
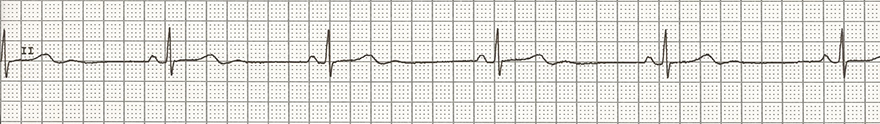
Sinus Bradycardia

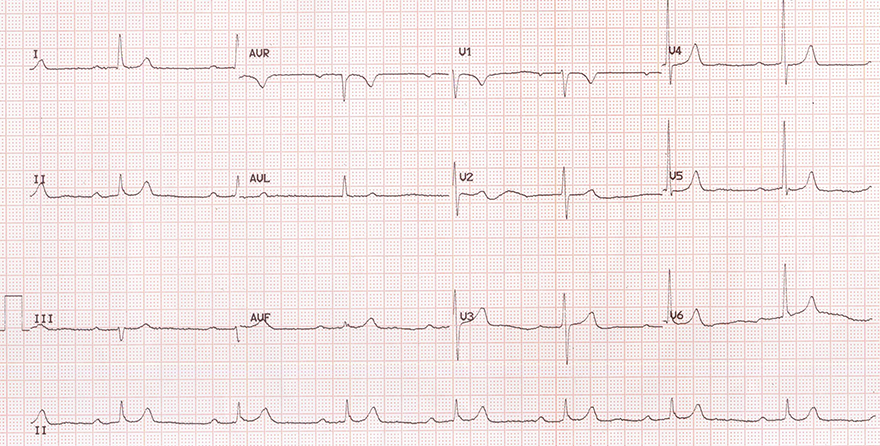
Sinus Bradycardia and First-Degree AV Block
- Frequency: 47/min
- P waves present
- First-degree AV block
- Prolonged PQ interval (0.32s)
- With sinus bradycardia and first-degree AV block, consider:
- This patient was overdosed with beta blockers

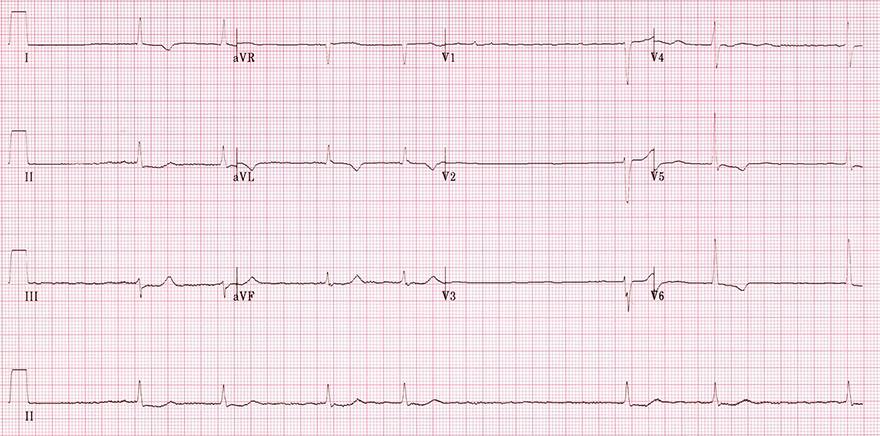
Atrial Fibrillation
- No P waves on the ECG, so it is not sinus bradycardia
- Heart rate is irregularly irregular (RR intervals are of varying lengths)
- Frequency <60/min. (6-second rule)
- The ECG shows atrial fibrillation
- The patient is likely undergoing treatment for slowing AV node conduction
- Hypothermia can also slow AV conduction
- This is fine atrial fibrillation
- Amplitude of fibrillatory waves in V1 <0.5mm
- ST depressions and negative T waves in lateral leads (I, aVL, V5, V6) are seen in
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers

Home /
Sinus Bradycardia
Sinus bradycardia
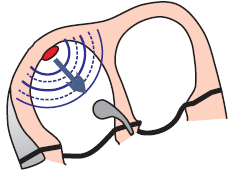
Sinoatrial Node
- Automaticity
- Overdrive suppression
- Impulses propagate through the conduction system from the site
- that generates impulses with the highest frequency
- The site with the highest frequency deactivates the sites
- Sinoatrial Node (SA node)
- Spontaneously generates impulses with a frequency of 60 - 100/min.
- Other sites generate impulses with a lower frequency
|

|
Frequency and Sinus Rhythm
- SA node is partially under the control of the nervous system, which adjusts the frequency of the SA node within the range of 60-100/min
- Sympathetic nervous system - increases the frequency of the SA node
- Parasympathetic nervous system - decreases the frequency of the SA node
- Physiological variants of sinus rhythm:
- Sinus Tachycardia: f > 100/min. (in adults, or above the upper limit of normal in children)
- Sinus Bradycardia: f < 60/min. (in adults, or below the lower limit of normal in children)
- Sinus Arrhythmia. It is an irregular sinus rhythm, which is a normal variant in young trained individuals
- Physiological frequency of the SA node by age:
- Newborns: 130/min.
- 2-year-old: 120/min.
- 4-year-old: 110/min.
- 6-year-old: 100/min.
- 10-year-old: 90/min.
- 14-year-old: 80/min.
- 18-year-old: 70/min.
Sinus Bradycardia
- Sinus Bradycardia is a sinus rhythm with a frequency <60/min. (sometimes reported as a frequency of <50/min.)
- In children, it is a frequency below the lower limit of normal
- Athletes have a higher systolic cardiac output, so a lower frequency is sufficient for their resting heart rate
- Sinus Bradycardia is considered a normal variant in athletes
- In cases of severe sinus bradycardia, a secondary pacemaker is activated: junctional rhythm
ECG and Sinus Bradycardia
- Frequency < 60/min. (in adults, or below the lower limit of normal in children)
- Physiological P waves (which are a fundamental sign of sinus rhythm)
- positive in leads I, II
- negative in lead aVR
- Impulses then pass to the ventricles through the AV junction
|

|
Sinus Bradycardia
Most Common Causes of Sinus Bradycardia
Vagal Maneuvers
- Stimulate the vagus nerve and subsequently cause:
- Most well-known vagal maneuvers:
- Carotid Sinus Massage
- Slows the automaticity of the SA node and atria (not reentry in the atria)
- Massage the neck with two fingers below the lower edge of the jaw
- Valsalva Maneuver
- The patient occludes their nose with their hand and forcefully exhales through the blocked nose
- Or bears down as if having a bowel movement
- Induction of the Gag Reflex
- The patient places their fingers on the root of the tongue
- Applying Pressure to the Eyeball
- Apply pressure to the patient's eyeball, though this is rarely used
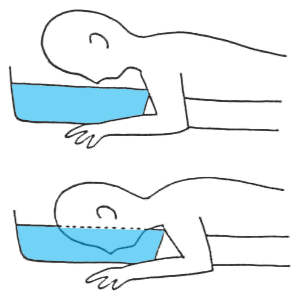
- Divine Reflex
- Submerge the face in water colder than 21 °C
|

|
Mammalian Diving Reflex
- It is a protective reflex in mammals against extreme cold
- The reflex is triggered by water that is colder than 21°C
- Water must be in contact with the face
- If the patient immerses their face in water colder than 21°C
- it will cause sinus bradycardia
- Divers can have bradycardia down to 20/min.
- This helps the body use less oxygen underwater
- In hypothermia (<35°C), a J wave appears on the ECG
|
|
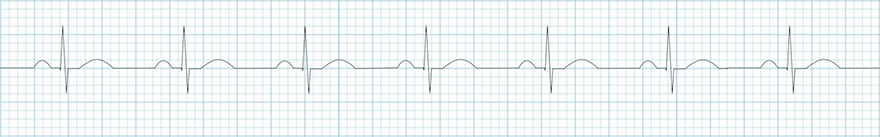
Sinus Rhythm
- Frequency: 77/min.
- If the frequency is < 60/min., it would be sinus bradycardia
- Normal P wave

|
Sinus Bradycardia
|

|

|
Sinus Bradycardia and First-Degree AV Block
- Frequency: 47/min
- P waves present
- First-degree AV block
- Prolonged PQ interval (0.32s)
- With sinus bradycardia and first-degree AV block, consider:
- This patient was overdosed with beta blockers
|

|

|
Atrial Fibrillation
- No P waves on the ECG, so it is not sinus bradycardia
- Heart rate is irregularly irregular (RR intervals are of varying lengths)
- Frequency <60/min. (6-second rule)
- The ECG shows atrial fibrillation
- The patient is likely undergoing treatment for slowing AV node conduction
- Hypothermia can also slow AV conduction
- This is fine atrial fibrillation
- Amplitude of fibrillatory waves in V1 <0.5mm
- ST depressions and negative T waves in lateral leads (I, aVL, V5, V6) are seen in
|

|
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers
| 
























