Home /
Tricyclic antidepressants Overdose (Sodium-Channel Blocker Toxicity)



Tricyclic Antidepressants (Intoxication)
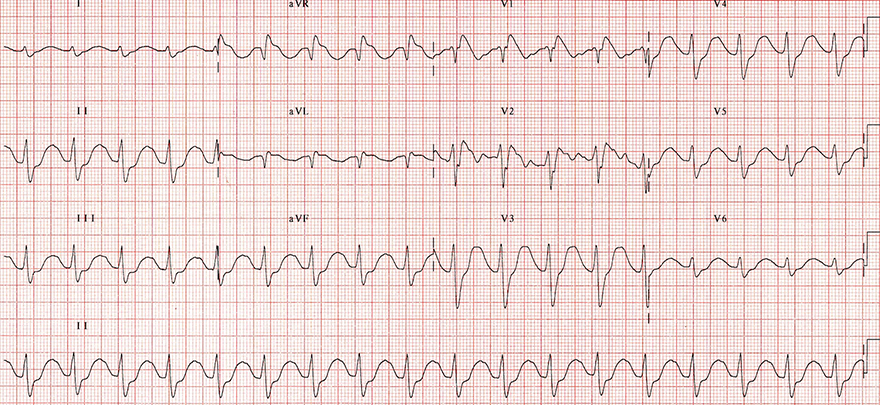
ECG 1/3: Tricyclic Antidepressants (Intoxication)
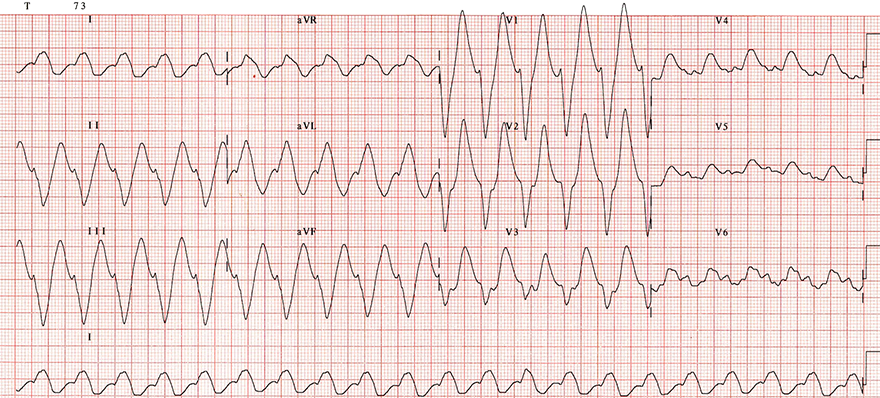
ECG 2/3: Tricyclic Antidepressants (Progression of Intoxication)
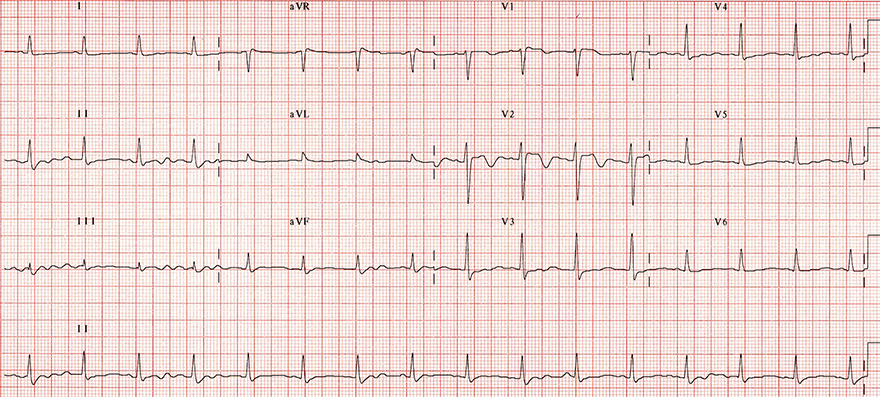
ECG 3/3: Tricyclic Antidepressants (Post-Treatment of Intoxication)
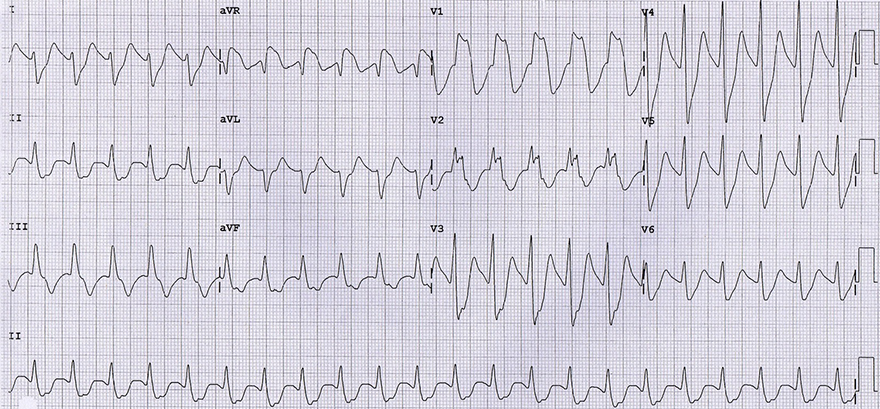
Tricyclic Antidepressants (Intoxication)

Flecainide (Intoxication)
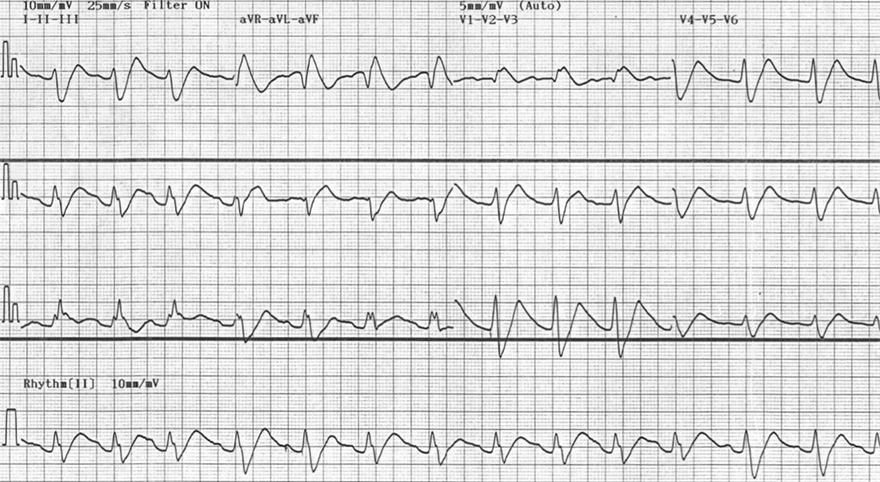
Flecainide (Intoxication)
Sources
Home /
Tricyclic antidepressants Overdose (Sodium-Channel Blocker Toxicity)
Depression
|

|
Tricyclic Antidepressants
|

|
|
 |

Tricyclic Antidepressants (Intoxication)

ECG 1/3: Tricyclic Antidepressants (Intoxication)

ECG 2/3: Tricyclic Antidepressants (Progression of Intoxication)

ECG 3/3: Tricyclic Antidepressants (Post-Treatment of Intoxication)

Tricyclic Antidepressants (Intoxication)

Flecainide (Intoxication)

Flecainide (Intoxication)
Sources