Depolarization and Repolarization of the Ventricles
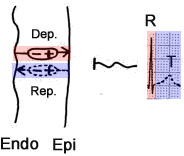
- Positive wave (deflection) is generated in the lead
- towards which the electrical vector is directed, specifically the (+) part of the vector
- Ventricular Depolarization (Dep.)
- It proceeds from the endocardium (Endo) to the epicardium (Epi)
- The vector (+) is directed towards the epicardium (towards the corresponding lead)
- It occurs quickly and generates a narrow, high R wave
- Ventricular Repolarization (Rep.)
- It proceeds from the epicardium to the endocardium (opposite direction)
- The vector (+) BUT is directed towards the epicardium
- The direction of the vector is the same as during depolarization
- It occurs slowly, generating a wide T wave
Depolarization and Repolarization of the Atria
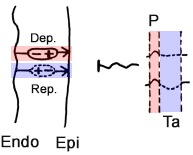
- Atrial Depolarization
- Proceeds from the endocardium to the epicardium
- The vector (+) is directed towards the epicardium (towards the corresponding lead)
- Generates the P wave
- Atrial Repolarization
- Proceeds from the endocardium to the epicardium (same direction)
- In the atrial myocardium, the action potential has the same duration everywhere
- The vector (+) is directed towards the endocardium (opposite direction)
- Generates a broad, flat, or even negative Ta wave
Ta Wave
- Represents repolarization of the atria
- Atrial myocardium is thin
- Therefore, it has a small amplitude, sometimes none
- Most commonly, it is isoelectric
- Sometimes it is flat-negative (< 2mm)
- It is overlapped by the QRS complex
- Deepens under:
- Shortens under:

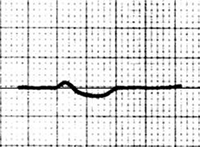
ECG and Ta Wave
- Most commonly is isoelectric
- Flat-negative Ta wave:
- Starts at the end of the P wave
- Depth < 2mm
- Width < 320ms (8 small squares)
- May extend up to 180ms (4.5 small squares) beyond the QRS
- PTa interval (from the beginning of the P wave to the end of the Ta wave)
- It is overlapped by the QRS complex
- It is clearly visible if the QRS does not follow immediately after the P wave:
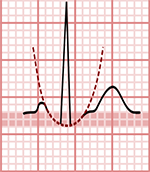

Ta Wave and ST Segment
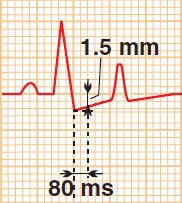
- The ST segment is the main marker
- The height of the ST segment is measured between
- the end of the PQ segment
- and the point 80ms from the J point (connecting the QRS and ST segment)
- The Ta wave is most commonly isoelectric
- The height of the ST segment is more difficult to assess with a flat-negative Ta wave
Isoelectric Ta Wave
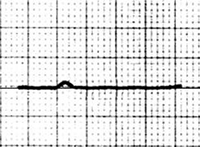

Isoelectric Ta Wave ST Segment
Flat-negative Ta Wave

Flat-negative Ta Wave ST Segment

Ta Wave and Sinus Tachycardia
- Sinus Tachycardia
- Flat-negative Ta wave (Best seen in leads II, V5)
- Width: 280ms (7 small squares)
- Depth: 2mm (measured from the end of the P wave)
- Seen as a descendant PQ segment and an ascendant ST segment
- It is overlapped by the QRS complex
- It may not indicate atrial ischemia, it can also occur due to sympathetic predominance (stress, pain)
- ST segment is without deviation
- End of PQ segment has the same height as the point 80ms after the J point
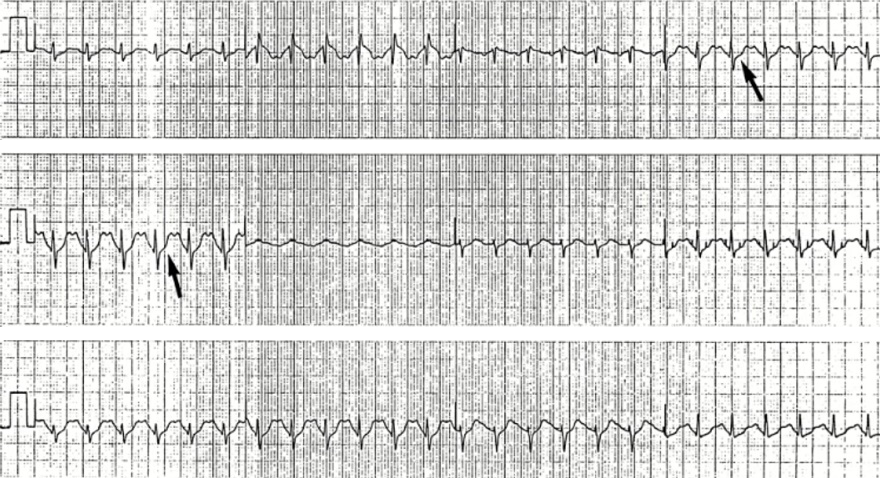
Ta Wave and Sinus Tachycardia
- The patient was just after ergometry (bicycling - physical exertion)
- Sinus Tachycardia
- Flat-negative Ta wave
- Width 200ms (5 small squares)
- Depth 2mm (measured from the end of the P wave)
- It is overlapped by the QRS complex
- ST segment is without deviation
- End of PQ segment has the same height as the point 80ms after the J point
- Atrial ischemia or ventricular ischemia is not present
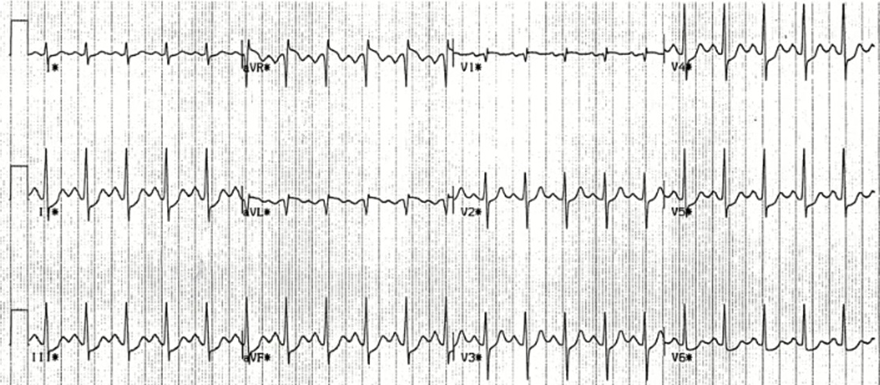
Ta Wave and Sinus Tachycardia, ST Depression
- Sinus Tachycardia
- Flat-negative Ta wave
- Width 200ms (5 small squares)
- Depth 1mm (the curve of the Ta wave needs to be inferred)
- It is overlapped by the QRS complex
- ST Depression 1mm
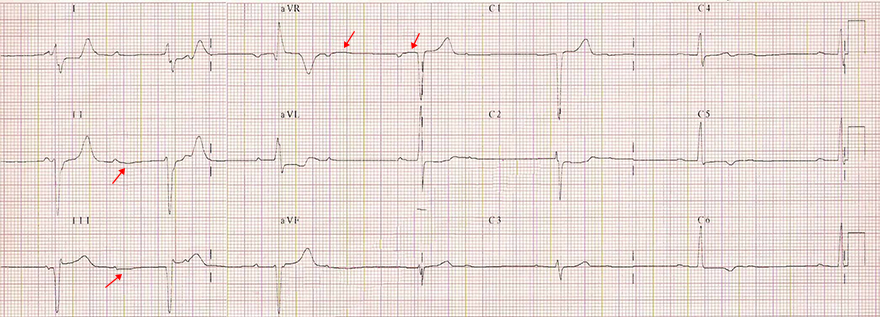
Ta Wave and AV Block II Degree (2:1)
- AV Block II Degree (2:1)
- Every 2nd P wave is blocked
- Left Anterior Fascicular Block
- Flat-negative Ta wave
- Every 2nd P wave is blocked (not followed by a QRS)
- After it, there is a suggested Ta wave (negative arc)
- In lead aVR, the P wave is negative and the Ta wave is positive
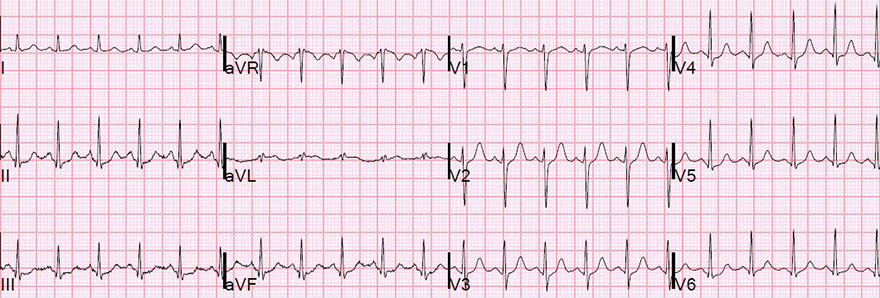
Ta Wave and Sinus Tachycardia
- Sinus Tachycardia
- Flat-negative Ta wave (Best visible in lead II)
- Width: 200ms (5 squares)
- Depth: 1mm (measured from the end of the P wave)
- Seen as a descending PQ segment and ascending ST segment
- It is covered by the QRS complex
- ST segment shows no deviation
- End of PQ segment has the same height as the point 80ms after the J point
- In lead aVR, the P wave is negative and the Ta wave is positive
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers

































