Home /
Transition Zone
Transition zone
Electrical Axis of EKG Leads

Positive and Negative EKG Deflection
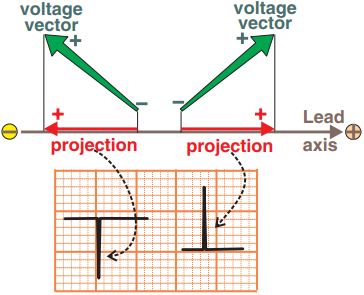
- Cardiac Electrical Vector
- Must always project onto the electrical axis of the EKG lead
- Positive EKG Deflection occurs
- Negative EKG Deflection occurs
- When the vector is directed away from the surface electrode (+)
Biphasic EKG Deflection
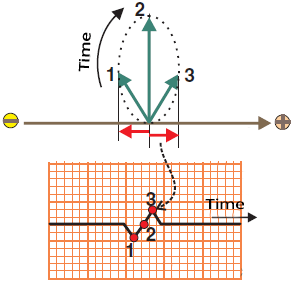
- Myocardium depolarizes gradually
- The electrical vector thus rotates around a point
- e.g., ventricular depolarization
- EKG lead records the vectors sequentially and generates an EKG curve
- 1st vector points away from the electrode (+)
- 2nd vector is perpendicular to the electrode (+)
- 3rd vector points towards the electrode (+)
- A biphasic EKG deflection is gradually formed
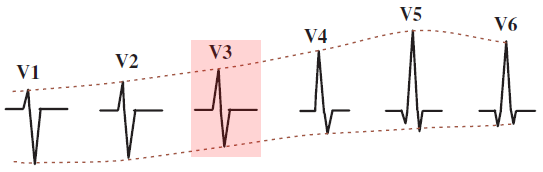
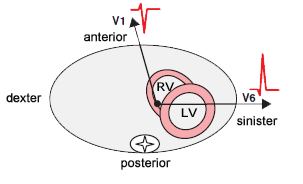
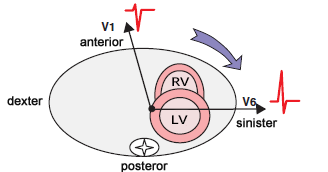
Precordial Leads
- Precordial leads (V1-V6)
- are oriented towards the heart in the horizontal plane
- Main cardiac vector (VH)
- Straightest direction is towards lead V6
- Between the vector and V6 are the lungs (insulator)
- Dominant R wave is in V5
- Points away from lead V1
- where there will be a negative S wave
- In precordial leads, there is progression of the R wave
- R wave amplitude increases from lead V1 to V4-5

- Transition Zone
- If the main vector (VM) is perpendicular to the chest lead
- A biphasic QRS complex (R=S) appears in the lead
- which is referred to as the transition zone
- The image shows the transition zone in V3
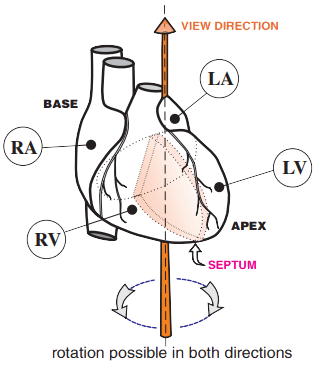
Cardiac Rotation and Transition Zone
- Transition Zone
- Indicates rotation of the heart around the longitudinal axis
- Similar to rotating your head (right - left)
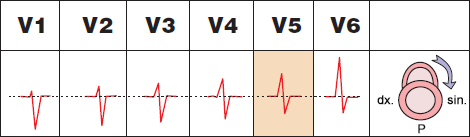
ECG and Transition Zone
Transition Zone
- Assessed only in precordial leads (V1-V6)
- RS wave (R wave = S wave)
- Most commonly found in lead V3
Normal Heart Rotation
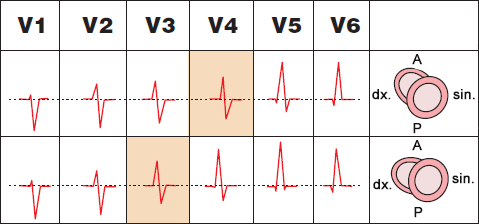
Normal Heart Rotation
- Transition zone is in V3-V4
- Sometimes considered a normal variant:
- Early transition zone in V2 (Early transition zone)
- Delayed transition zone in V5 (Delayed/Late transition zone)
Counterclockwise Heart Rotation
Counterclockwise (CCW) rotation, Early transition zone
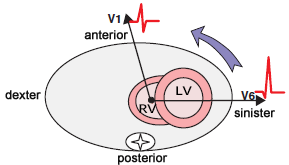
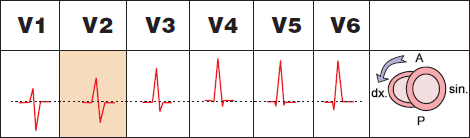
Counterclockwise Heart Rotation
- Main cardiac vector rotates toward the right ventricle
- Transition zone is in V1-V2
- Sometimes considered a normal variant:
- Early transition zone in V2 (Early transition zone)
- Most common causes:
Clockwise Heart Rotation
Clockwise (CW) rotation, Delayed transition zone, Late transition zone
Clockwise Heart Rotation
- Main cardiac vector rotates toward the left ventricle
- Transition zone is in V5-V6
- Sometimes considered a normal variant:
- Delayed transition zone in V5 (Delayed/Late transition zone)
- Most common causes:
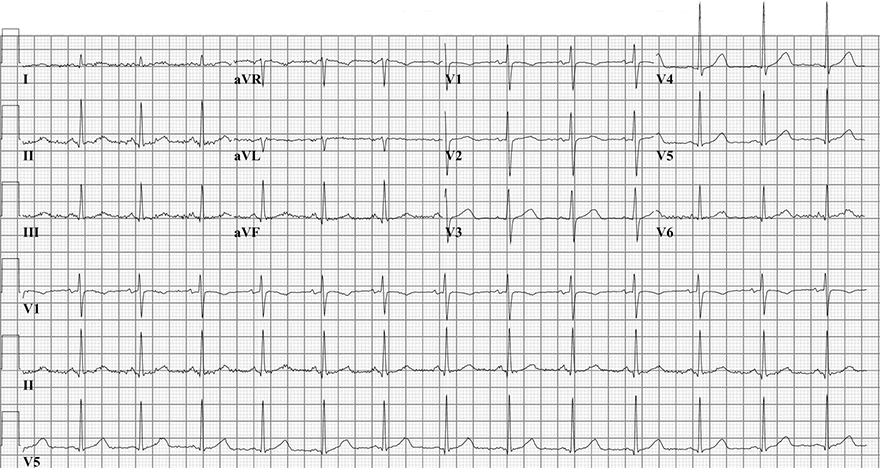
Normal Heart Rotation and Sinus Rhythm
- Sinus Rhythm
- Transition zone V3 (R = S wave)
- This represents normal heart rotation
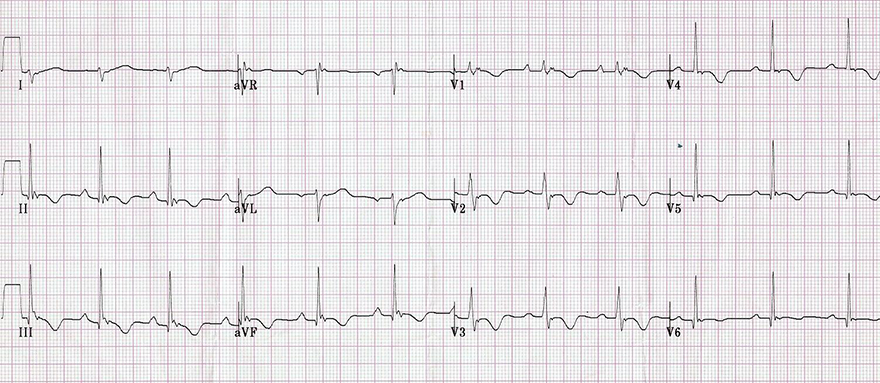
Heart Rotation Counterclockwise and Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
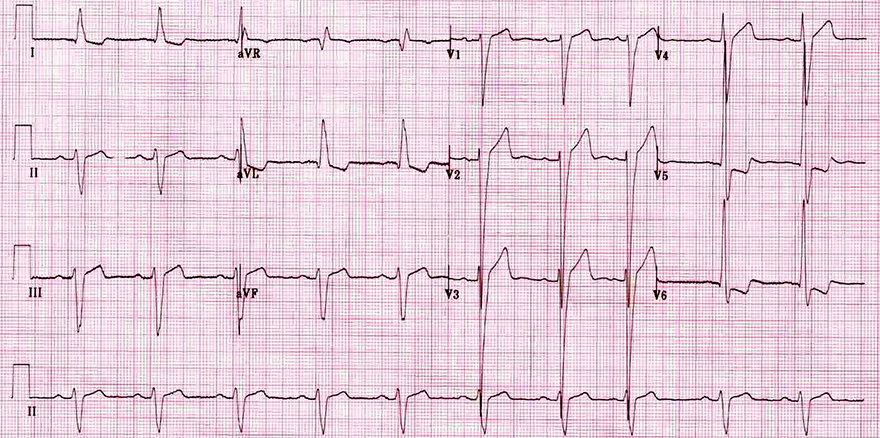
Heart Rotation Clockwise and Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
- Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
- Positive Sokolow index: S (V2) + R (V6) > 35mm
- Left ventricular overload: ST depression and negative T waves (V5-V6, I, aVL)
- Transition Zone V4/V5
- Transition zone is located between V4 and V5
- The heart is rotated clockwise (towards the left ventricle)
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers































