Home /
Wellens Syndrome
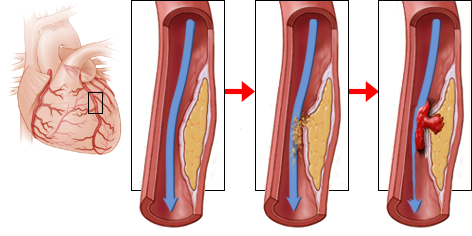
Wellens syndrome (critical stenosis of the left anterior descending artery - LAD)
Critical Proximal LAD Stenosis

- Occlusion is a blockage, while stenosis is a narrowing
- Patients with atherosclerosis
- have stenosed coronary arteries
- In the case of acute progression of stenosis (plaque rupture), the following may occur:
- Wellens' Syndrome is a critical proximal stenosis of the LAD
- Patients typically develop anterior STEMI within about one week
Wellens' Syndrome
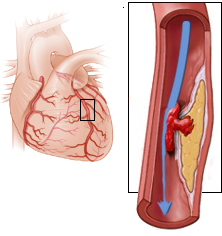
- Wellens and De Zwann described it in 1982
- Wellens' Syndrome
- Is a pre-infarction (precursor of infarction)
- On the ECG, it shows atypical T waves (V2-V3)
- It is present in 15% of patients with unstable angina pectoris
- Patient should not undergo ergometry (stress test ECG)
- During ergometry, the patient could experience an infarction
- The patient must receive a stent in the proximal LAD
ECG and Wellens' Syndrome
- Patients have critical proximal LAD stenosis and are asymptomatic
- ECG changes are in leads V2-V3 (rarely in leads V1-V6)
- There are 2 types of Wellens' Syndrome:
- Type I - more common form (75%)
- Symmetrical deep negative T waves
- which descend almost vertically downwards
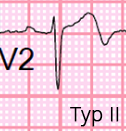
- Type II - less common form (25%)
- Biphasic T waves
- The first part is positive, the second is negative
- ST elevations up to 2mm may be present in precordial leads (V1-V6)
- Both types of Wellens' Syndrome can alternate in a single patient
ECG and Wellens' Syndrome (Type I)
- Symmetrical deep negative T waves (V2-V3)
- which descend almost vertically downward
- Minimal ST elevations < 1mm
- No Q wave (V1-V6)
- Progression of R wave is preserved
- ECG changes occur while the patient is asymptomatic
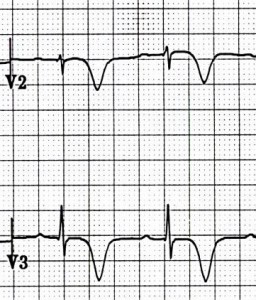
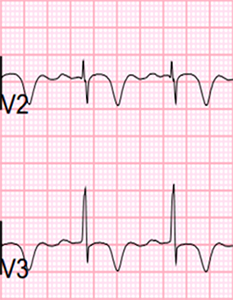
ECG and Wellens' Syndrome (Type II)
- Biphasic T waves (V2-V3)
- The first part is positive, the second is negative
- Minimal ST elevations < 1mm
- No Q wave (V1-V6)
- Progression of R wave is preserved
- ECG changes occur while the patient is asymptomatic
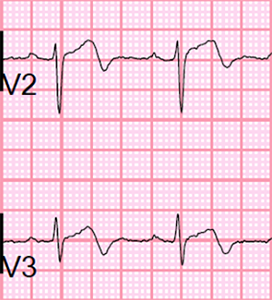
Windowmaker Artery

- Refers to
- critical stenosis or occlusion of the proximal LAD (left anterior descending artery)
- Critical stenosis of the proximal LAD
- Is Wellens' syndrome
- The patient will experience anterior STEMI within one week
- Occlusion of the proximal LAD
- Windowmaker artery has a very poor prognosis
Coronary Angiography of the LAD and Wellens' Syndrome
- A 50-year-old patient who had experienced repeated angina at home
- During the subsequent coronary angiography, the patient was asymptomatic
Windowmaker Artery
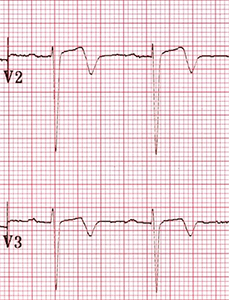
- The patient had Wellens' syndrome (Type I) on the ECG
- Symmetrical deep negative T waves (V2-V3)
- 75% of these patients will experience anterior wall STEMI within a week
- The patient was subjectively asymptomatic
- Only experienced recurrent chest pain at home
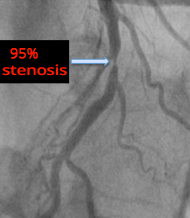
- Coronary angiography revealed 95% stenosis of the proximal LAD
- Proximal stenosis (or occlusion) of the LAD is referred to as the windowmaker artery
Stent Placement
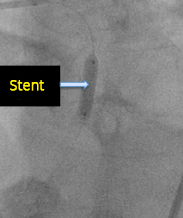
- The patient received a stent in the proximal part of the LAD
Recanalization of LAD
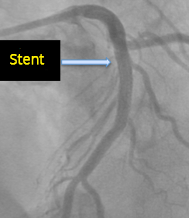
- After stenting, the proximal LAD is completely recanalized
- The patient has a physiological ECG
- Repeated chest pain has resolved
 Windowmaker artery
Windowmaker artery (top left)
Complete recanalization, after stent placement (right)
Pseudo-normalization of T Waves and Wellens Syndrome
- Wellens syndrome primarily occurs in patients with chronic stenosis of the LAD (atherosclerosis)
- During an atheroma rupture, occlusion of the LAD occurs
- A STEMI of the anterior wall begins to develop (Patient experiences chest pain)
- This stage cannot be captured on EKG
- Later, the LAD spontaneously recanalizes (within minutes)
- (due to aspirin use, spontaneous thrombolysis)
- After recanalization of the LAD
- The stenosis is greater than before recanalization
- The patient now has critical asymptomatic LAD stenosis
- Patient is symptom-free
- 75% of patients will experience a STEMI of the anterior wall (LAD occlusion) within one week
- At this stage, the patient will show Wellens syndrome (V2-V3) on EKG
- Pseudo-normalization of T Waves and LAD Re-occlusion
- The patient is symptom-free and has Wellens syndrome on EKG (negative T waves V2-V3, very rarely V1-V6)
- If the patient experiences LAD re-occlusion, then STEMI of the anterior wall will begin to develop
- Hyperacute STEMI (high T waves) in the context of Wellens syndrome (deep T waves)
- Creates normal T waves - T waves normalize (this is pseudo-normalization)
- Because hyperacute T waves developed in the context of negative T waves (Wellens syndrome)
- LAD Occlusion
- If LAD occlusion persists
Differential Diagnosis and Wellens Syndrome
- Wellens Syndrome
- Patients have a history of angina pectoris
- EKG changes are in V2-V3 (very rarely V1-V6)
- EKG changes are present when the patient has no chest pain
- If chest pain occurs, STEMI will begin to develop
- Myocardial necrosis does not occur (troponin is not elevated)
- Similar negative T waves, but without the above features, are created by:
De Winter T Waves and Wellens Syndrome

De Winter T Waves
- Refers to proximal LAD occlusion
- Patient has angina (chest pain)
- Considered an equivalent of STEMI

ECG and De Winter T Waves
- Changes are in V1-V6
- Symmetrical high T waves
- Ascending ST depressions
- (De Winter T Waves)
Wellens Syndrome
- Refers to critical proximal LAD stenosis
- Patients do not have angina
- STEMI will develop within a week

ECG and Wellens Syndrome
- Changes are in V2-V3
- Wellens Syndrome has 2 types:
- Symmetrical deep T waves (Type I)
- Bifid T waves (Type II)

Wellens Syndrome (Type II)
- Bifid T waves (V2-V3)
- The first part is positive, the second part is negative
- Minimal ST elevations < 1mm
- The progression of R wave (R in V3 > 3mm) is preserved
- Patient has asymptomatic critical proximal LAD stenosis

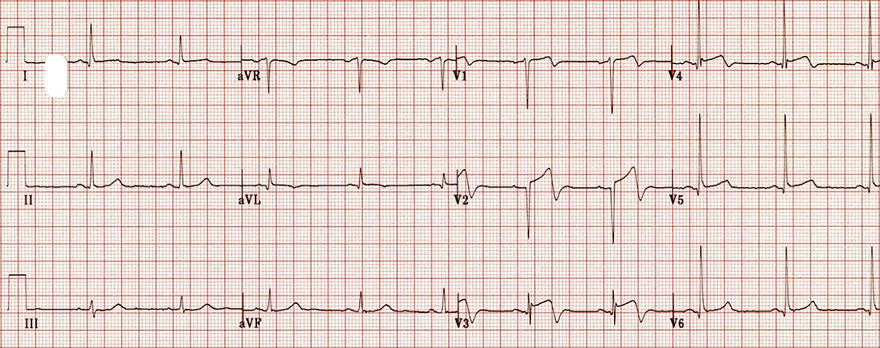
Wellens Syndrome (Type II)
- Bifid T waves (V2-V3)
- The first part is positive, the second part is negative
- Minimal ST elevations < 1mm
- The progression of R wave (R in V3 > 3mm) is preserved
- Patient has asymptomatic critical proximal LAD stenosis

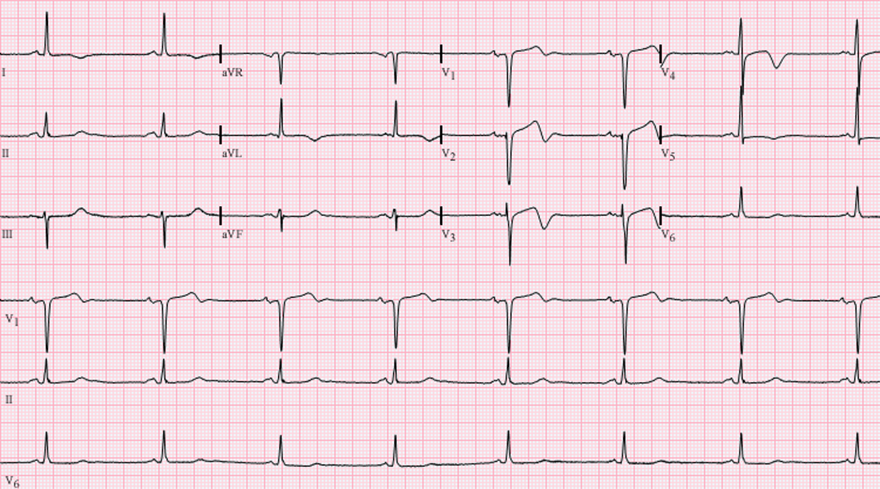
Wellens Syndrome (Type II)
- Bifid T waves (V1-V4)
- Changes may be rare (V1-V6), but most often observed in (V2-V3)
- The first part is positive, the second part is negative
- Minimal ST elevations < 1mm
- The progression of the R wave (R in V3 > 3mm) is preserved
- Patient has asymptomatic critical proximal LAD stenosis

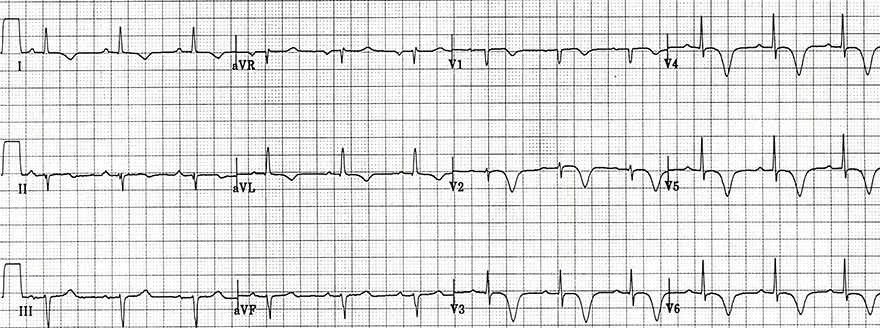
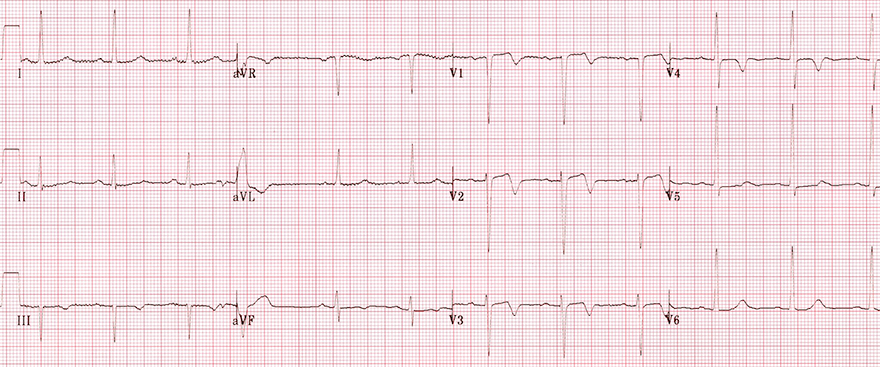
Wellens Syndrome (Type I)
- Symmetrical deep negative T waves (V1-V6, aVL, I)
- Changes may be rare (V1-V6), but most commonly observed in (V2-V3)
- The progression of the R wave (R in V3 > 3mm) is preserved
- Patient has asymptomatic critical proximal LAD stenosis
- Left anterior fascicular block


De Winter's T Waves
- High peaked T waves (V2-V5)
- Ascending ST depression (with J-point depression > 1mm)
- ST elevation up to 1mm (aVR)
- Patient had symptoms of STEMI
- De Winter's T waves are considered an equivalent of STEMI
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers





















































