Home /
Repetitive Nonreentrant Ventriculoatrial synchrony
Repetitive nonreentrant ventriculoatrial synchrony (RNRVAS)
Dual-Chamber Pacemaker
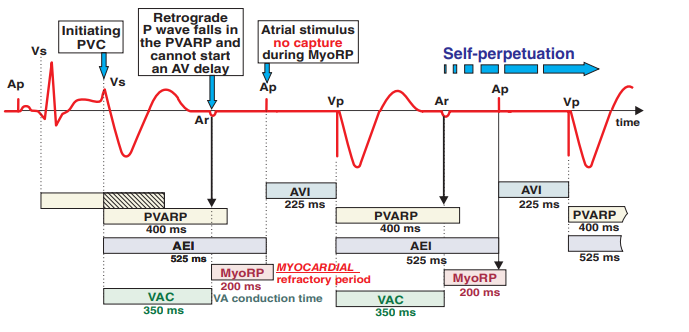
Repetitive Non-Reentry Ventriculo-Atrial Synchronization (RNRVAS)
- VAC (VA Conduction)
- KES (Ventricular Extrasystole)
- Depolarizes the ventricles (QRS) and the impulse travels retrograde through the AV node to the atria
- A retrograde P wave is generated but during the PVARP interval (400ms)
- During the PVARP interval, the pacemaker ignores the retrograde P wave
- AEI (Atrial Escape Interval)
- This is the interval between ventricular pacing and atrial pacing (525ms)
- If within 525ms after ventricular pacing (sensing) no spontaneous P wave occurs
- then the pacemaker activates atrial pacing (Ap)
- However, Ap occurs during the refractory period of the atrial myocardium (MyoRP)
- Thus, the pacemaker-generated P wave (Ap) is blocked
- However, the pacemaker counts the AV interval (225ms) from the blocked P wave (Ap)
- It then initiates ventricular pacing
- The cycle then repeats
- Repetitive non-reentry VA synchronization is most commonly triggered by

Repetitive Non-Reentry VA Synchronization (Trigger)
- The patient has a DDD pacemaker
- The first two beats have effective pacing of the atria and ventricles (ApVp)
- The third beat is ventricular safety pacing (VSP)
- The fourth beat is a ventricular extrasystole (KES) with retrograde (VA) conduction
- The retrograde P wave is not visible
- This is followed by ineffective atrial pacing
- No P waves follow
- Because the atrial pacing occurs during the refractory period of the atrial myocardium (MyoRP)
- After ineffective atrial pacing
- There is effective ventricular pacing

Repetitive Non-Reentry VA Synchronization (Termination)
- The patient has a DDD pacemaker
- The fourth beat is a ventricular extrasystole (KES)
- With retrograde conduction
- The fifth beat is a ventricular extrasystole
- This is followed by effective atrial pacing (Ap) because Ap occurs:
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers









