
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
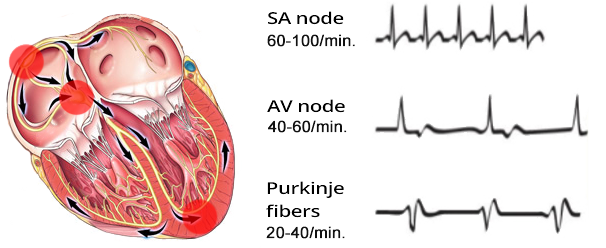
Basic Heart Rhythms
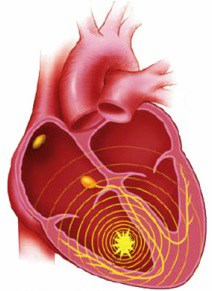
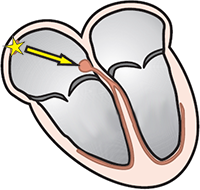
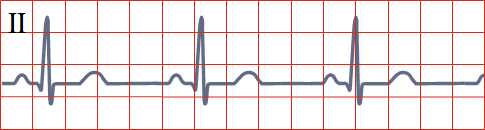
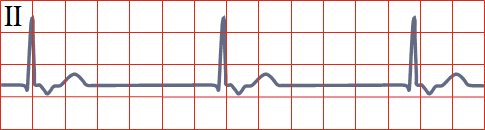
Sinus Rhythm

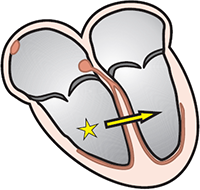
Junctional Rhythm
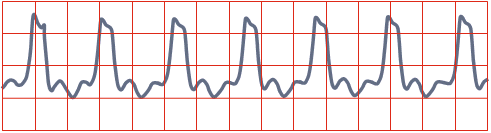
Ventricular Rhythm

Ventricular Rhythm
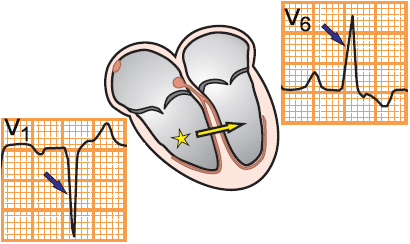
Ectopic Focus in the Right Ventricle
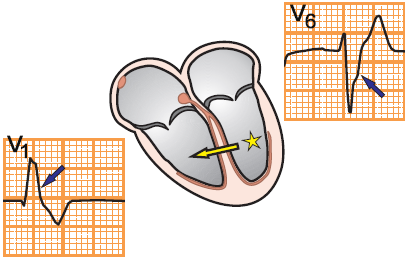
Ectopic Focus in the Left Ventricle

Ventricular Rhythm
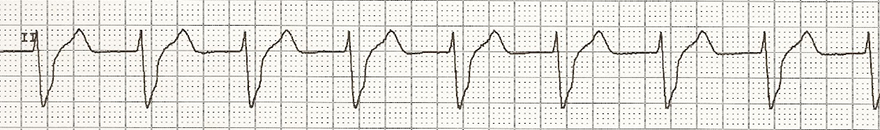
Accelerated Ventricular Rhythm
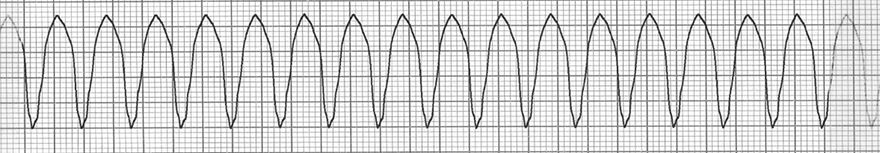
Ventricular Tachycardia
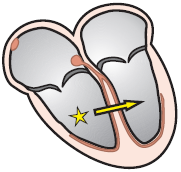
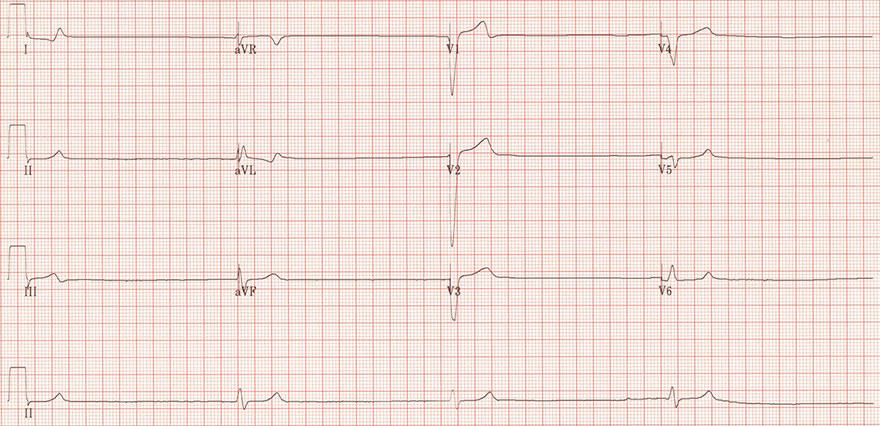
Ventricular Rhythm and Sinus Pause
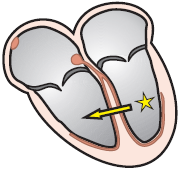
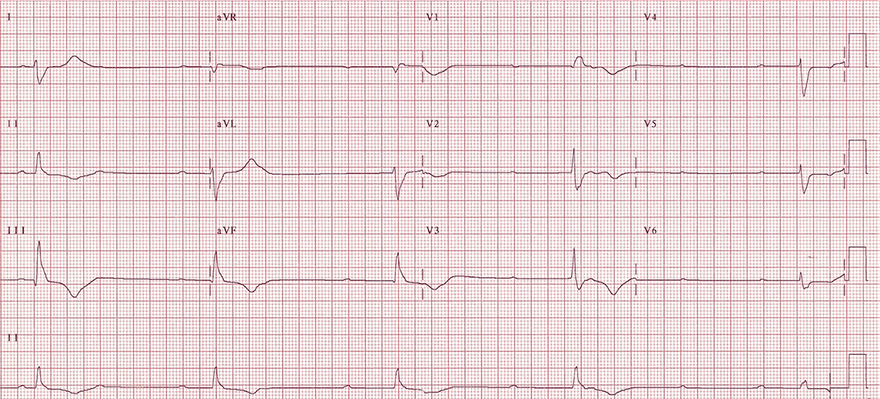
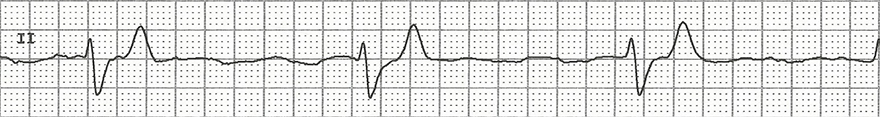
Ventricular Rhythm and AV Block III Degree

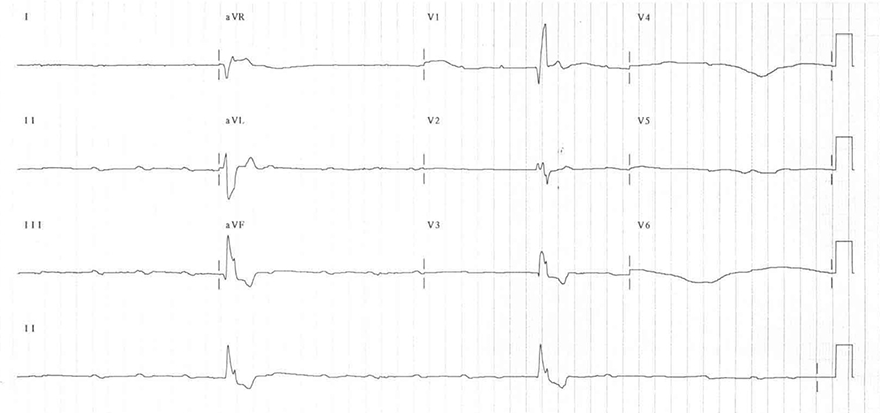
Ventricular Rhythm and AV Block III Degree
Sources

Basic Heart Rhythms
Ventricular Rhythm
|

|

|

Sinus Rhythm
|

|

Junctional Rhythm
|

|

Ventricular Rhythm
|
ECG and Ventricular Rhythm
|

|

Ventricular Rhythm

Ectopic Focus in the Right Ventricle
|

Ectopic Focus in the Left Ventricle
|

Ventricular Rhythm

Accelerated Ventricular Rhythm

Ventricular Tachycardia

|
Ventricular Rhythm and Sinus Pause
|

|

|
Ventricular Rhythm and AV Block III Degree
|

|

|
Ventricular Rhythm and AV Block III Degree
|

|
Sources