
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Sources
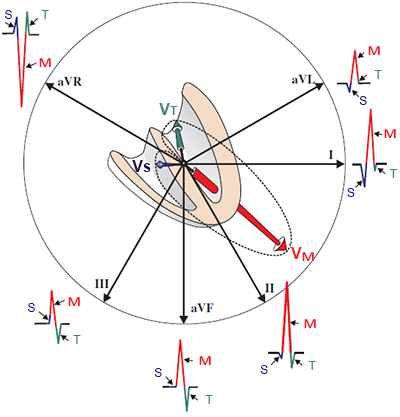
Electrical Vector
|

|
|

|
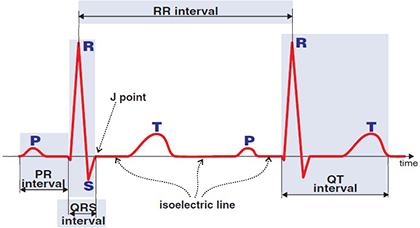
Interval
|

|
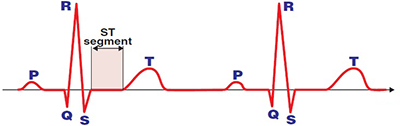
Segment
|

|
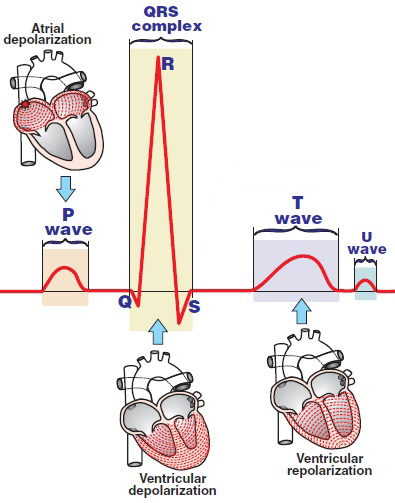
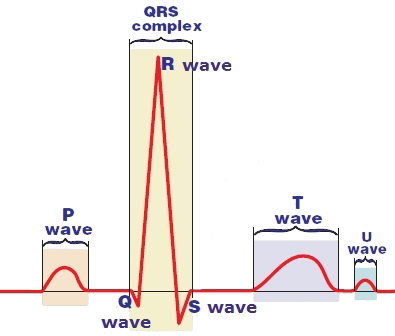
Waves and Deflections
|

|
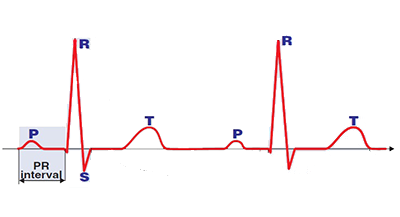
PQ Interval
|

|
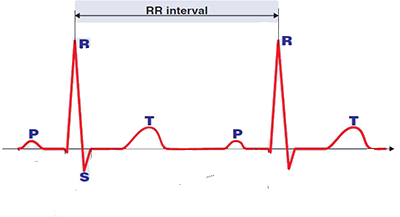
RR Interval
|

|
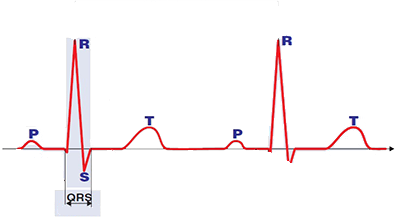
QRS Complex
|

|
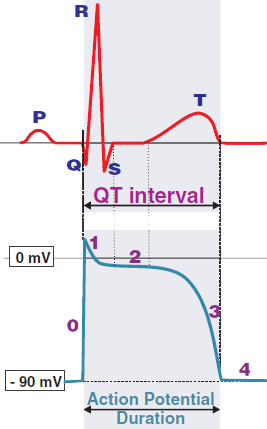
QT Interval
|

|
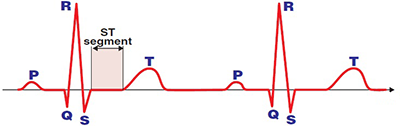
ST Segment
|

|
T Wave
|

|
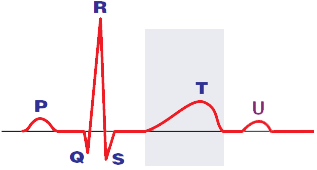
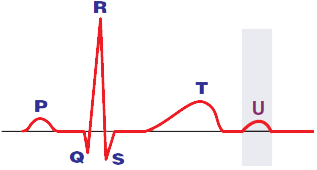
U Wave
|

|
Sources