Home /
RVOT Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) - ECG
Right Ventricular Outflow Tract (RVOT) Tachycardia, Adenosine Sensitive VT
Idiopathic Ventricular Tachycardia

- Idiopathic VT occurs in a structurally intact heart
- In idiopathic VT, an ectopic focus originates in the area of:
- Ventricular outflow tracts
- Fascicles of the left bundle branch
- There are 3 idiopathic ventricular tachycardias
Ventricular Tachycardias from Outflow Tracts
- VT in the context of arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia in the outflow tract region
- It is not idiopathic VT, as it involves a structurally altered right ventricle (and outflow tract)
- Ventricular tachycardias from the outflow tract region are mostly idiopathic
- There are 2 idiopathic VT from outflow tracts:
- Mechanism is triggered activity
- They respond well to adenosine, so they are often referred to as adenosine-sensitive VTs
- VTs from the outflow tract in arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia do not respond to adenosine
- Outflow tract VTs are
Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Tachycardia

- Right Ventricular Outflow Tract (RVOT) Tachycardia
- It is the most common idiopathic VT
- Accounts for 70% of all idiopathic VTs
- Common location of the ectopic focus is
- 1-2 cm below the level of the pulmonary artery
- On the side of the ventricular septum
- Mechanism is triggered activity
- Occurs in young individuals aged 20-50 years
- Triggered by physical or emotional stress
- Responds well to adenosine (it is an adenosine-sensitive VT)
- Main vector points toward the left ventricle and downward
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
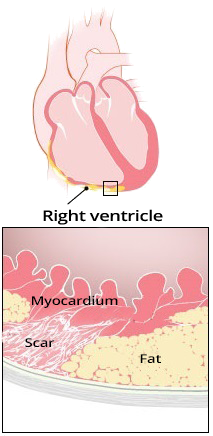
- Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia (ARVD)
- It is a congenital genetic disorder
- There is adipose and fibrotic (scarring) remodeling of the right ventricle
- The right ventricle is structurally altered
- If VT occurs in the outflow tract area with ARVD
- Then this VT is no longer idiopathic
- The same ECG pattern is produced by:
- Idiopathic VT from the right ventricular outflow tract
- VT from the right ventricular outflow tract with ARVD
- ARVD is diagnosed using
- echocardiography - shows structurally altered right ventricle
- Resting ECG during sinus rhythm:

Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
ECG and Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Tachycardia
ECG and Localization of Ectopic Focus
- Ectopic focus in the outflow tract can be precisely localized based on:
- Polarity of QRS complexes in Lead I
- Determines the location of the focus as posterior or anterior
- Notches in the leads (II, III, aVF) and transition zone
- Determine the location of the focus as septal or on the right ventricular wall
|
Interventricular Septum |
Right Ventricular Wall |
| Posterior |
Anterior |
Posterior |
Anterior |
| QRS Polarity in Lead I |
Positive |
Negative |
Positive |
Negative |
Notch (Notching)
in (II, III, aVF) |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
| Transition Zone |
=V3 |
=V3 |
≥V4 |
≥V4 |

Ventricular Tachycardia from the Right Ventricular Outflow Tract
- Heart Rate: 160/min.
- Wide QRS complexes (>0.12s)
- Transition Zone (V3)
- The location of the transition zone distinguishes VT from the right and left outflow tracts
- Pattern of left bundle branch block
- Wide QRS complexes
- Deep S (V1)
- Dominant R (V6)
- Vertical Axis (+ 90°)
- Positive QRS (II, III, aVF)
- AV Dissociation
- P waves are visible in continuous Lead II, which deform the QRS complexes
- AV dissociation is a key feature of ventricular tachycardia
- Ectopic focus is located in the posterior interventricular septum
- Positive QRS in Lead I
- Transition Zone V3

Ventricular Tachycardia from the Right Ventricular Outflow Tract
- Heart Rate 150/min.
- Wide QRS complexes (>0.12s)
- Transition Zone (V4)
- The location of the transition zone distinguishes VT from the right and left outflow tracts
- Pattern of left bundle branch block
- Wide QRS complexes
- Deep S (V1)
- Dominant R (V6)
- Vertical Axis (+ 120°)
- Positive QRS (II, III, aVF)
- Ectopic Focus is located in the anterior wall of the right ventricle
- Negative QRS in Lead I
- Transition Zone V4

Ventricular Tachycardia from the Right Ventricular Outflow Tract
- The first QRS complex is sinusoidal, then ventricular tachycardia starts
- Heart Rate 180/min.
- Wide QRS complexes (>0.12s)
- Transition Zone (V3)
- The location of the transition zone distinguishes VT from the right and left outflow tracts
- Pattern of left bundle branch block
- Wide QRS complexes
- Deep S (V1)
- Dominant R (V6)
- Vertical Axis (+ 90°)
- Positive QRS (II, III, aVF)
- Ectopic Focus is located in the posterior part of the ventricular septum
- Positive QRS in Lead I
- Transition Zone V3
- No notches in QRS (II, III, aVF)

Ventricular Tachycardia from the Right Ventricular Outflow Tract
- Heart Rate 230/min.
- Wide QRS complexes (>0.12s)
- Transition Zone (V4)
- The location of the transition zone distinguishes VT from the right and left outflow tracts
- Pattern of left bundle branch block
- Wide QRS complexes
- Deep S (V1)
- Dominant R (V6)
- Vertical Axis (+ 110°)
- Positive QRS (II, III, aVF)
- Ectopic Focus is located in the anterior part of the right ventricular wall
- Negative QRS in Lead I
- Transition Zone V4
- No notches in QRS (II, III, aVF)
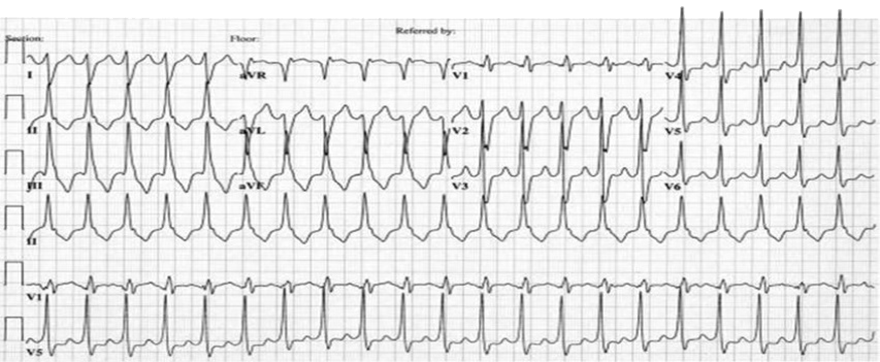
Ventricular Tachycardia from the Left Ventricular Outflow Tract
- Heart Rate 140/min.
- Wide QRS complexes (>0.12s)
- Pattern of left bundle branch block
- Wide QRS complexes
- Deep S (V1)
- Dominant R (V6)
- Vertical Axis (+ 100°)
- Positive QRS (II, III, aVF)
- Transition Zone (V3)
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers

















