does not have descending ST elevations in V1-3
- The ECG shows Brugada syndrome
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers

















































