
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Localisation of the origin of a ventricular tachycardia
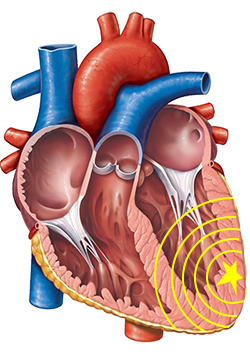
| ECG finding: | Localization: |
| QRS Morphology: | |
| Shape of LBBB | Left ventricular septum, Right ventricle, Bundle branch reentry VT |
| Shape of RBBB | Left ventricle outside the septum |
| Cardiac Axis: | |
| Superior | Inferior wall |
| Inferior | Upper septum, Upper lateral wall |
| Rightward | Left lateral wall, Apex |
| Transition Zone: | |
| Transition zone ≤ V3 | Base of the heart |
| Transition zone ≥ V4 | Apex of the heart |
| Precordial Concordance: | |
| Positive | Base of the heart |
| Negative | Apex of the heart |
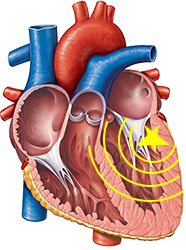
Ventricular Tachycardia
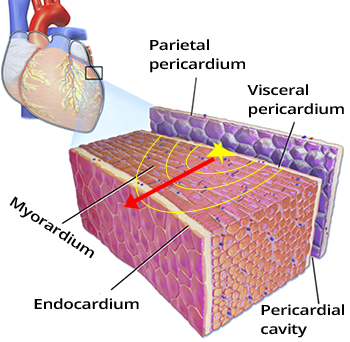
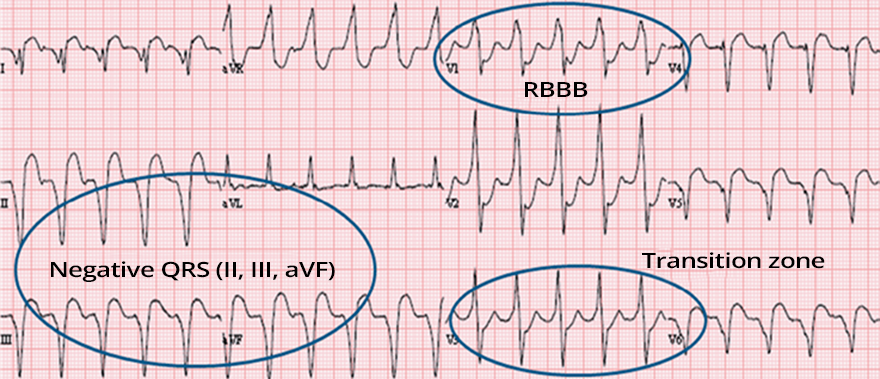
| ECG Criteria: | Definition: |
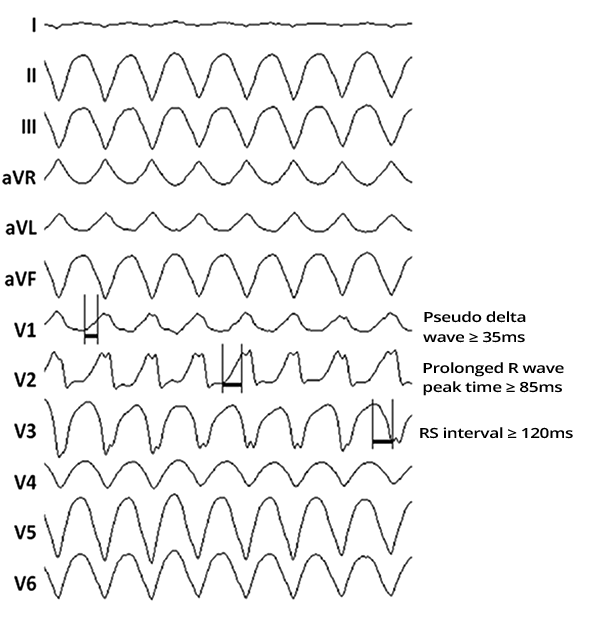
| Pseudo delta wave ≥ 35ms | From the beginning of the QRS to the end of the pseudo delta wave In any precordial lead |
| Prolonged R wave peak time ≥ 85ms | From the beginning of the QRS to the peak of the R wave In lead V2 |
| RS interval ≥ 120ms | From the beginning of the QRS to the peak of the S wave In any lead |
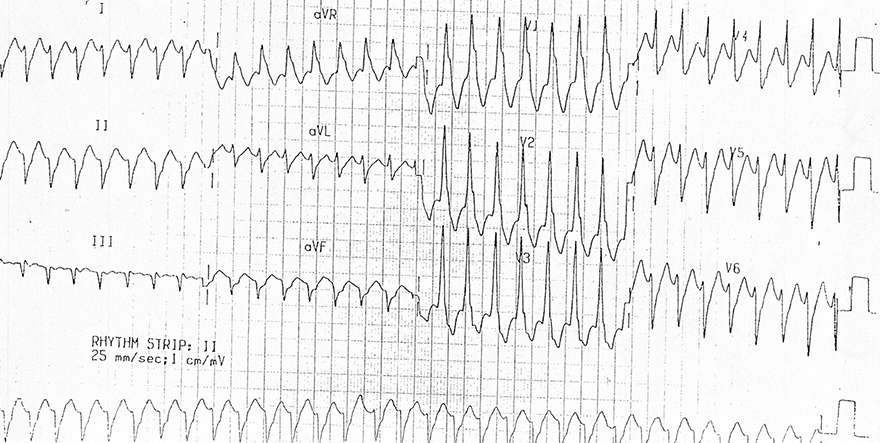
Ventricular Tachycardia

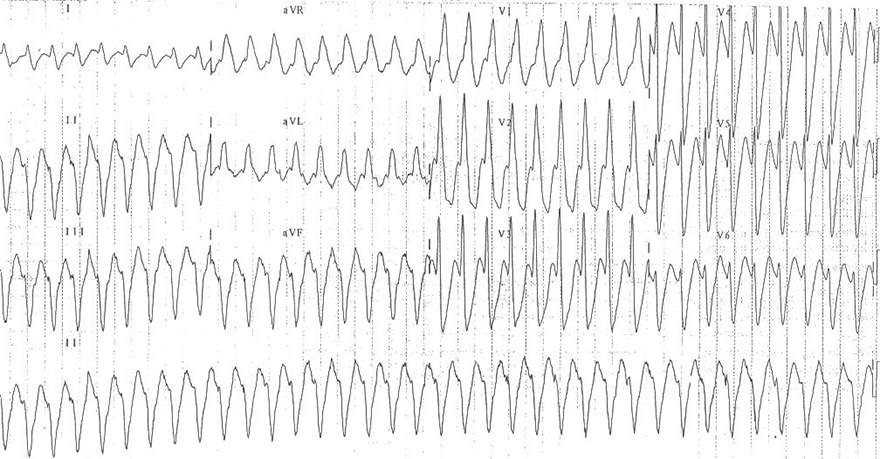
Ventricular Tachycardia
Sources
Home /
Localisation of the origin of a ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular Tachycardia
|

|
| ECG finding: | Localization: |
| QRS Morphology: | |
| Shape of LBBB | Left ventricular septum, Right ventricle, Bundle branch reentry VT |
| Shape of RBBB | Left ventricle outside the septum |
| Cardiac Axis: | |
| Superior | Inferior wall |
| Inferior | Upper septum, Upper lateral wall |
| Rightward | Left lateral wall, Apex |
| Transition Zone: | |
| Transition zone ≤ V3 | Base of the heart |
| Transition zone ≥ V4 | Apex of the heart |
| Precordial Concordance: | |
| Positive | Base of the heart |
| Negative | Apex of the heart |

|
Ventricular Tachycardia
|

|
Epicardial VT
|

|
| ECG Criteria: | Definition: |
| Pseudo delta wave ≥ 35ms | From the beginning of the QRS to the end of the pseudo delta wave In any precordial lead |
| Prolonged R wave peak time ≥ 85ms | From the beginning of the QRS to the peak of the R wave In lead V2 |
| RS interval ≥ 120ms | From the beginning of the QRS to the peak of the S wave In any lead |


|
Ventricular Tachycardia
|

|

|
Ventricular Tachycardia
|

|
Sources