
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
STEMI infarction and ventricular paced rhythm (Sgarbossa criteria)

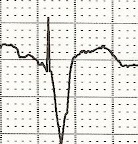


| Ventricular Pacing: | Ventricular Pacing + Acute STEMI: | Criteria: |
 |
 |
Concordant ST elevation > 1mm
|
 |
 |
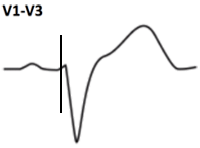
Disconcordant ST elevation ≥ 5mm
|
 |
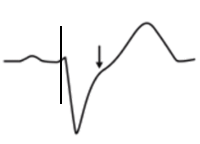 |
Concordant ST depression > 1mm
|
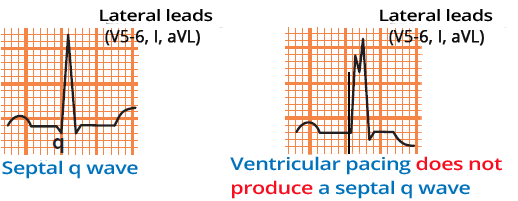
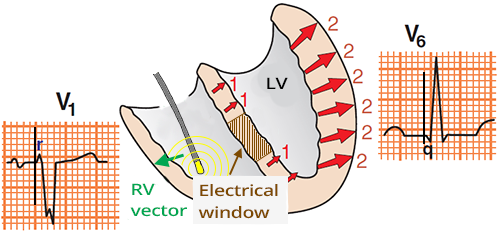
Septal Infarction and Ventricular Pacing
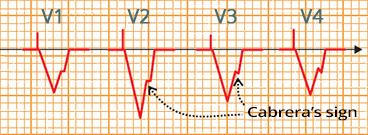

Old Anteroseptal STEMI and Ventricular Pacing
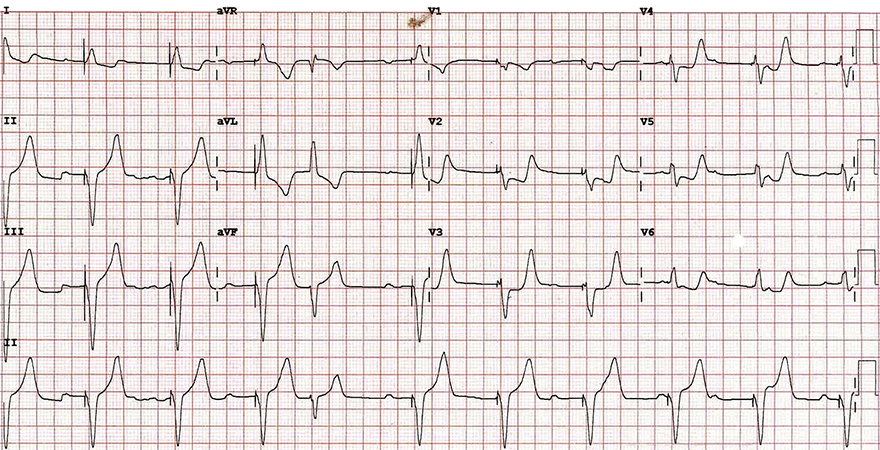
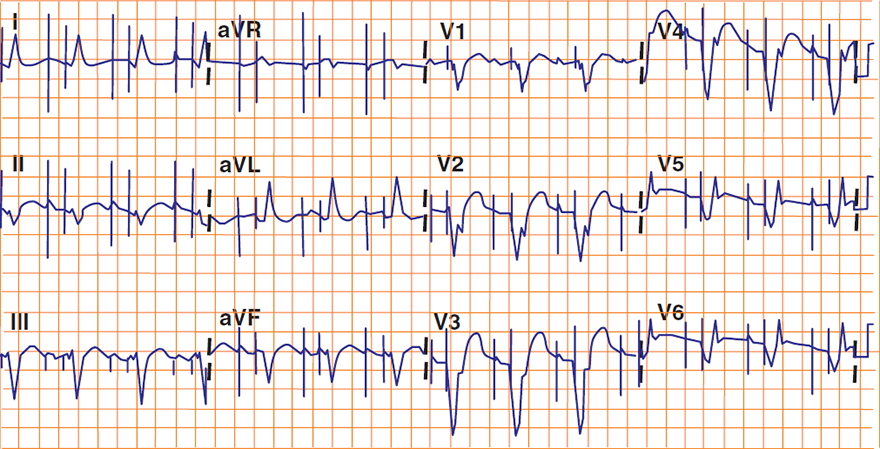
Acute STEMI and Ventricular Pacing
Sources
Home /
STEMI infarction and ventricular paced rhythm (Sgarbossa criteria)
Ventricular Pacing
|
 
|
|

|
|
 |
|
|
| Ventricular Pacing: | Ventricular Pacing + Acute STEMI: | Criteria: |
 |
 |
Concordant ST elevation > 1mm
|
 |
 |
Disconcordant ST elevation ≥ 5mm
|
 |
 |
Concordant ST depression > 1mm
|


Septal Infarction and Ventricular Pacing
|

|

|
Old Anteroseptal STEMI and Ventricular Pacing
|

|

|
Acute STEMI and Ventricular Pacing
|

|
Sources