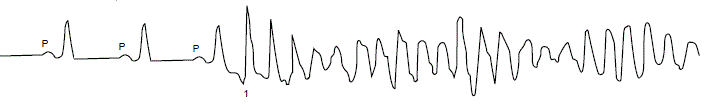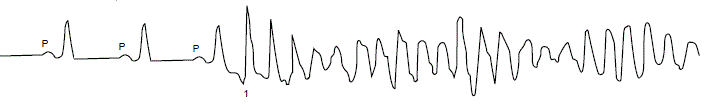Home /
Torsades de Pointes (TdP) - ECG
Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia associated with a long QT, Twisting of the points
Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
Torsades de Pointes

Prolonged QT Interval
- QTC = 0.58s (QTC > 440ms)
- First described in 1966 by the French physician François Dessertenne
- It is the most common polymorphic VT
- Heart rate is 160-250/min.
- It is a polymorphic VT that occurs with a prolonged QT interval
- TdP has a characteristic onset
- It is triggered by a ventricular premature beat (R-on-T phenomenon)
- At the onset, a typical short-long-short RR interval occurs
- During TdP, QRS complexes change amplitude, "twisting" around their axis
- Because the direction of the main vector changes
- TdP is translated as "twisting of the spikes" ("dancing spikes")
- The QRS complex cycle repeats approximately every 5-20 beats
- It is a "short-lived" nonsustained ventricular tachycardia
- Because it spontaneously resolves within 30 seconds
- Rarely, it does not resolve spontaneously and may progress to ventricular fibrillation
Torsades de Pointes
- The patient had a prolonged QT interval during sinus rhythm
- At the onset, a typical short-long-short (SLS) sequence (short-long-short RR interval) is observed
- Torsades de Pointes
- Wide QRS complexes (>0.12s) that vary in amplitude and width
Torsades de Pointes vs. Polymorphic VT
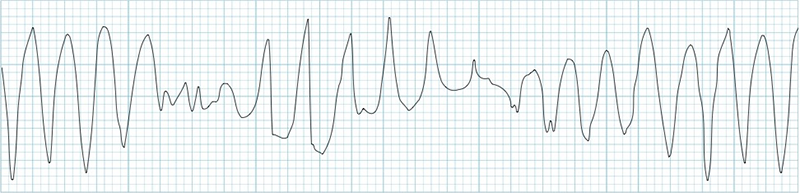
Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
- According to the provided ECG, we cannot determine whether it is TdP or polymorphic VT
- The onset of tachycardia is not visible
- It is unknown whether the patient has a prolonged QT interval
- Polymorphic VT and Torsades de Pointes present the same appearance on the ECG during tachycardia (as shown in the ECG)
- Distinguishing between polymorphic VT and Torsades de Pointes is important for treatment
- Torsades de Pointes should not be treated with antiarrhythmics that prolong the QT interval
Interventricular Dispersion of Repolarization
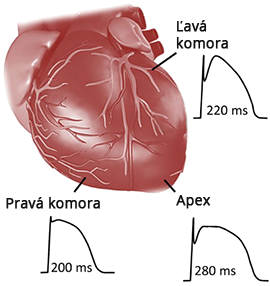
- Action Potential during conduction through the myocardium does not have the same shape
- The main difference is the duration of repolarization
- Interventricular Dispersion of Repolarization
- It is the difference in the duration of repolarization between the ventricles
- The action potential curve has a different duration (repolarization) in:
- The right ventricle
- The apex
- The left ventricle
Transmural Dispersion of Repolarization

- Action Potential has a different duration
- Even during conduction through the myocardial wall
- Transmural Dispersion of Repolarization
- It is the difference in the duration of repolarization within the ventricular wall, in:
- The endocardium
- The mid-myocardium (M-cells)
- The epicardium
ECG and Transmural Dispersion of Repolarization
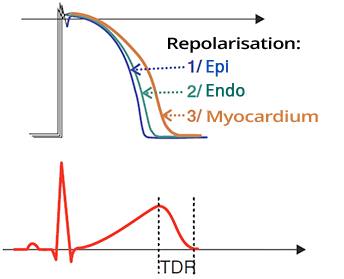
- Transmural Dispersion of Repolarization (TDR):
- First, the epicardium repolarizes
- Then, the endocardium
- Lastly, the mid-myocardium (M-cells)
- TDR on ECG corresponds to the descending part of the T wave
- This part of the T wave is called the vulnerable period
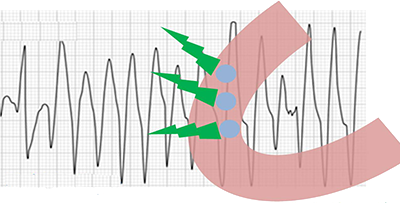
- R on T phenomenon is a ventricular extrasystole
- Which occurs during the vulnerable period
- It can trigger Torsades de Pointes
Prolonged QT Interval

Prolonged QT Interval and Transmural Dispersion of Repolarization
- Transmural Dispersion of Repolarization (TDR)
- Mainly refers to the difference between repolarization of the epicardium and the mid-myocardium (M-cells)
- If a patient has a prolonged QT interval
- The repolarization of the mid-myocardium (M-cells) is mainly prolonged
- Prolongation of the epicardial repolarization is not significant
- Therefore, transmural dispersion of repolarization is also prolonged
- There is a greater distance between the repolarization of the epicardium and the mid-myocardium (M-cells)
- The likelihood increases that a ventricular extrasystole will "strike" during the vulnerable period
- Because the vulnerable period is prolonged
Early Afterdepolarization and Torsades de Pointes
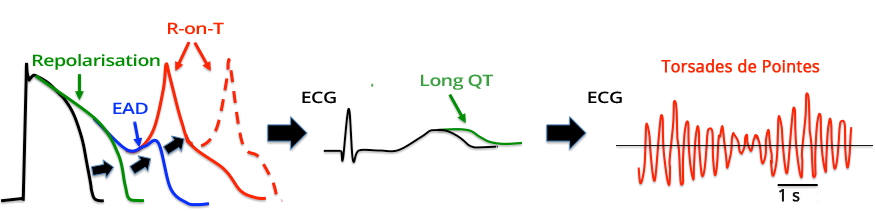
Early Afterdepolarization and Torsades de Pointes
- With a prolonged QT interval
- The action potential is prolonged - mainly repolarization (green curve)
- Prolonged repolarization appears on the ECG during sinus rhythm as a prolonged QT interval
- Early Afterdepolarization (EAD)
- Is a new action potential that occurs earlier (during repolarization)
- On the ECG, it appears as a ventricular extrasystole (R-on-T phenomenon)
- Which triggers Torsades de Pointes
- TdP is then sustained by a reentry mechanism due to transmural dispersion of repolarization
Re-entry and Torsades de Pointes
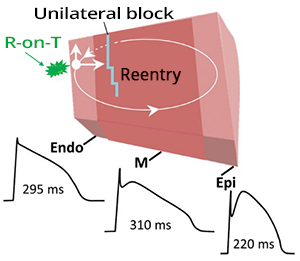
- Prolonged Transmural Dispersion of Repolarization
- Changes in the refractory period of the myocardial wall layers
- The impulse can start to circulate in the myocardial wall
- Ventricular Extrasystole (R-on-T phenomenon)
- Triggers the circulation of the impulse through the myocardial wall layers
- The mechanism of maintaining TdP is re-entry in the myocardial wall
ECG and Torsades de Pointes
- During sinus rhythm, the patient has a prolonged QT interval
- Frequency 160-250/min.
- Wide QRS complexes (>0.12s)
- Width and amplitude change (QRS "dance around their axis")
- Most often starts as an SLS sequence (short-long-short interval)
- On ECG, a short-long-short RR interval
- Most frequently manifests as nonsustained ventricular tachycardia
- Spontaneously resolves within 30s

Torsades de Pointes
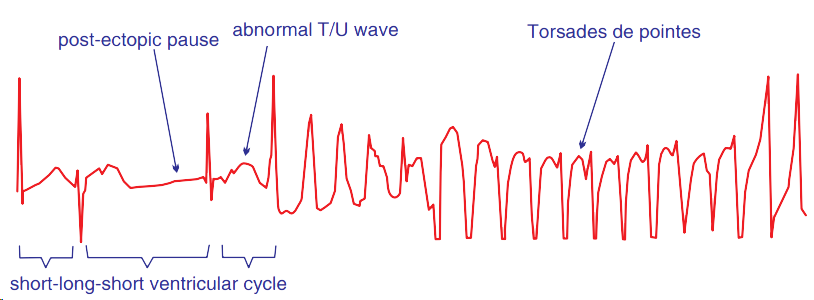
- SLS sequence (short-long-short interval "short-long-short interval")
- Short interval
- The sinus beat is followed by a ventricular extrasystole (with a short coupling interval)
- Long interval
- After the ventricular extrasystole, a compensatory pause occurs followed by a sinus beat
- Short interval
- Following the compensatory pause, another ventricular extrasystole occurs (with a short coupling interval)
- This is the onset of Torsades de Pointes
- Torsades de Pointes
- Wide QRS complexes that change in amplitude and width
ECG and the Onset of Torsades de Pointes
- Based on the onset of TdP on the ECG, there are 2 types of TdP:
- Pause-dependent Torsades de Pointes
- Pause-independent Torsades de Pointes
- Short-coupled Torsades de Pointes
- Very rare (approximately 14 cases described)
Pause-dependent Torsades de Pointes

Pause-dependent Torsades de Pointes
- (Pause-dependent SLS Torsades de Pointes)
- Most common variant
- Has a SLS sequence (short-long-short interval)
- Sinus beat (1)
- Ventricular extrasystole (2)
- Sinus beat (3)
- Ventricular extrasystole (4)
- Before TdP there is a pause in the RR interval (2 - 3)
- Patient has a prolonged QT interval (during sinus rhythm)
Pause-independent Torsades de Pointes
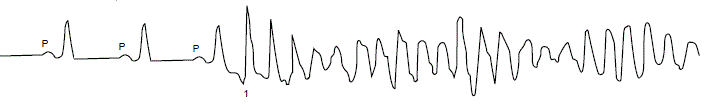

Pause-independent Torsades de Pointes
- (Short-coupled Torsades de Pointes)
- It is rare (approximately 14 documented cases)
- Starts with a ventricular extrasystole (1)
- Family history includes sudden death
- Which suggests genetic etiology (congenital channelopathy)
- Affects young people
- Without structural heart damage
- Presents as syncope (loss of consciousness) or sudden death
- Often manifests as non-sustained ventricular tachycardia
- Does not respond to antiarrhythmic treatment like polymorphic VT
- Patient has a normal QT interval
- The extrasystole likely causes transmural dispersion of the myocardium, possibly sustaining re-entry?
- Short-coupled Torsades de Pointes is not polymorphic VT
- Despite having a normal QT interval
- This is a paradox, and the discussion is more academic than clinical
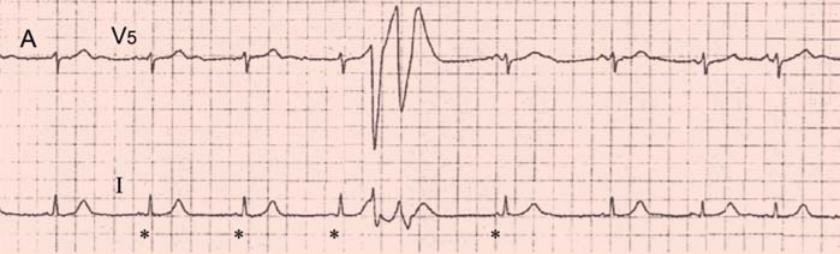
Sinus Rhythm and Ventricular Couplets
- The patient is young and has no structural heart damage
- The patient came to the hospital for recurrent syncopes (loss of consciousness)
- Sinus Rhythm
- QT Interval is not prolonged (400ms)
- Ventricular Couplet (2 extrasystoles in a row)
- The patient was given a 24-hour ECG Holter monitor

Torsades de Pointes (Short-coupled TdP)
- This is an ECG from a previous patient
- 24-hour ECG Holter recorded Torsades de Pointes
- After sinus rhythm follows a ventricular extrasystole with a shortened coupling interval <300ms
- The patient does not have a prolonged QT interval
- Short-coupled Torsades de Pointes
- It is a very rare form of TdP
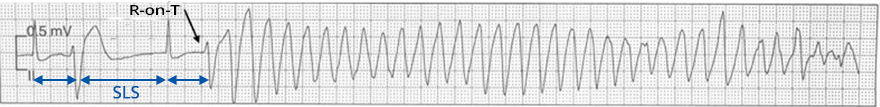
Torsades de Pointes (SLS Sequence)
- The patient had a prolonged QT interval
- At the beginning, we see a typical SLS sequence (short-long-short RR interval)
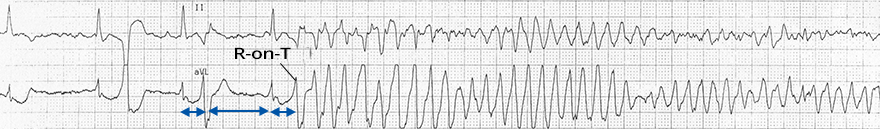
Torsades de Pointes (SLS Sequence) and Ventricular Fibrillation

Torsades de Pointes (SLS Sequence)
- The patient had a prolonged QT interval
- Continuous Lead II:
- After the end of TdP, an SLS sequence follows (short-long-short RR interval)
- After the SLS sequence, Torsades de Pointes reappears
- TdP is often nonsustained ventricular tachycardia
- Spontaneously ends within 30 seconds
- The patient had paroxysms of TdP
- Recurring episodes of TdP that spontaneously ended within 30 seconds
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers
Home /
Torsades de Pointes (TdP) - ECG
Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia associated with a long QT, Twisting of the points
Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
Torsades de Pointes
- First described in 1966 by the French physician François Dessertenne
- It is the most common polymorphic VT
- Heart rate is 160-250/min.
- It is a polymorphic VT that occurs with a prolonged QT interval
- TdP has a characteristic onset
- It is triggered by a ventricular premature beat (R-on-T phenomenon)
- At the onset, a typical short-long-short RR interval occurs
- During TdP, QRS complexes change amplitude, "twisting" around their axis
- Because the direction of the main vector changes
- TdP is translated as "twisting of the spikes" ("dancing spikes")
- The QRS complex cycle repeats approximately every 5-20 beats
- It is a "short-lived" nonsustained ventricular tachycardia
- Because it spontaneously resolves within 30 seconds
- Rarely, it does not resolve spontaneously and may progress to ventricular fibrillation
|

Prolonged QT Interval
- QTC = 0.58s (QTC > 440ms)
|

Torsades de Pointes
- The patient had a prolonged QT interval during sinus rhythm
- At the onset, a typical short-long-short (SLS) sequence (short-long-short RR interval) is observed
- Torsades de Pointes
- Wide QRS complexes (>0.12s) that vary in amplitude and width
Torsades de Pointes vs. Polymorphic VT

Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
- According to the provided ECG, we cannot determine whether it is TdP or polymorphic VT
- The onset of tachycardia is not visible
- It is unknown whether the patient has a prolonged QT interval
- Polymorphic VT and Torsades de Pointes present the same appearance on the ECG during tachycardia (as shown in the ECG)
- Distinguishing between polymorphic VT and Torsades de Pointes is important for treatment
- Torsades de Pointes should not be treated with antiarrhythmics that prolong the QT interval
Interventricular Dispersion of Repolarization

|
- Action Potential during conduction through the myocardium does not have the same shape
- The main difference is the duration of repolarization
- Interventricular Dispersion of Repolarization
- It is the difference in the duration of repolarization between the ventricles
- The action potential curve has a different duration (repolarization) in:
- The right ventricle
- The apex
- The left ventricle
|
Transmural Dispersion of Repolarization

|
- Action Potential has a different duration
- Even during conduction through the myocardial wall
- Transmural Dispersion of Repolarization
- It is the difference in the duration of repolarization within the ventricular wall, in:
- The endocardium
- The mid-myocardium (M-cells)
- The epicardium
|
ECG and Transmural Dispersion of Repolarization

|
- Transmural Dispersion of Repolarization (TDR):
- First, the epicardium repolarizes
- Then, the endocardium
- Lastly, the mid-myocardium (M-cells)
- TDR on ECG corresponds to the descending part of the T wave
- This part of the T wave is called the vulnerable period
- R on T phenomenon is a ventricular extrasystole
- Which occurs during the vulnerable period
- It can trigger Torsades de Pointes
|
Prolonged QT Interval

Prolonged QT Interval and Transmural Dispersion of Repolarization
- Transmural Dispersion of Repolarization (TDR)
- Mainly refers to the difference between repolarization of the epicardium and the mid-myocardium (M-cells)
- If a patient has a prolonged QT interval
- The repolarization of the mid-myocardium (M-cells) is mainly prolonged
- Prolongation of the epicardial repolarization is not significant
- Therefore, transmural dispersion of repolarization is also prolonged
- There is a greater distance between the repolarization of the epicardium and the mid-myocardium (M-cells)
- The likelihood increases that a ventricular extrasystole will "strike" during the vulnerable period
- Because the vulnerable period is prolonged
Early Afterdepolarization and Torsades de Pointes

Early Afterdepolarization and Torsades de Pointes
- With a prolonged QT interval
- The action potential is prolonged - mainly repolarization (green curve)
- Prolonged repolarization appears on the ECG during sinus rhythm as a prolonged QT interval
- Early Afterdepolarization (EAD)
- Is a new action potential that occurs earlier (during repolarization)
- On the ECG, it appears as a ventricular extrasystole (R-on-T phenomenon)
- Which triggers Torsades de Pointes
- TdP is then sustained by a reentry mechanism due to transmural dispersion of repolarization
Re-entry and Torsades de Pointes

|
- Prolonged Transmural Dispersion of Repolarization
- Changes in the refractory period of the myocardial wall layers
- The impulse can start to circulate in the myocardial wall
- Ventricular Extrasystole (R-on-T phenomenon)
- Triggers the circulation of the impulse through the myocardial wall layers
- The mechanism of maintaining TdP is re-entry in the myocardial wall
|
ECG and Torsades de Pointes
- During sinus rhythm, the patient has a prolonged QT interval
- Frequency 160-250/min.
- Wide QRS complexes (>0.12s)
- Width and amplitude change (QRS "dance around their axis")
- Most often starts as an SLS sequence (short-long-short interval)
- On ECG, a short-long-short RR interval
- Most frequently manifests as nonsustained ventricular tachycardia
- Spontaneously resolves within 30s

Torsades de Pointes
- SLS sequence (short-long-short interval "short-long-short interval")
- Short interval
- The sinus beat is followed by a ventricular extrasystole (with a short coupling interval)
- Long interval
- After the ventricular extrasystole, a compensatory pause occurs followed by a sinus beat
- Short interval
- Following the compensatory pause, another ventricular extrasystole occurs (with a short coupling interval)
- This is the onset of Torsades de Pointes
- Torsades de Pointes
- Wide QRS complexes that change in amplitude and width
ECG and the Onset of Torsades de Pointes
- Based on the onset of TdP on the ECG, there are 2 types of TdP:
- Pause-dependent Torsades de Pointes
- Pause-independent Torsades de Pointes
- Short-coupled Torsades de Pointes
- Very rare (approximately 14 cases described)
Pause-dependent Torsades de Pointes

Pause-dependent Torsades de Pointes
- (Pause-dependent SLS Torsades de Pointes)
- Most common variant
- Has a SLS sequence (short-long-short interval)
- Sinus beat (1)
- Ventricular extrasystole (2)
- Sinus beat (3)
- Ventricular extrasystole (4)
- Before TdP there is a pause in the RR interval (2 - 3)
- Patient has a prolonged QT interval (during sinus rhythm)
Pause-independent Torsades de Pointes
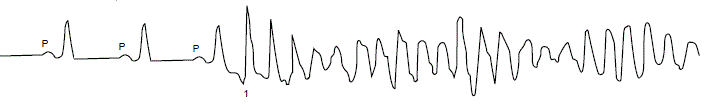
Pause-independent Torsades de Pointes
- (Short-coupled Torsades de Pointes)
- It is rare (approximately 14 documented cases)
- Starts with a ventricular extrasystole (1)
- Family history includes sudden death
- Which suggests genetic etiology (congenital channelopathy)
- Affects young people
- Without structural heart damage
- Presents as syncope (loss of consciousness) or sudden death
- Often manifests as non-sustained ventricular tachycardia
- Does not respond to antiarrhythmic treatment like polymorphic VT
- Patient has a normal QT interval
- The extrasystole likely causes transmural dispersion of the myocardium, possibly sustaining re-entry?
- Short-coupled Torsades de Pointes is not polymorphic VT
- Despite having a normal QT interval
- This is a paradox, and the discussion is more academic than clinical
|

|

Sinus Rhythm and Ventricular Couplets
- The patient is young and has no structural heart damage
- The patient came to the hospital for recurrent syncopes (loss of consciousness)
- Sinus Rhythm
- QT Interval is not prolonged (400ms)
- Ventricular Couplet (2 extrasystoles in a row)
- The patient was given a 24-hour ECG Holter monitor

Torsades de Pointes (Short-coupled TdP)
- This is an ECG from a previous patient
- 24-hour ECG Holter recorded Torsades de Pointes
- After sinus rhythm follows a ventricular extrasystole with a shortened coupling interval <300ms
- The patient does not have a prolonged QT interval
- Short-coupled Torsades de Pointes
- It is a very rare form of TdP

Torsades de Pointes (SLS Sequence)
- The patient had a prolonged QT interval
- At the beginning, we see a typical SLS sequence (short-long-short RR interval)

Torsades de Pointes (SLS Sequence) and Ventricular Fibrillation

Torsades de Pointes (SLS Sequence)
- The patient had a prolonged QT interval
- Continuous Lead II:
- After the end of TdP, an SLS sequence follows (short-long-short RR interval)
- After the SLS sequence, Torsades de Pointes reappears
- TdP is often nonsustained ventricular tachycardia
- Spontaneously ends within 30 seconds
- The patient had paroxysms of TdP
- Recurring episodes of TdP that spontaneously ended within 30 seconds
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers