
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
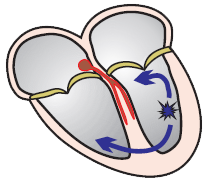
Lead II R wave peak time (RWPT) criterion, Pavas criteria
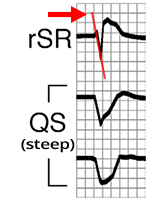
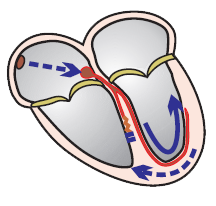

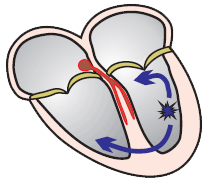

Wide-Complex Tachycardia

Wide-Complex Tachycardia


Wide-Complex Tachycardia


Wide-Complex Tachycardia

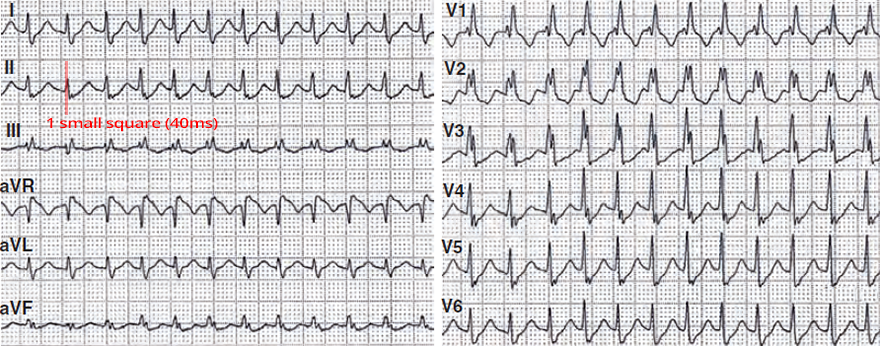
Wide-Complex Tachycardia
Sources
Home /
Lead II R wave peak time (RWPT) criterion, Pavas criteria

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

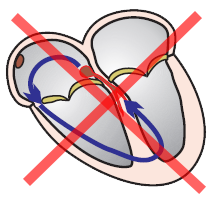
Wide-Complex Tachycardia

Wide-Complex Tachycardia

|
Wide-Complex Tachycardia
|

|

|
Wide-Complex Tachycardia
|

|

|
Wide-Complex Tachycardia
|
 |
Sources