
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |



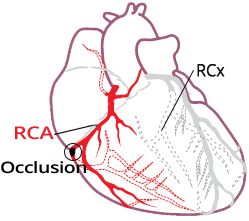
Proximal RCA Occlusion


Distal RCA Occlusion
Left Circumflex Occlusion




Acute Inferior and Right Ventricular STEMI


Acute Inferior and Right Ventricular STEMI

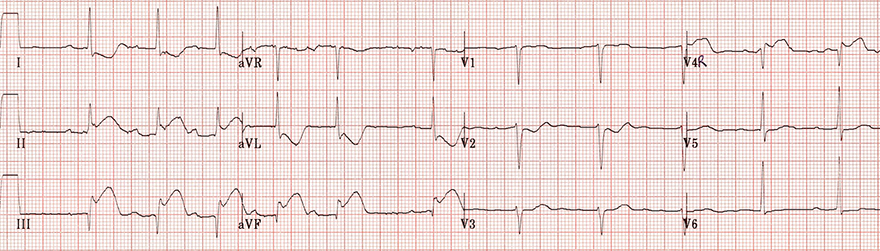
Acute Inferior and Right Ventricular STEMI

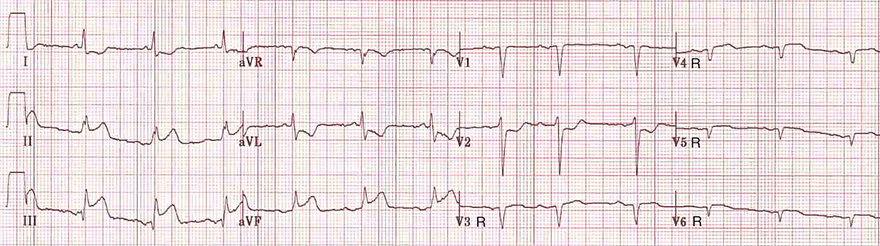
Acute Inferior and Right Ventricular STEMI
Sources
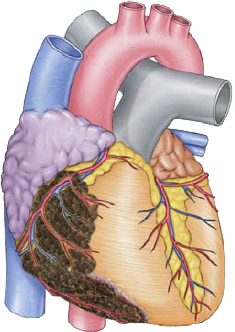
Right Coronary Artery
|

|
Right Ventricular Infarction
|

|
Inferior Wall Infarction
|

|
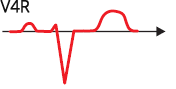
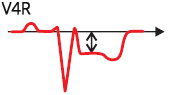
Right-sided Leads (V4R-V6R)
|

|

|
Proximal RCA Occlusion
|

|

|
Distal RCA Occlusion
|

|

|
Left Circumflex Occlusion
|

|
ECG and Right Ventricular STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Inferior and Right Ventricular STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Inferior and Right Ventricular STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Inferior and Right Ventricular STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Inferior and Right Ventricular STEMI
|

|
Sources