
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Sick sinus syndrome, Tachycardia-Bradycardia (Tachy-Brady) syndrome, Sinus node dysfunction, Sinoatrial node disease
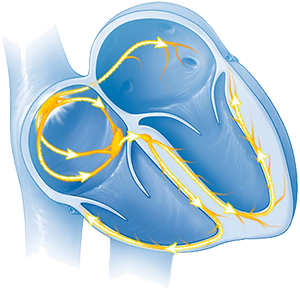
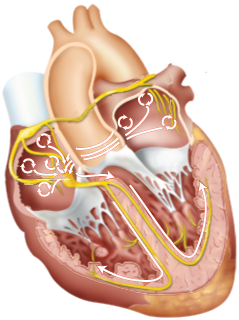
Sick Sinus Syndrome (Tachy-Brady Syndrome)
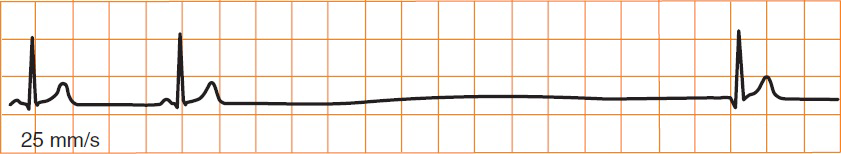
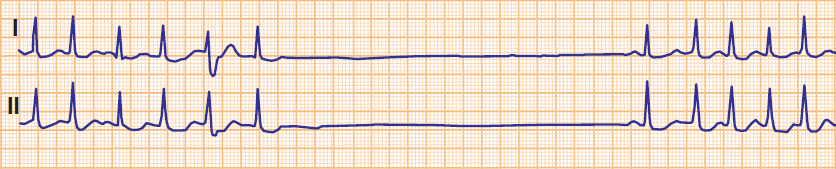
Sick Sinus Syndrome
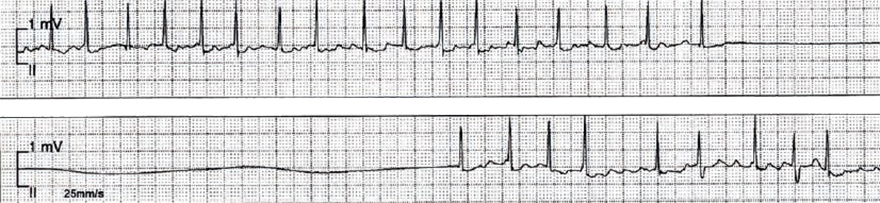
Sick Sinus Syndrome (Tachy-Brady Syndrome)
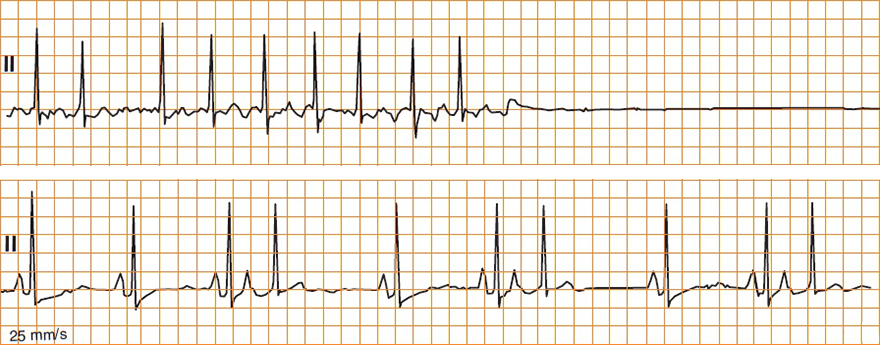
Sick Sinus Syndrome (Tachy-Brady Syndrome)
Sources
Home /
Sick sinus syndrome, Tachycardia-Bradycardia (Tachy-Brady) syndrome, Sinus node dysfunction, Sinoatrial node disease
|

|
|

|

Sick Sinus Syndrome (Tachy-Brady Syndrome)

Sick Sinus Syndrome

Sick Sinus Syndrome (Tachy-Brady Syndrome)

Sick Sinus Syndrome (Tachy-Brady Syndrome)
Sources