
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
STEMI infarction with left bundle branch block (LBBB), Sgarbossa criteria

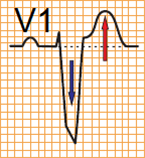
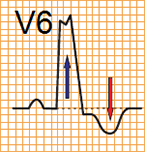

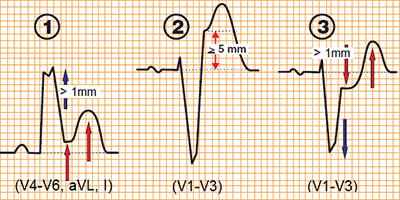
| LBBB: | LBBB + Acute STEMI: | Criteria: |
 |
 |
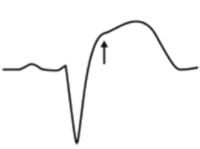
Concordant ST elevation > 1mm
|
 |
 |
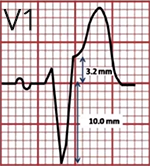
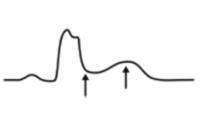
Discordant ST elevation ≥ 5mm
|
 |
 |
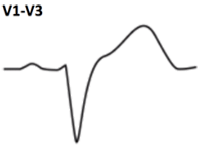
Concordant ST depression > 1mm
|

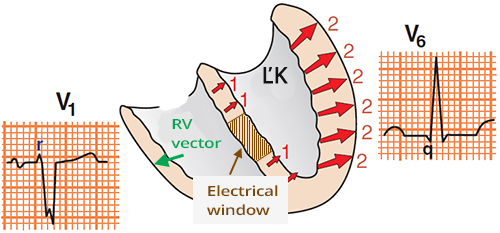
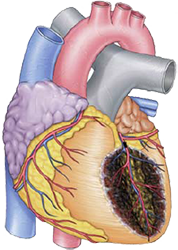
Ventricular Septal Infarction and Left Bundle Branch Block
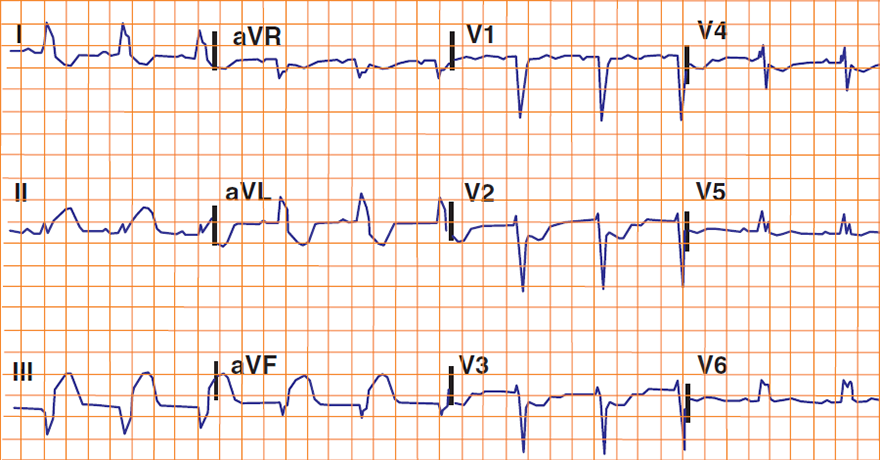
Acute STEMI and LBBB


Acute STEMI and LBBB

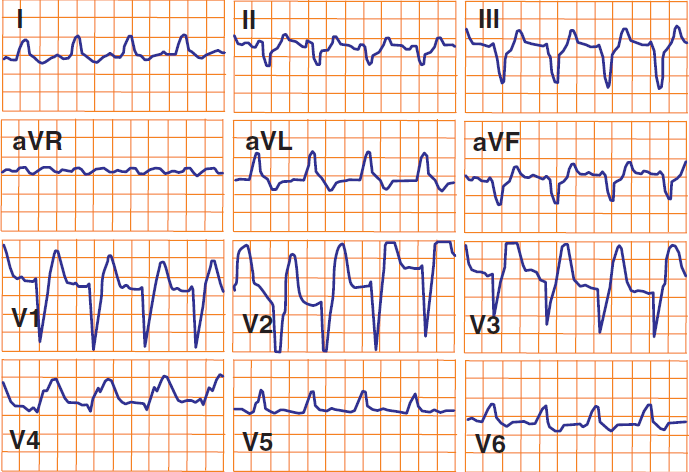
Acute STEMI and LBBB


Acute STEMI and LBBB
Sources
Home /
STEMI infarction with left bundle branch block (LBBB), Sgarbossa criteria
|

|
ECG and LBBB
|


|
STEMI and LBBB
|

|
ECG and Acute STEMI with LBBB
|

|
|
 |
|
|
| LBBB: | LBBB + Acute STEMI: | Criteria: |
 |
 |
Concordant ST elevation > 1mm
|
 |
 |
Discordant ST elevation ≥ 5mm
|
 |
 |
Concordant ST depression > 1mm
|


Ventricular Septal Infarction and Left Bundle Branch Block

|
Acute STEMI and LBBB
|

|

|
Acute STEMI and LBBB
|

|

|
Acute STEMI and LBBB
|

|

|
Acute STEMI and LBBB
|

|
Sources