Home /
T Wave - ECG
T wave
Depolarization and ECG
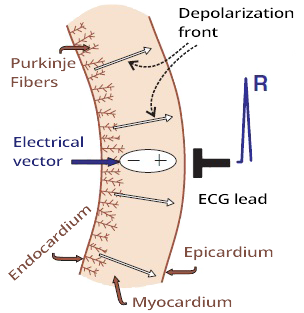
Propagation of the Depolarization Wave and ECG
- The depolarization wave (extracellular change from + to -) propagates in the myocardial wall from the endocardium to the epicardium
- The electrical vector always points from the (-) to the (+) part of the myocardium
- The depolarization wave propagates very quickly
- Because sodium channels open rapidly at the beginning of the action potential in cardiomyocytes
- A depolarization wave that moves towards the ECG electrode
- Creates a narrow positive spike
- The spike is narrow because depolarization occurs very quickly
- The width of the R wave is the time it takes to depolarize the ventricles
Repolarization and ECG

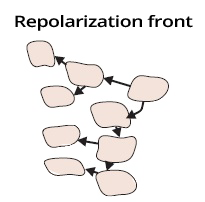
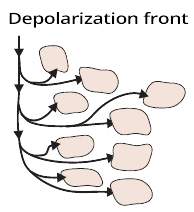
Propagation of the Repolarization Wave and ECG
- The repolarization wave (extracellular change from - to +) propagates in the myocardial wall from the epicardium to the endocardium
- Because the epicardium starts to repolarize earlier
- The wave has the opposite direction compared to depolarization
- However, the electrical vector always points from the (-) to the (+) part of the myocardium
- The electrical vector has the same direction during both depolarization and repolarization
- The repolarization wave propagates slowly
- Because the calcium and potassium channels open slowly at the end of the action potential in cardiomyocytes
- The repolarization wave moves away from the ECG electrode, but the electrical vector points towards the ECG electrode
- Repolarization occurs slowly, resulting in a wide T wave
- The width of the T wave is the time it takes to repolarize the ventricles
Depolarization and Repolarization of the Myocardium


Depolarization and Repolarization of Ventricular Myocardium
- The depolarization and repolarization waves have opposite directions
- However, the electrical vector always points in the same direction
- Depolarization occurs quickly
- Thus, a narrow R wave is produced
- Repolarization occurs more slowly
- Thus, a broad T wave is produced
Depolarization and Repolarization in the Ventricles
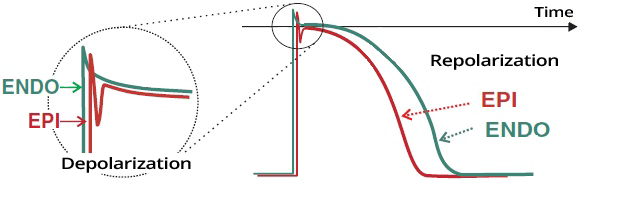
Action Potential in the Endocardium and Epicardium
- The action potential of cardiomyocytes in the endocardium and epicardium has different electrical properties
- The conduction system activates the myocardium in the endocardium
- Thus, depolarization begins in the endocardium
- Depolarization in the endocardium and epicardium is nearly synchronous
- Therefore, the depolarization wave travels rapidly through the myocardial wall
- Cardiomyocytes in the epicardium begin to repolarize earlier than those in the endocardium
- Therefore, the repolarization wave starts in the epicardium
- However, the electrical vector of depolarization and repolarization points in the same direction
Depolarization and Repolarization in the Atria
- The myocardium of the atria is very thin
- Atrial depolarization begins in the endocardium (P wave)
- Atrial repolarization begins in the endocardium (Ta wave - usually not visible, hidden in the QRS complex)
- Ventricular repolarization begins in the epicardium (T wave)
T Wave (Most Variable Wave)
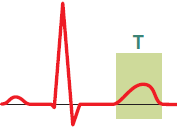
- It is the most variable wave on the ECG
- It represents ventricular repolarization
- It is low and wide
- Repolarization (T wave) is more asynchronous than depolarization (QRS complex)
ECG and Normal T Wave
- It is concordant (has the same polarity as QRS)
- Positive QRS - positive T wave
- Negative QRS - negative T wave
- It is positive (I, II, V3-V6)
- It can be isolated negative (III, aVL)
- It is negative in aVR
- Amplitude
- For ECG diagnosis, the dynamic of the T wave is important
- If the T wave remains the same - often not a serious condition
- If the T wave changes - often a serious condition (ischemia)
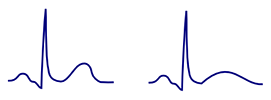
Concordant T Wave
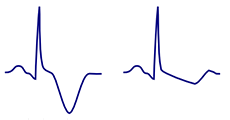
Discordant T Wave
High Peaked T Wave
- It is tall, sometimes taller than the R wave
- In hyperkalemia, it is symmetrical (resembling the Eiffel Tower)
- In hyperacute ischemia, it has a broad base and is not symmetrical
- It is referred to as a hyperacute T wave

Tall Broad T Wave
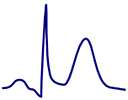
Inverted T Wave
- Concordant inverted T wave is not pathological
- In lead III, it may be discordantly inverted
- Pathological inverted T wave is
- Inverted T wave > 3mm or newly appeared

- Normal variant in children (V1-V3)
- Persistent juvenile T waves (in adults V1-V3)
- Athletes (V1-V3)
- Myocardial ischemia (at least in 2 adjacent leads)
- Hyperventilation (V1-V5)
- Left bundle branch block (I, aVL, V5-V6)
- Right bundle branch block (V1-V3)
- Left ventricular hypertrophy (I, aVL, V5-V6)
- Right ventricular hypertrophy (V1-V3) (II, III, aVF)
- Pulmonary embolism (V1-V3) (II, III, aVF)
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (V1-V3)
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (V1-V6)
- Intracranial hypertension (V1-V6) (II, III, aVF)
- Wellens syndrome (Type I: V2-V3)
- WPW syndrome: Type A: (V1-V3), Type B: (V4-V6)
- Hypothyroidism (V1-V6)
- Pacemaker
Biphasic T Wave
- A biphasic T wave is always assessed according to the terminal amplitude of the T wave
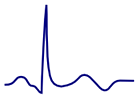
- Biphasic negative T wave (Terminal part is negative)
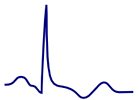
- Biphasic positive T wave (Terminal part is positive)
Double T Wave
- The T wave has 2 positive amplitudes, with a notch in the middle
- In reality, it is a T wave that is associated with a P wave or a U wave

Flat T Wave
- Concordant flat T waves are a nonspecific change on the ECG
- Rarely can occur with certain diagnoses
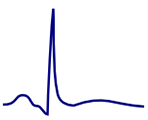
Normal T Wave
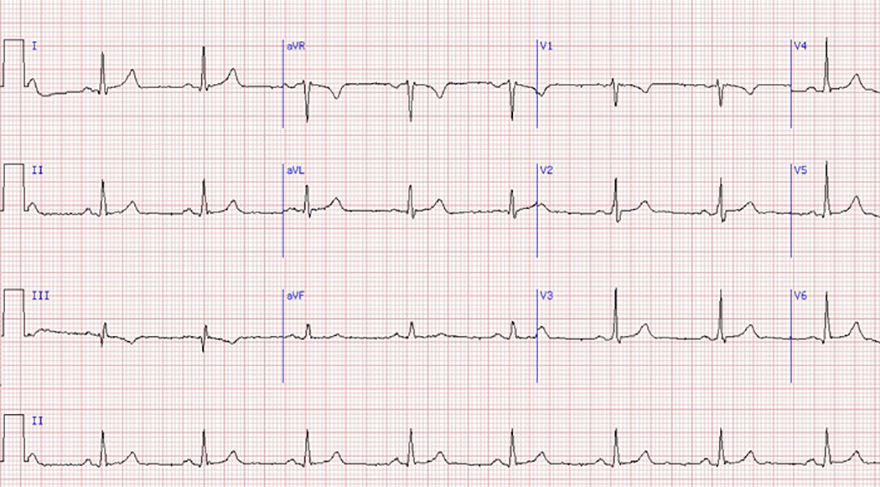
Normal T Wave and Sinus Rhythm
- Normal T Wave
- Is always positive (I, II, V3-V6)
- Is concordant (has the same polarity as QRS complex)
- Is negative (aVR, V1) if the QRS is also negative
- In lead III, it may be discordantly negative
- Amplitude
- Sinus Rhythm
Tall T Wave

Hyperkalemia

Hyperacute T Wave
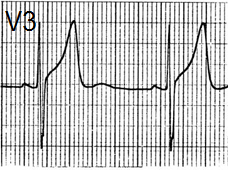
Benign Early Repolarization

Hyperkalemia
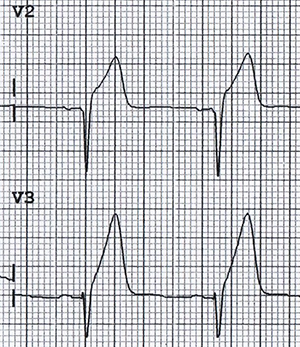
Hyperacute T Wave
- Indicates hyperacute ischemia
- Typical hyperacute T wave
- It is tilted to the right
- The second part is steeper
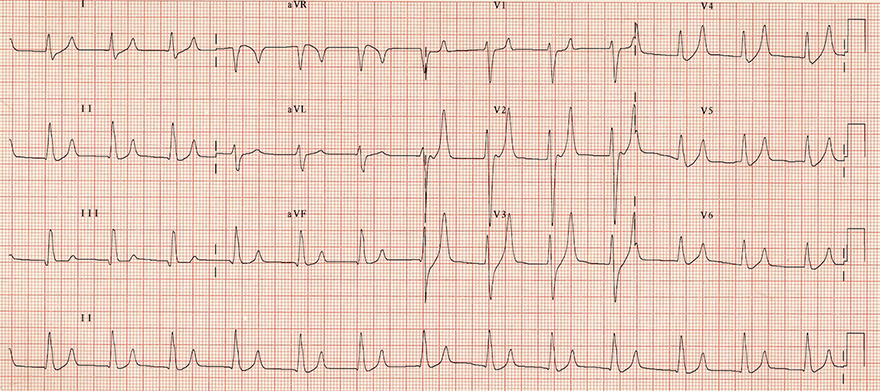
Tall Peaked T Waves and Hyperkalemia
- Symmetrical peaked T waves (resembling the Eiffel Tower)
- T wave amplitude
- In precordial leads > 5mm
- In chest leads > 15mm
- The patient had hyperkalemia of 7.1mmol/l
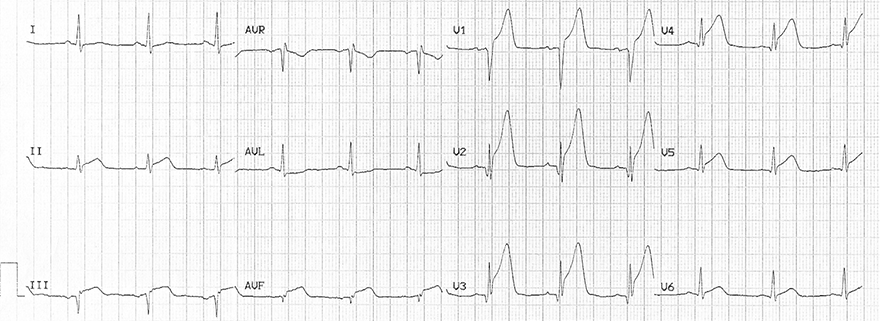
Hyperacute T Waves and Acute Anterior-Inferior STEMI
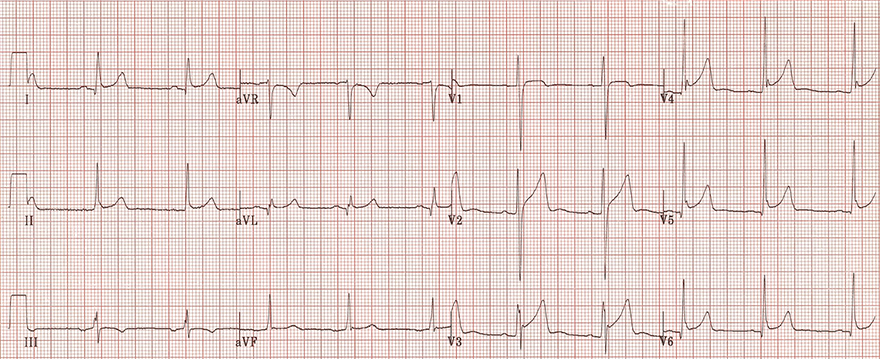
High T Waves and Benign Early Repolarization
- High peaked T waves (V2-V6)
- T waves in benign early repolarization do not change—they persist for years
- T waves in STEMI infarction change; the patient should have a different EKG in an hour (STEMI dynamics)
- Benign early repolarization
- Concave ST elevations (V2-V5)
- In leads (V3-V5) there is a fishhook
Inverted T Waves
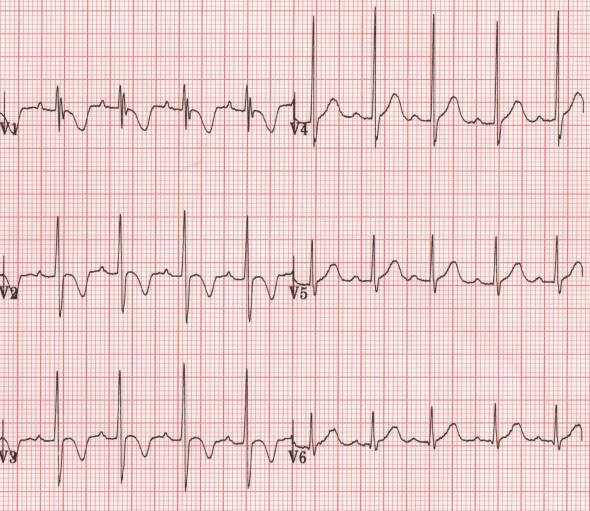
Inverted T Waves - Pediatric
- Children have negative T waves (V1-V3) due to right ventricular dominance
- Refers to a 2-year-old boy
- These negative T waves are physiological in children
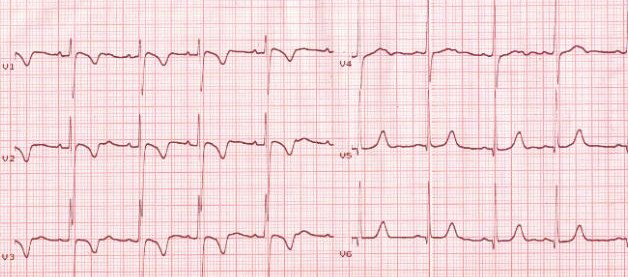
Inverted T Waves - Persistent Juvenile
- Negative T waves in V1-V3
- If these T waves were new, it would indicate ischemia
- Persistent juvenile T waves
- Present from childhood and persist into adulthood (do not change)
- Most common in Afro-Caribbean women
- Usually deep, max. 3mm (though this is not a strict rule)
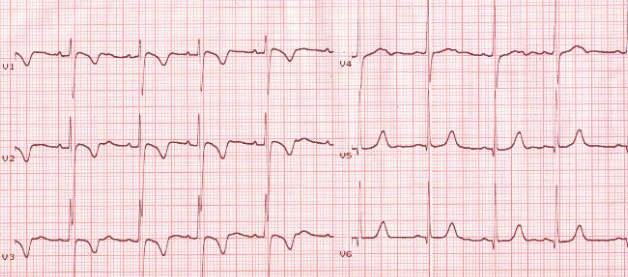
Inverted T Waves in Athletes

Inverted Ischemic T Waves and Unstable Angina Pectoris

Inverted T Waves and Hyperventilation
- The patient was a 24-year-old woman with no treatment, who was hyperventilating (she was frightened)
- Inverted T waves (V1-V5)
- After calming down, the EKG was normal, with no inverted T waves
- In this case, we must immediately rule out serious diagnoses
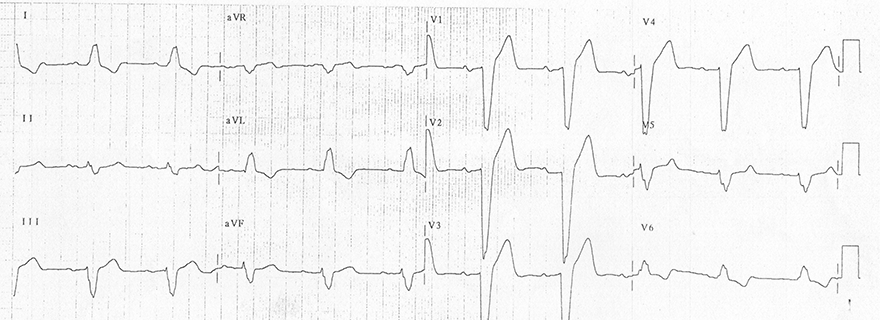
Inverted T Waves and Left Tawar Branch Block
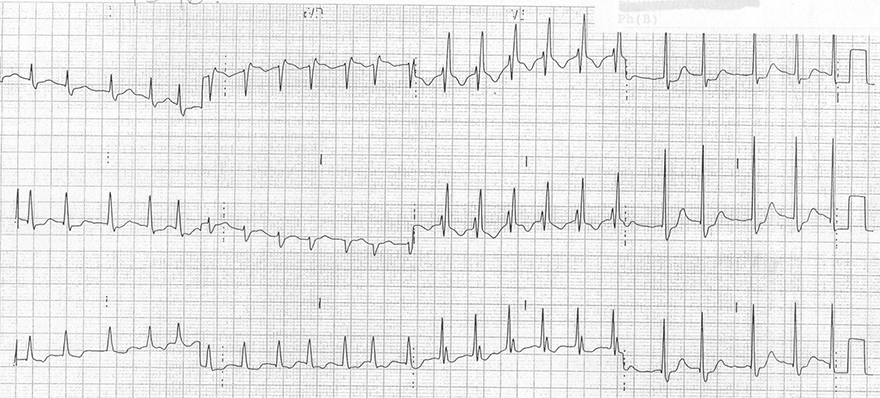
Inverted T Waves and Right Tawar Branch Block
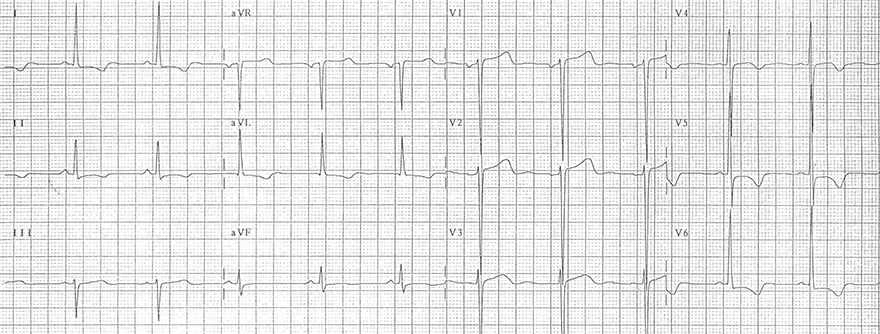
Inverted T Waves and Left Ventricular Hypertrophy

Inverted T Waves and Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
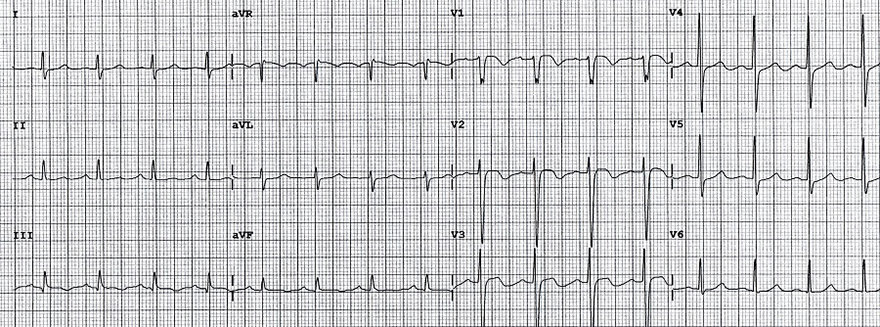
Inverted T Waves and Pulmonary Embolism
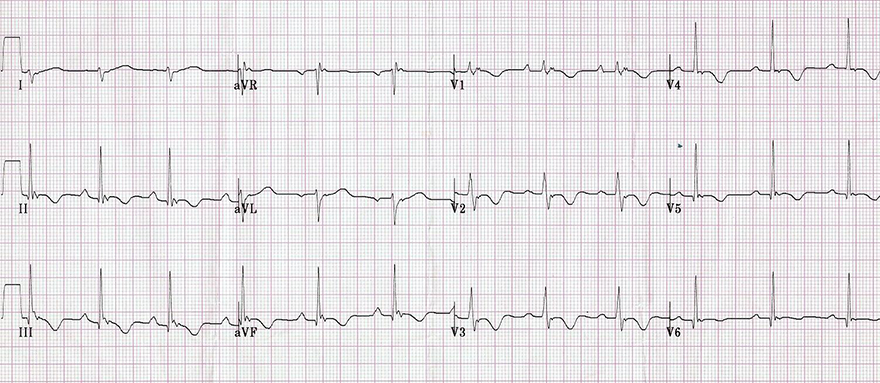
Inverted T Waves and Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia

Inverted T Waves and Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
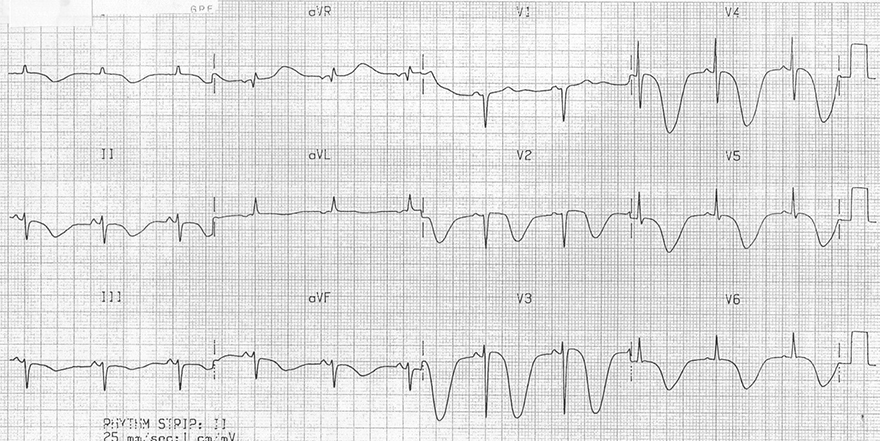
Inverted T Waves and Intracranial Hypertension

Inverted T Waves and Wellens Syndrome (Type I)
- Wellens Syndrome (Type I)
- Creates deep T waves (V2-V3) (rarely V1-V6)
- Type II is more common, producing negative bifasic T waves (the terminal part of the T wave is negative)

Inverted T Waves and WPW Syndrome (Type A)
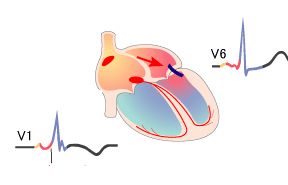

Inverted T Waves and WPW Syndrome (Type B)
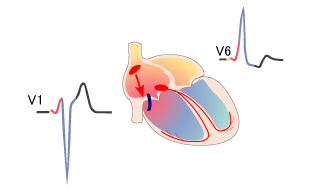
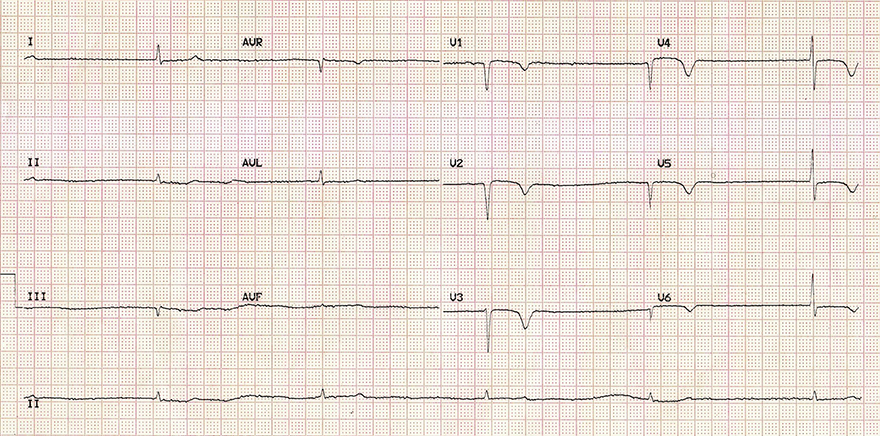
Inverted T Waves and Severe Hypothyroidism
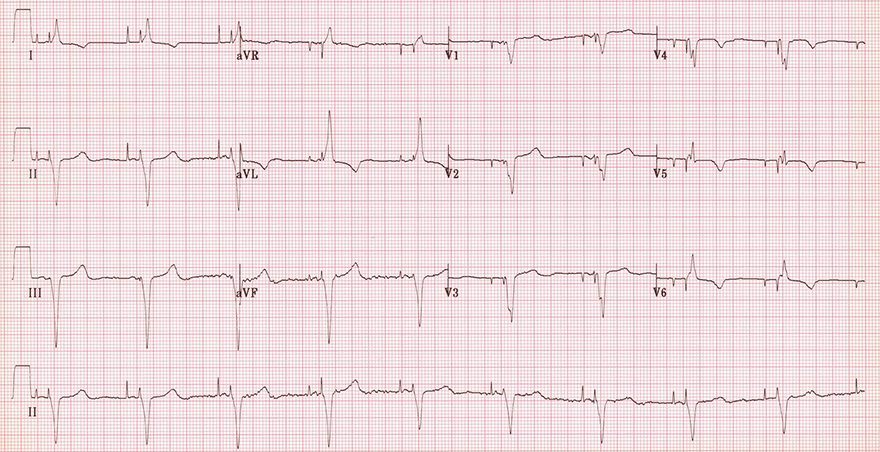
Inverted T Waves and Pacemaker
- This concerns pacing of both atria and ventricles
- Stimulus artifacts are observed before the P wave and before the QRS
- The ventricles are stimulated from the right ventricle (the electrode is in the right ventricle)
Biphasic T Wave
- A biphasic T wave is always evaluated based on the terminal amplitude of the T wave
- Biphasic negative T wave (The terminal portion is negative)
- Biphasic positive T wave (The terminal portion is positive)

Biphasic Negative T Waves and Unstable Angina Pectoris
- It involved a patient with unstable angina pectoris due to stenosis of the RIA and RCx
- ST depression (V4-V6)
- Biphasic negative T waves (V2-V6)
- After stent placement (recanalization), the T waves later normalized
- For acute subendocardial ischemia, they are characteristic
- There is no precisely defined boundary between inverted and biphasic negative T waves
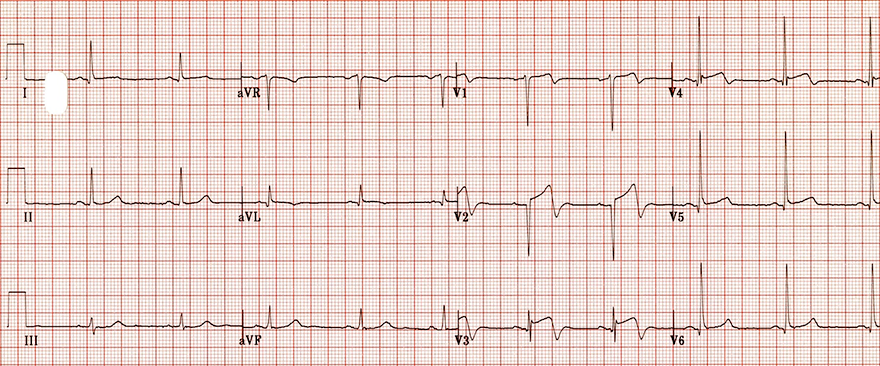
Biphasic Negative T Waves and Wellens' Syndrome (Type II)
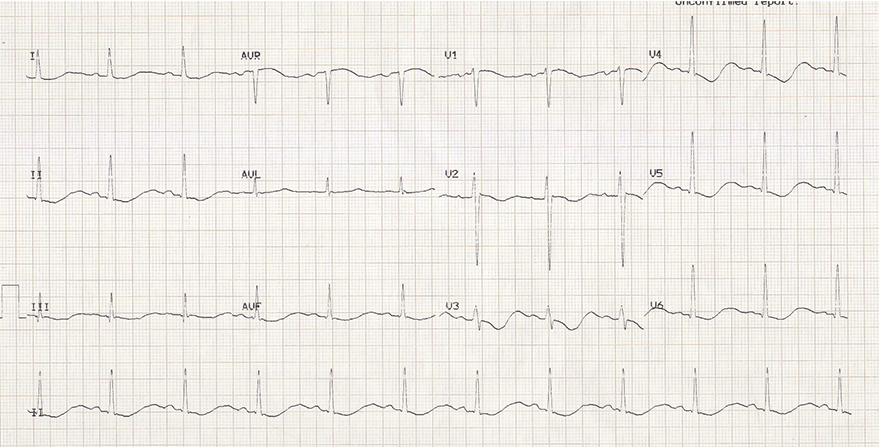
Biphasic Positive T Waves and Hypokalemia
Double T Wave
- The T wave has 2 positive amplitudes and a notch in the middle
- In reality, this is a T wave that is combined with a P wave or a U wave
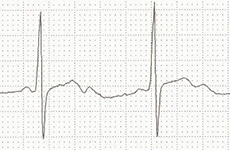
Double T Wave and Hypokalemia
- In hypokalemia, a U wave occurs
- Double T wave
- A U wave follows closely after the T wave (T + U wave)
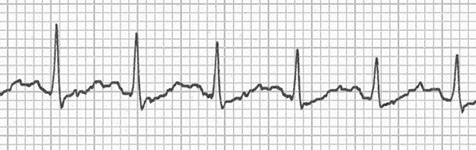
Double T Wave and Sinus Tachycardia
- In sinus tachycardia, a P wave follows closely after the T wave
- Double T wave
- A P wave follows closely after the T wave (T + P wave)
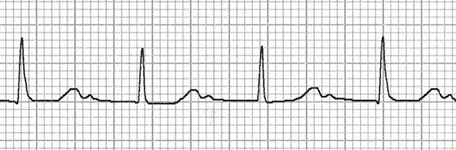
Double T Wave and First-Degree AV Block
- In first-degree AV block
- There is a prolonged PQ interval (>0.2s)
- The QRS-T complex occurs later
- The T wave thus moves closer to the P wave
- Double T wave
- A P wave follows closely after the T wave (T + P wave)
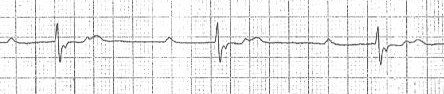
Double T Wave and Second-Degree AV Block (2:1)
- In second-degree AV block (2:1)
- Every 2nd P wave is blocked
- The PQ interval may be prolonged (>0.2s)
- Double T wave
- A P wave follows closely after the T wave (T + P wave)
Flattened T Wave
- Concordant flattened T wave is a non-specific change on the ECG
- It rarely occurs with certain diagnoses
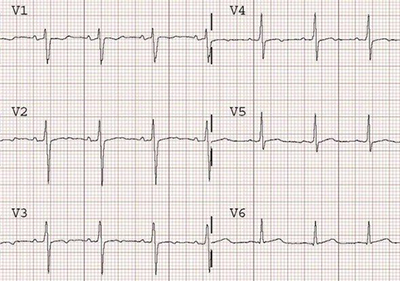
Ischemia and Flattened T Waves
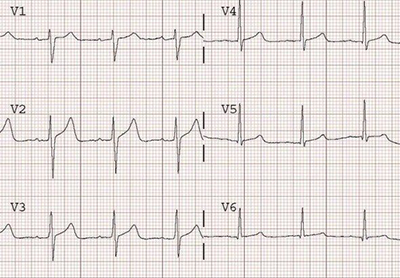
Sinus Rhythm and Normal T Waves
- This is an ECG from the patient on the left
- The patient stopped bicycling on the ergometer
- After the cessation of exertion (ischemia), the ECG normalized
- The ECG shows a sinus rhythm
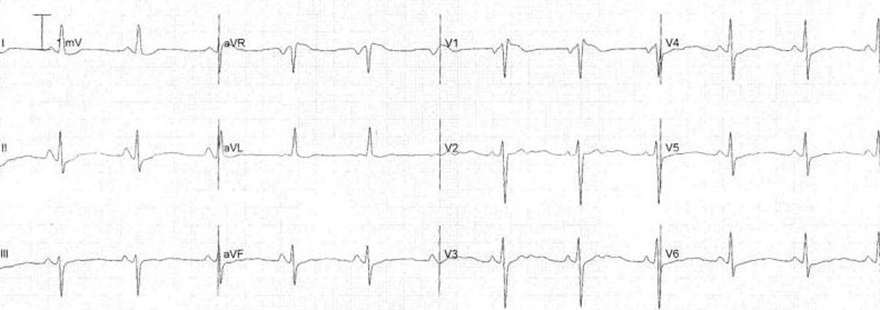
Flattened T Waves and Hypokalemia
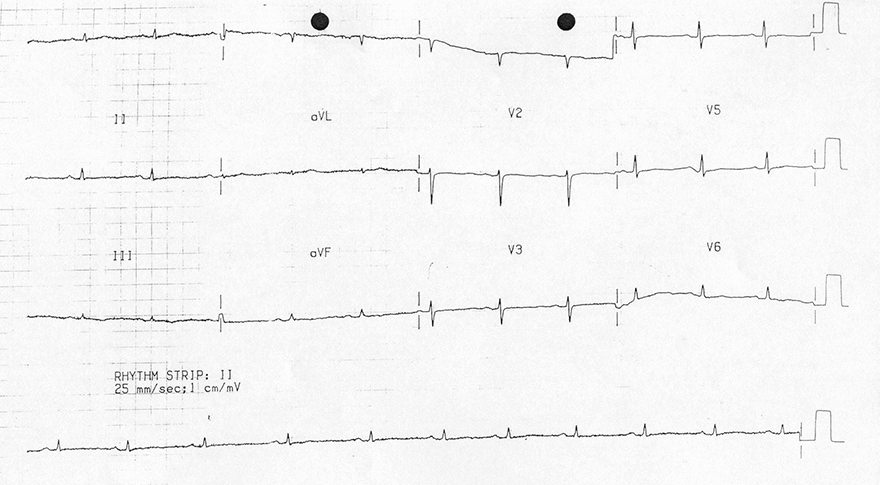
Flattened T Waves and Severe Hypothyroidism
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers
Home /
T Wave - ECG
T wave
Depolarization and ECG
Propagation of the Depolarization Wave and ECG
- The depolarization wave (extracellular change from + to -) propagates in the myocardial wall from the endocardium to the epicardium
- The electrical vector always points from the (-) to the (+) part of the myocardium
- The depolarization wave propagates very quickly
- Because sodium channels open rapidly at the beginning of the action potential in cardiomyocytes
- A depolarization wave that moves towards the ECG electrode
- Creates a narrow positive spike
- The spike is narrow because depolarization occurs very quickly
- The width of the R wave is the time it takes to depolarize the ventricles
Repolarization and ECG
Propagation of the Repolarization Wave and ECG
- The repolarization wave (extracellular change from - to +) propagates in the myocardial wall from the epicardium to the endocardium
- Because the epicardium starts to repolarize earlier
- The wave has the opposite direction compared to depolarization
- However, the electrical vector always points from the (-) to the (+) part of the myocardium
- The electrical vector has the same direction during both depolarization and repolarization
- The repolarization wave propagates slowly
- Because the calcium and potassium channels open slowly at the end of the action potential in cardiomyocytes
- The repolarization wave moves away from the ECG electrode, but the electrical vector points towards the ECG electrode
- Repolarization occurs slowly, resulting in a wide T wave
- The width of the T wave is the time it takes to repolarize the ventricles
Depolarization and Repolarization of the Myocardium


Depolarization and Repolarization of Ventricular Myocardium
- The depolarization and repolarization waves have opposite directions
- However, the electrical vector always points in the same direction
- Depolarization occurs quickly
- Thus, a narrow R wave is produced
- Repolarization occurs more slowly
- Thus, a broad T wave is produced
Depolarization and Repolarization in the Ventricles

Action Potential in the Endocardium and Epicardium
- The action potential of cardiomyocytes in the endocardium and epicardium has different electrical properties
- The conduction system activates the myocardium in the endocardium
- Thus, depolarization begins in the endocardium
- Depolarization in the endocardium and epicardium is nearly synchronous
- Therefore, the depolarization wave travels rapidly through the myocardial wall
- Cardiomyocytes in the epicardium begin to repolarize earlier than those in the endocardium
- Therefore, the repolarization wave starts in the epicardium
- However, the electrical vector of depolarization and repolarization points in the same direction
Depolarization and Repolarization in the Atria
- The myocardium of the atria is very thin
- Atrial depolarization begins in the endocardium (P wave)
- Atrial repolarization begins in the endocardium (Ta wave - usually not visible, hidden in the QRS complex)
- Ventricular repolarization begins in the epicardium (T wave)
T Wave (Most Variable Wave)
- It is the most variable wave on the ECG
- It represents ventricular repolarization
- It is low and wide
- Repolarization (T wave) is more asynchronous than depolarization (QRS complex)
|

|
ECG and Normal T Wave
- It is concordant (has the same polarity as QRS)
- Positive QRS - positive T wave
- Negative QRS - negative T wave
- It is positive (I, II, V3-V6)
- It can be isolated negative (III, aVL)
- It is negative in aVR
- Amplitude
- For ECG diagnosis, the dynamic of the T wave is important
- If the T wave remains the same - often not a serious condition
- If the T wave changes - often a serious condition (ischemia)
|

Concordant T Wave

Discordant T Wave
|
High Peaked T Wave
- It is tall, sometimes taller than the R wave
- In hyperkalemia, it is symmetrical (resembling the Eiffel Tower)
- In hyperacute ischemia, it has a broad base and is not symmetrical
- It is referred to as a hyperacute T wave
Inverted T Wave
- Concordant inverted T wave is not pathological
- In lead III, it may be discordantly inverted
- Pathological inverted T wave is
- Inverted T wave > 3mm or newly appeared

|
- Normal variant in children (V1-V3)
- Persistent juvenile T waves (in adults V1-V3)
- Athletes (V1-V3)
- Myocardial ischemia (at least in 2 adjacent leads)
- Hyperventilation (V1-V5)
- Left bundle branch block (I, aVL, V5-V6)
- Right bundle branch block (V1-V3)
- Left ventricular hypertrophy (I, aVL, V5-V6)
- Right ventricular hypertrophy (V1-V3) (II, III, aVF)
- Pulmonary embolism (V1-V3) (II, III, aVF)
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (V1-V3)
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (V1-V6)
- Intracranial hypertension (V1-V6) (II, III, aVF)
- Wellens syndrome (Type I: V2-V3)
- WPW syndrome: Type A: (V1-V3), Type B: (V4-V6)
- Hypothyroidism (V1-V6)
- Pacemaker
|
Biphasic T Wave
- A biphasic T wave is always assessed according to the terminal amplitude of the T wave


|
- Biphasic negative T wave (Terminal part is negative)
- Biphasic positive T wave (Terminal part is positive)
|
Double T Wave
- The T wave has 2 positive amplitudes, with a notch in the middle
- In reality, it is a T wave that is associated with a P wave or a U wave
Flat T Wave
- Concordant flat T waves are a nonspecific change on the ECG
- Rarely can occur with certain diagnoses
Normal T Wave

Normal T Wave and Sinus Rhythm
- Normal T Wave
- Is always positive (I, II, V3-V6)
- Is concordant (has the same polarity as QRS complex)
- Is negative (aVR, V1) if the QRS is also negative
- In lead III, it may be discordantly negative
- Amplitude
- Sinus Rhythm
Tall T Wave

|

|

|
|
Hyperkalemia
|
Hyperacute T Wave
|
Benign Early Repolarization
|

Hyperkalemia
|

Hyperacute T Wave
- Indicates hyperacute ischemia
- Typical hyperacute T wave
- It is tilted to the right
- The second part is steeper
|

Tall Peaked T Waves and Hyperkalemia
- Symmetrical peaked T waves (resembling the Eiffel Tower)
- T wave amplitude
- In precordial leads > 5mm
- In chest leads > 15mm
- The patient had hyperkalemia of 7.1mmol/l

Hyperacute T Waves and Acute Anterior-Inferior STEMI

High T Waves and Benign Early Repolarization
- High peaked T waves (V2-V6)
- T waves in benign early repolarization do not change—they persist for years
- T waves in STEMI infarction change; the patient should have a different EKG in an hour (STEMI dynamics)
- Benign early repolarization
- Concave ST elevations (V2-V5)
- In leads (V3-V5) there is a fishhook
Inverted T Waves

Inverted T Waves - Pediatric
- Children have negative T waves (V1-V3) due to right ventricular dominance
- Refers to a 2-year-old boy
- These negative T waves are physiological in children

Inverted T Waves - Persistent Juvenile
- Negative T waves in V1-V3
- If these T waves were new, it would indicate ischemia
- Persistent juvenile T waves
- Present from childhood and persist into adulthood (do not change)
- Most common in Afro-Caribbean women
- Usually deep, max. 3mm (though this is not a strict rule)

Inverted T Waves in Athletes

Inverted Ischemic T Waves and Unstable Angina Pectoris

Inverted T Waves and Hyperventilation
- The patient was a 24-year-old woman with no treatment, who was hyperventilating (she was frightened)
- Inverted T waves (V1-V5)
- After calming down, the EKG was normal, with no inverted T waves
- In this case, we must immediately rule out serious diagnoses

Inverted T Waves and Left Tawar Branch Block

Inverted T Waves and Right Tawar Branch Block

Inverted T Waves and Left Ventricular Hypertrophy

Inverted T Waves and Right Ventricular Hypertrophy

Inverted T Waves and Pulmonary Embolism

Inverted T Waves and Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia

Inverted T Waves and Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy

Inverted T Waves and Intracranial Hypertension

Inverted T Waves and Wellens Syndrome (Type I)
- Wellens Syndrome (Type I)
- Creates deep T waves (V2-V3) (rarely V1-V6)
- Type II is more common, producing negative bifasic T waves (the terminal part of the T wave is negative)

|
Inverted T Waves and WPW Syndrome (Type A)
|

|

|
Inverted T Waves and WPW Syndrome (Type B)
|

|

Inverted T Waves and Severe Hypothyroidism

Inverted T Waves and Pacemaker
- This concerns pacing of both atria and ventricles
- Stimulus artifacts are observed before the P wave and before the QRS
- The ventricles are stimulated from the right ventricle (the electrode is in the right ventricle)
Biphasic T Wave
- A biphasic T wave is always evaluated based on the terminal amplitude of the T wave
- Biphasic negative T wave (The terminal portion is negative)
- Biphasic positive T wave (The terminal portion is positive)

Biphasic Negative T Waves and Unstable Angina Pectoris
- It involved a patient with unstable angina pectoris due to stenosis of the RIA and RCx
- ST depression (V4-V6)
- Biphasic negative T waves (V2-V6)
- After stent placement (recanalization), the T waves later normalized
- For acute subendocardial ischemia, they are characteristic
- There is no precisely defined boundary between inverted and biphasic negative T waves

Biphasic Negative T Waves and Wellens' Syndrome (Type II)

Biphasic Positive T Waves and Hypokalemia
Double T Wave
- The T wave has 2 positive amplitudes and a notch in the middle
- In reality, this is a T wave that is combined with a P wave or a U wave

Double T Wave and Hypokalemia
- In hypokalemia, a U wave occurs
- Double T wave
- A U wave follows closely after the T wave (T + U wave)

Double T Wave and Sinus Tachycardia
- In sinus tachycardia, a P wave follows closely after the T wave
- Double T wave
- A P wave follows closely after the T wave (T + P wave)

Double T Wave and First-Degree AV Block
- In first-degree AV block
- There is a prolonged PQ interval (>0.2s)
- The QRS-T complex occurs later
- The T wave thus moves closer to the P wave
- Double T wave
- A P wave follows closely after the T wave (T + P wave)

Double T Wave and Second-Degree AV Block (2:1)
- In second-degree AV block (2:1)
- Every 2nd P wave is blocked
- The PQ interval may be prolonged (>0.2s)
- Double T wave
- A P wave follows closely after the T wave (T + P wave)
Flattened T Wave
- Concordant flattened T wave is a non-specific change on the ECG
- It rarely occurs with certain diagnoses

Ischemia and Flattened T Waves
|

Sinus Rhythm and Normal T Waves
- This is an ECG from the patient on the left
- The patient stopped bicycling on the ergometer
- After the cessation of exertion (ischemia), the ECG normalized
- The ECG shows a sinus rhythm
|

Flattened T Waves and Hypokalemia

Flattened T Waves and Severe Hypothyroidism
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers













































































































